Abstract
The #linear combination f12 = 2 f(O) - f(H) of elemental balances: f1 = f(H) for H and f2
= f(O) for O is the keystone in formulation of #Generalized Electron Balance (GEB), which completes the set of equations necessary for
resolution of an electrolytic redox system according to Approach II to
GEB in aqueous media. The f does not involve the numbers of free and
hydrating water molecules. The linear dependency or independency of f12 from charge balance (f0 = ChB) and other elemental/core balances fk = f(Yk) (k=3...,K) for elements/cores Yk
of the system is the general criterion distinguishing between non-redox
and redox systems. This criterion is provided by linear combination 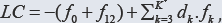 where K* (≤K) is the number of electron-non-active elements (fans) of
the system, and dk are the multipliers related to oxidation numbers
(ONs) of the elements involved in Yk. For non-redox systems, LC is transformed into identity, 0 = 0, whereas for #redox systems, the LC and each linear combination
where K* (≤K) is the number of electron-non-active elements (fans) of
the system, and dk are the multipliers related to oxidation numbers
(ONs) of the elements involved in Yk. For non-redox systems, LC is transformed into identity, 0 = 0, whereas for #redox systems, the LC and each linear combination 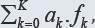 are different from identity. The ONs, reductant, oxidant are derivative
concepts in this formulation. All these interesting regularities are
illustrated by #simulated titration in a #symproportionating redox system,
resolved according to Generalized Approach to Electrolytic Systems
(GATES) principles.
are different from identity. The ONs, reductant, oxidant are derivative
concepts in this formulation. All these interesting regularities are
illustrated by #simulated titration in a #symproportionating redox system,
resolved according to Generalized Approach to Electrolytic Systems
(GATES) principles.
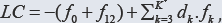 where K* (≤K) is the number of electron-non-active elements (fans) of
the system, and dk are the multipliers related to oxidation numbers
(ONs) of the elements involved in Yk. For non-redox systems, LC is transformed into identity, 0 = 0, whereas for #redox systems, the LC and each linear combination
where K* (≤K) is the number of electron-non-active elements (fans) of
the system, and dk are the multipliers related to oxidation numbers
(ONs) of the elements involved in Yk. For non-redox systems, LC is transformed into identity, 0 = 0, whereas for #redox systems, the LC and each linear combination 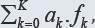 are different from identity. The ONs, reductant, oxidant are derivative
concepts in this formulation. All these interesting regularities are
illustrated by #simulated titration in a #symproportionating redox system,
resolved according to Generalized Approach to Electrolytic Systems
(GATES) principles.
are different from identity. The ONs, reductant, oxidant are derivative
concepts in this formulation. All these interesting regularities are
illustrated by #simulated titration in a #symproportionating redox system,
resolved according to Generalized Approach to Electrolytic Systems
(GATES) principles.
For more articles on BJSTR Journal please click on https://biomedres.us/
For more Bio-psychological Medicine Articles on BJSTR
The Distinguishing Role of 2.f(O) - f(H) in Electrolytic Systems by Tadeusz Micha∤owski in BJSTR


No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.