Questionnaire Based Study about Association between Blood Oxygen Level and Mysophobia
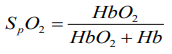
More BJSTR Articles : https://biomedres01.blogspot.com
BJSTR is a multidisciplinary, scholarly Open Access publisher focused on Genetic, Biomedical and Remedial missions in relation with Technical Knowledge as well. Our BJSTR maintains a scrupulous, methodical, fair peer review System. Besides, quality control is riveted in each step of the publication process.
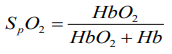


More BJSTR Articles : https://biomedres01.blogspot.com
More BJSTR Articles : https://biomedres01.blogspot.com
More BJSTR Articles : https://biomedres01.blogspot.com
More BJSTR Articles : https://biomedres01.blogspot.com
Blood oxygen level represents the fraction of oxygen i.e. saturation or unsaturation in haemoglobin of Erythrocytes. Blood should maintain normal levels of oxygen for aerobic metabolism which helps in Breathing. Human body needs specific oxygen level in blood and normal oxygen level in blood of human beings should be 97 percent and it can fluctuate during exercise. Haemoglobin of red blood cells collects oxygen in the lungs by using respiratory system and distributes it to the whole body. Oxygen level below 90 percent (low partial pressures of oxygen) leads to hypoxemia because hemoglobin is deoxygenated. The symptoms of low blood oxygen level include changes in the color of nails and skin i.e. bluish color appears. Blood oxygen level below 40 percent leads to compromise the function of Brain and Heart and Blood oxygen level below 20 percent leads to comma and ultimately, it causes death. Continue low levels of Blood oxygen causes many serious problems like cardiac, respiratory and neurological problems. A pulse Oximeter is an instrument which indicates the oxygen level in our blood. Oxygen therapy can be used to raise blood oxygen levels.
In ancient years, Tea was used as an aromatic beverage for many medicinal problems because it helps in improving our health i.e. it contains a chemical known as Nicotine. Now a days, Tea is also used to regulate the blood level of human beings because it has boosting antioxidants like catechins and ingredients which helps in the activation of human Brain and releases tension of the persons. Tea is simply prepared by the addition of teabags and milk in kettles of boiling water with a bit sugar according to one’s taste. It is considered as White tea and it is the simplest tea. Tea is also considered as a lifestyle for the present generation. Many types of tea have been discovered yet i.e. White tea, Black tea, Green tea and Kashmiri tea etc. Black tea is considered as a strong tea because it contains potential ingredients in it and it is taken mostly in Europe. Green tea has its own great importance because it is taken as a diet tea i.e. it is helpful in the dieting. Kashmiri tea is used mainly in gatherings and it is used as a trend in Asian countries to serve Kashmiri chaye to guests. In short, Different types of tea have different nutritional and health values. By addition of Fruit flavors to the tea, we can get natural health benefits. We can also add the flavors of different things like chocolate. Tea has given us many benefits like it can reduce cancer related diseases and heart diseases. Furthermore, it gives us energy and refreshes our mind but excess of everything is bad. Therefore, we should not take more than 4 cups of tea per day. The aim of the recent study was to interlink the Blood oxygen level with Tea likeliness [1-5].
Approximately 200 participants took part in this research and Blood oxygen level of every participant was checked by using Oximeter. To interlink Peripheral oxygen saturation with Tea likeliness, Questionnaire was prepared to estimate the likeliness and Dislikeliness among participants.
Peripheral Oxygen Saturation represents the oxygen levels in blood, and it can be measured by using a device named Pulse Oximeter which clips to the finger or earlobe, light sensitive sensors in the device measure absorption of red and infrared light and it calculates the Blood Oxygen Level by finding the difference between oxygenated and deoxygenated hemoglobin levels in blood. By using a Formula, we can calculate the Blood Oxygen Level with Pulse Oximeter as follows:
Spo2 = Hbo2/Hbo2 +Hb
Where HbO2 = Oxygenated Hemoglobin
Hb= Deoxygenated Hemoglobin
Statistical Analysis was done by using state software. To analyze the results, t-Test was done, and p-value was observed by considering p<0.05 as significant value.
