Cds and Cdse Quantum Dot Solar Cells Production and Improving Efficiency of the Cells by Ion-Doped Quantum Points Cds Holmium
Abstract
This project aims to improve the efficiency of solar cells doped by CdS quantum dot and Ho+3
ion. Successive Ionic Layer Absorption and Reaction (SILAR) and
Chemical Bath Deposition method (CBD), were used to deposit a CdS/CdSe
layer on TiO2 film. According to J-V diagram, it is concluded that adding holmium ions (Ho3+) will enhance the efficiency of quantum dot sensitized solar cells up to 2.53%.
Keywords: Solar Cells; Quantum Dots; Holmium
Abbrevations: QD: Quantum Dots; SILAR:
Successive Ionic Layer Absorption and Reaction; CBD: Chemical Bath
Deposition Method; MEG: Multiple Excitation Generation; EIS:
Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy; XRD: X-ray Diffraction; FTO:
Fluorine Doped Tin Oxide
Introduction
Nowadays, energy issues have been challenged as the most important
human necessities. In the meantime solar or photovoltaic cells have been
attended in order to transferring of solar energy to electricity in
which solar energy has been used as a clean, unexpansive and available
energy source [1-3]. Solar cells are divided into different types such
as dye sensitized, silicone solar cells, molecular, GaAs and quantum
dots (QD) [4, 5]. Recently, QD solar cells have attracted great
attention because of their low cost, high surface area and more quantum
yield [6-8]. In QDs, Multiple excitation generation properties (MEG)
cause a few electron transfers from valance band to conductive band by
incident of just one photon which increases absorption in solar cell and
finely leads to high performance of solar cell [9]. Some QDs are used
in preparation of solar cells such as: InAs, CdTe, PbS, InPO4,
CdS, CdSe, etc. Using CdS and CdSe simultaneously has a good effect on
emission of light because of increasing of band gap via a synergic
effect [10-12]. There are some methods for deposition of QDs onto TiO2 like chemical bath deposition (CBD), SILAR and hot injection growth method. In cathode electrode, Pt or Cu2S is used which because of high cost of Pt using the Cu2S is more popular and common [13,14]. In order to increase electron injection from QD to TiO2, coating a layer of ZnS has a great effect via omitting surface-nods made on TiO2 that this layer improves quality and efficiency of solar cells. In many inves
tigations, I-/I3- solution is used as electrolyte. However,
because of corrosion of solar cells by this redox complex solution,
polysulfide solution S2-/Sx2- is used as a substitute electrolyte.
A new method for improving the solar cell performance is introducing
some metals such as Mn, Ni, Ag, Cd etc to cells [15-18]. In this work
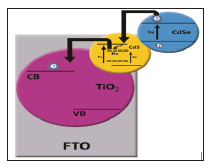
existence of Ho3+ ion in QDSCS cells was used for the first time in order to improvement in photovoltaic performance of QDSCS (Figure 1).
Figure 1: Schematic of the FTO TiO2/CdS: Ho/CdSe
electronic structure. Direct arrows indicate the electron hole
photogeneration. Dashed arrow indicates the electron transfer from CdS
CB to the midgap electronic states and direct curved arrows are related
to electron transfer from CdSe to CdS QDs and from CdS trap states to
TiO2 CB.
Figure 1: Schematic of the FTO TiO2/CdS: Ho/CdSe
electronic structure. Direct arrows indicate the electron hole
photogeneration. Dashed arrow indicates the electron transfer from CdS
CB to the midgap electronic states and direct curved arrows are related
to electron transfer from CdSe to CdS QDs and from CdS trap states to
TiO2 CB.
Experimental Section
Apparatus: SEM-EDX model Irost was applied for. Solar simulator
model SIM800. Bath-Ultrasonic model (Sonica). Water purification
system model No. F3JN94307E. Electrochemical Impedance
Spectroscopy (EIS) was performed on IM6ex Electrochemical
Workstation (ZAHNER) over a frequency range of (1×105–1×10−1)
Hz with 10 mV ac amplitude under forward bias of (-0.6) V in
the dark. Formation of cells by ion-doped quantum points CdS
holmium were analyzed by means of a Philips X-ray diffraction
(XRD) equipfped. The XRD data were collected in the scale of 2Ɵ =
10–80˚ a scanning speed of 3˚ min-1.
Materials: Cadmium nitrate tetrahydrate (Cd(NO3)2.4H2O, Alfa
Aesar, 98.5%), Sodium sulfide nonahydrate (Na2S.9H2O, aladdin,
≥98.0%), Nitriloacetic acid (N(CH2COO)3, sigmaaldrich, ≥99.0%),
Copper(II) sulfate pentahydrate (CuSO4.5H2O, sigmaaldrich,
99.99%), Holmium (III) hexahydrate (HoCl3.6H2O, sigmaaldrich,
99.9%), Sodium hydroxide (NaOH, Merck, 99.0%), Sodium sulphite
(Na2SO3, sigmaaldrich, ≥98.0%), Zinc acetate (Zn (CH3COO)2.2H2O,
Merck, 99.5%), Selenium powder (Se, Acros, 99.5%), Copper (II)
nitrate (Cu(NO3)2.3H2O) and Sulphur powder (S, VWR Chemicals,
99.5%), Fluorine doped tin oxide (FTO) glass, TiO2 nanoparticle. All
reagents and solvents were purchased from commercial sources
and were used without further purification.