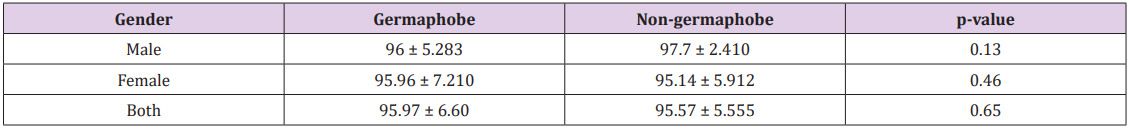
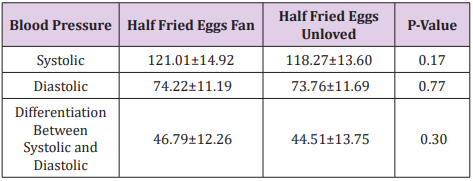
t-Test was used to analyze the Correlation of peripheral oxygen saturation with Tea likeliness. In Table 1, Correlation of Peripheral Oxygen Saturation (Mean±SD) with Tea likeliness among males, females and Both (Males and Females) is given as follows in which p-value is calculated by t-Test is greater than 0.05 i.e. it is non- significant (p-value smaller than 0.05 is referred as significant while p-value larger than 0.05 is referred as non- significant) and it means that there is no correlation of Peripheral Oxygen saturation with Tea likeliness [6-8]. This Questionnaire based studies will give great importance to the latest researches because no research has done before this about correlation of normal blood oxygen level with Tea likeliness. Such type of researches show advancement in the scientific era and give us broad idea to relate different variables with different Blood factors. In this way, we can also know about the diagnosis of different diseases related to human beings.
Table 1: Co-rrelation of Peripheral Oxygen Saturation (Mean±SD) with Tea likeliness among Males, Females and Both (Males and Females).
Note: Results were non-significant ( p<0.05).
By Statistical Analysis, it was interpreted from the recent research that Peripheral Oxygen Saturation with Tea likeliness does not correlate in human beings because p-value was larger than significant value which was calculated by using t-Test (p<0.05).
Active Probe Emitting HF Electromagnetic Fields and Piezoelectric Emissions in Association with Local Carbon Nanotubes : Preliminary Tests in C6 Glioma Cell Death Induction: A Possible Application in Glioblastoma Therapeutics ?-https://biomedres01.blogspot.com/2021/02/active-probe-emitting-hf.html
More BJSTR Articles : https://biomedres01.blogspot.com
Introduction
Malignant Glioma (MGs) variants, Glioblastoma (GBM) is the most common malignant tumor in the central nervous system. His prevalence is about 1/100 000, with a survival time post-diagnosis of 15 months and a mortality rate exceeding 95% [1]. Common treatments for GBM include surgical resection, radiotherapy, chemotherapy, or combinations of these three modalities [2,3]. Nevertheless, there is no general agreement on the radiation pro tocol to use. If fractionation seems to be the most appropriate, the choice mainly depends on the radiotherapy options available to the treating physician. In case of recurrent glioblastoma, the treatment is then focused on the use of chemotherapy. Numerous studies have demonstrated the safety and efficiency of various agents, both alone and in combination [4-8]. GBM have an extremely low survival rate due to the high infiltrating properties of the glioma cells. Typically, these cells could infiltrate up to 2 cm exceeding the volume of visible tumor, making them difficult to detect and treat. Treatment of GBM is also limited by several other factors such as, the insufficient delivery of chemotherapy drugs caused by the blood-brain-barrier, the radio resistance of the cells and the need to preserve functional parenchyma.
Despite the existence of different therapeutic strategy treatments, the evolution of the post-diagnosis median survival only increased from 13 to 15 month, highlighting the need of curative approaches. In the recent past, some new innovative researches have produced promising results or are the subject of ongoing investigations [9-16]. Among them, we can find biophysics approaches using electromagnetic fields or nanoparticles. The results of Kirson’s group highlighted the first point. This team have shown a decrease of the malignant cell proliferation with no or minimal side effects in animal tumor models and human brain tumors [11.12] by using an alternative electric field (also called TT Fields for Tumor Treating Field). According to the authors, the mechanism involved is related to the disintegration of the mitotic spindle [11]. NovoTTF therapy is a new therapy using this observation and has undertaken the phase III clinical trial [13].
Another Group (Magforce AG) is using iron nanoparticles combined with an alternative magnetic field (100 kHz). This field induces nanoparticle’s vibrations and then, locally increases the temperature leading to the tumor cells death. The main drawback of such approach is the lack of specificity. Even if nanoparticles are addressed to malignant cells, the increase in temperature destroys all the cells located in the vicinity of the particle. However, this therapy seems efficient and safe with no or moderate side effects [14-16]. We propose an alternative project using these two different aspects by using both nanoparticles and electromagnetic field without inducing any thermal effect. This new approach is inspired by recent works [17] showing a strong interaction between Carbon Nanotubes (CNTs) and electromagnetic field.