Preparation of CdS/CdSe/Ho3+ Solar Cells: First, we deposited
a thin film of TiO2 on FTO transparent conductive layer According
to doctor blade method. Secondly, the electrode was heated up to
125 °C for 6 minutes and then cool down to 25 °C. This process
was repeated until a desired thickness was achieved. To prepare
X electrode, TiO2 photoanodes were placed in a 10mL of cadmium
nitrate solution (1.17g in water) for 5 minutes and then were washed
with distilled water. Then, TiO2 photoanodes were immersed in a
10mL solution containing 2.14g sodium sulfide for 5 minutes. This
cycle was repeated for three times. The resulting electrode was
used as the control electrode. To prepare Y photoanode, plunge
a photoanode was immersed in a 10mL of solution with 1.17g of
dissolved cadmium nitrate and 0.284g Ho3+ for 5 minutes, and
then the sample was dried. The sample is added to the solution of
2.4g of Na2S per 10mL H2O. This cycle was repeated for 3 times.
The electrodes were dried at room temperature. Based on reported
synthesis by Samadpour et al. [19]. In order to prepare CdSe, 1.26g
of sodium sulfite and 0.315g of selenium powder was refluxed
in 50mL of distilled water under nitrogen gas for 5 hours at a
temperature of 80-85 °C at 400-500rpm.
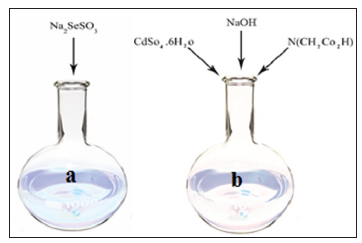
The result is the formation of sodium selenosulphate (Solution of
a). According to Figure 2, different solutions with different volumes
were prepared. 1.2g of cadmium sulphate were dissolved in 50mL of
distilled water. Separately, 1.40g of sodium hydroxide was dissolved
in 10mm of distilled water. Moreover, 1.65g nitriloacetic acid was
dissolved in 40mL of distilled water in a round-bottom flask and
then three samples were mixed and finally added to the b solution
(Figure 2). The final products of a and b was placed in a beaker of
200mL. The synthesized electrodes were kept away from sunlight
for 15 to 18 hours at 2 to 3 °C, Ultimatelly, the electrodes were
washed with distilled water (Figure 3). The electrode immersed in
a solution consist of 0.219g of zinc acetate, 10mL of distilled water
and 0.24g sodium sulfide Na2S. This cycle was repeated three times.
FTO glass was immersed in an aqueous solution of 1.2g copper
nitrate in 10mL of distilled water for 30 seconds and then was
washed with ethanol. This cycle was repeated for 5 times. Finally a
black thin layer of CuS appeared on FTO. Three aqueous solutions
containing 1.2g Na2S, 0.16g S, 0.2g NaOH were prepared separately
and 5mL of each solution was mixed in a round-bottom flask for 90
minutes at the room temperature.
Figure 2: Preparation of a solution (sodium sulfite+
selenium powder) and b solution (cadmium sulphate+
sodium hydroxide+ nitriloacetic acid).
Results and Discussion
SEM
To determine the particle sizes in anodic sub-layer coated by a
layer of TiO2 (20-40nm) and to measure the thikness of the layer’s
SEM-EDX analysis was performed. (Figure 4a) shows SEM image
of TiO2 layers (20 to 400nm) that indicates a porous surface and
uniform particle size. The diameters of first and second layers are
estimated to be 3.77μm (TiO2-400nm) and 4.72μm (TiO2-200 nm)
respectively. SEM images in Figure 4b shows that surface morphology
has been changed in the presence of CdS/CdSe quantum dotes
and shiny dots with 500nm size is appeared that can be related to
CdS/CdSe quantum dotes. The diameter of first and second layers
have changed to 4.03μm and 4.27μm, respectively. Finally, the
thicknesses of TiO2 layers are shown to be 4.04μm and 6.32μm for
first and second layers in Figure 4c, respectively.
Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS)
Figure 7 shows the electrochemical impedance spectra (EIS) of
the CdS/CdSe and CdS/CdSe/Ho. Nyquist curves obtained from EIS
measurements were fitted with equivalent circuit model as shown
in Figure 7. Recombination resistance (Rre) of CdS/CdSe and CdS/
CdSe/Ho samples are 263.30Ω and 628.23Ω, respectively, which
means the electrons and holes recombination in the Ho-doped
CdS/CdSe solar cells are less than that of CdS devices. Thus, the less
charge recombination can be observed in CdS/CdSe/Ho.
Conclusion
Doping of few amounts of Ho3+ ions improves electronic and
photo-physical properties of quantum dots and creates an electronic
level at the middle gap area. This electronic state changes charge
separation and reduces electron-hole recombination. Changing in
the type and amount of impurity causes different electronic and
photonic properties of nanocrystal semiconductors. In this work,
quantum dot solar cells were fabricated, and some investigations
were performed on their structure and it was indicated that quantum
yield increased from 0.87% to 2.53% by adding Ho3+ metal
ion. Using Ho3+ for surface modification leads to increase in yield
of solar cells which it can be concluded that adding lanthanides
ions increase the performance of quantum dots because of electron
transportation properties and these cases may increase quantum
yield of nanoparticle solar cells.
The Drive to Succeed: The Instructional Leader - https://biomedres01.blogspot.com/2020/03/the-drive-to-succeed-instructional.html
More BJSTR Articles : https://biomedres01.blogspot.com




No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.