According to this observation, a synergic toxic effect between electromagnetic fields (RF) and CNTs could be expected. CNTs could increase the toxicity of the RF by focusing them and inducing an electromagnetic field increase. The RF could also increase the toxicity of the CNTs by a direct helping of their dispersion and penetration into the cells. The intrinsic characteristics of CNTs make them specifically sensitive to electromagnetic field. Due to theirs high length compared to their diameter, they could be at the origin of a strong point effect (like a lightning rod) inducing a local increase of the fields’ strength. Both CNTs and electromagnetic field are major public health issues and many studies tried to determinate their toxicity [18-21].
The drawbacks of both Kirson and Magforce AG studies was that the field emitter (electrodes on the skin / external magnetic emitter) were located outside the body, i.e. far away from the target. As field power density generally decreases with the square of the distance, using an intra cerebral emitter, combined with CNTs induced local magnification of the field would be promising. Such mechanisms would clearly differ from those of Magforce AG team, since neither tissue heating nor thermal reaction occur in the former case. Final therapeutic hope would use a combination of the convective infusion technique [22,23] together with the inclusion of the RF emitter in the catheter used for intra-tumoral injection. The aim of this study was to evaluate the effects of a co-exposure to carbon nanotubes and combined electromagnetic field/ultrasounds on an in vitro glioma model.
The C6 cells (Rat Glioma) were obtained from the ATCC cell base (ATCC® CCL-107™). The cells were maintained in exponential growth in a 5% CO2 humidified incubator held at 37°C. The C6 cells were placed in cell culture flasks (75cm²) and were grown with 12 ml of DMEM, Glutamax supplemented with 10 % heat-inactivated fœtal bovine serum and antibiotics (100 U/ml penicillin and 100 µg/ml streptomycin).
Single wall carbon nanotubes (CNTs, quoted here CNTs, Figure 1) produced by Catalytic Chemical Vapor Deposition were purchased by SIGMA-Aldrich, St Quentin Fallavier, France. The CNTs diameter distribution was ranged from 0.7 to 1.3nm, and length between 450 and 2300nm, although bundles may be much longer (up to 100µm at least) with a density of 1.7-1.9 g/cm3 at 25°C.
Figure 1: Left : Electron microscope of CNTs in suspension in aqueous medium after dispersion Left : relative distribution of CNTs aggregates in suspension.
Particle size distribution of the stock solution used for cells exposure was analysed with a Laser Scattering Particle Size Distribution Analyser, LA-950V2 (HORIBA) with DMEM as solvent. Particles dispersion in cell culture medium and cells exposure : Stock solution of 5 mg/ml CNTs was prepared by dispersion of sterilised particles in DMEM containing 25 % FBS. Previous study has reported that serum produced particle suspensions were observed with the fewest large agglomerates [24]. The nanoparticles were homogeneously dispersed by vortexing for 30 seconds followed by sonication in a water bath (Al 04-02, Advantage Lab) for 5 min. This procedure was repeated five times. A “Sham Stock Solution” of sterile DMEM containing 25 % FBS was prepared and sonicated at the same time for use as control.
The stock solutions were kept at 4°C. The stock solution of CNTs was resuspended by vortexing for 30s followed by sonication for 5 min and diluted in cell culture medium to the required concentration (50 µg/ml, 120µl per flask). An equal volume of “Sham Stock Solution” was added to cell culture medium for control cells. Before any experiment, CNTs size were analyzed using a Laser Scattering Particle Size Distribution Analyser, LA-950V2 (HORIBA) with DMEM as solvent (10%) and a dilution at one centesimal (150µl in 15ml). The size of the CNTs measured by light scattering was defined as the equivalent spherical diameter and could not be related to the exact particle size but represent a relative size of nanotubes which are long cylinders. This led to identify different particle sizes in solution : 100µm diameter aggregates (35%), a minor component of intermediate aggregates (1µm-30µ). Sizes below 1µ were considered as unbounded carbon nanotubes.
The absence of temperature increase was controlled over 16Hrs exposure under the RF/CNTs conditions with probe immersed in the culture flask, using a FLIR A320 Temp screen camera. No significant variation was detected within the observation period.
Measurement of the electromagnetic field : The probe was composed of three parts (electric, magnetic and ultrasonic with a piezoelectric component, CNTs) realizing the emission of an electromagnetic signal and a piezoelectric operating phase. Electromagnetic fields were then applied by connecting the wires to an amplifier operated by a signal generator with frequency and amplitude controls. The probe was powered by a square wave modulated signal working at 100 kHz (low-intermediate frequency emission) from an Agilent 3312DA generator, peak to peak tension of 10Vpp, and duty cycle DC=50%. This first prototype version is presented Figure 2.
Figure 2: Top: Electronic wiring of the probe; Bottom: The probe, as connected with BNC connectors. GND: Ground; E: RF input via BNC connector; Q: 100KHz resonating piezo; C1,C2 tune capacitors; L1=1mH, L2=L3=16mH; L2L3-L1transformator; A1, A2: antennas.
Field estimations were attempted with a PM03 field meter and a H/E fieldmeter ESM-100, Meshket. As the exposure conditions (inside the flask) were obviously in reactive nearfield conditions, E values were extremely heterogenous (5dB , with a maximum of 80V/m in close vicinity of the probe extremity ) while H variations were found less important ( 3dB , maximum 90nT in close vicinity of the probe extremity). The 100kHz resonating piezo was a PRYY0073 from PICERAMIC, Germany. The electric field was evaluated with the help of a PMOR 03 field meter. In order to isolate the exposed flask, the electromagnetic exposed flask was placed into an absorbing chamber allowing an attenuation of the signal by 12 dB.
Each flask was randomly assigned to one of the four different groups: Sham / Sham, Sham / Nano exposed, Sham / Field exposed, and Nano / Field exposed (CNTs/RF+piezo, quoted CNTs/RF in the followings). All the cultures were realized in triplicate under the same conditions as the CNTs/RF group except that the generator was turned off, with the probe into the flask. The initial C6 cell population was 0.2* 106 cells per flask. 72h exposure starts immediately after the cells have been passaged. Sham / Sham and Sham / Field groups received 120µl of the Stock Sham solution (without CNTs), the double exposed and the Sham / Nano groups received 120µl of the Stock solution containing the CNTs. After exposure, in order to eliminate the SWCNTs in solution, each flask was rinsed 3 times with Phosphate Buffered Saline (PBS). The cells were chemically detached from the flask using trypsin EDTA. C6 cells were centrifuged 5 min at 300G. Cell pellets were resuspended in 1 ml cell culture medium. 50 µl of C6 cells solution were added to 50 µl of Trypan Blue. C6 cells were counted by a TC20TM automatic cell counter. Results were expressed as means ± Standard Deviation (S.D.)
In these experiments, cell counts were performed after 72h culture with/without RF exposure and/or in the presence or not of CNTs (see Figure 3). By comparison with reference sham values measured at 72h (2,84 106/mL) and also after 72Hr RF exposure (2,8 106/mL) an important reduction in absolute values of cells counts was found when CNTs were present alone (2.106 /mL) and especially when CNTs were associated with RF exposure (1,46 106/mL) . These results are all the more evident when expressed in percentage to reference sham values and showed an important decrease in the number of the cells compared to the control group (51% for the Nano / Field group; 75% for the Sham / Nano group; 98% for the Sham / Field group). Conversely, the survival rate of the cells within any group was only slightly decreased whatever the exposition factors considered : hence, the survival rate is maxima (100%) for the Sham / Sham control group and slowly decreases with the exposition of CNTs and electromagnetic field (97% survival rate for the Sham / Field group, 95% survival rate for the Sham / Nano group and 94% survival rate for the Nano / Field group. As this step it is worth to note than rinsing process (see methods) induced an averaging over the whole flask, this resulting in a smoothing of any possible local drastic effect. Morphological control had thus to be performed.
Figure 3: Cell count (cells/ml 106 related to sham / sham group (percentage) and survival rate distribution in C6 cell population with exposition of SWCNTs or electromagnetic field according to their respective group. The cells were exposed for 72h right after injection of the cells into the flask.
As mentioned above, microscopic observation (Figure 4) clearly shows the reduction of cell density in the flask, even like here after the rinsing process between CNTs/RF and sham groups. Moreover, the absence of morphological change was also in full agreement with the minor differences in cell viability between groups. Here differences appear between CNTs and CNTs/+RF groups. As noted in the methods section, CNTs spontaneously selforganized in µ-sized aggregates, with only a partial contribution of dispersed nanoparticles. This was observed on the Figure 5A, especially before rinsing of the flasks, where these aggregates are visible even at low magnification (x4). Such a distribution appeared partially overcome (or really dispersed) due to rinsing, as shown on Figure 5B, where higher magnification allows to detect smaller particles among the C6 cells, without specific contact or geometric distribution.
Figure 4: A: Sham / Sham group cells after 72h exposure time (X4 magnification); B: CNTs + RF group cells after 72h exposure time and rising of the flask (X4 magnification).
Figure 5: Sham / Nano group cells after 72h exposure time with nanotubes aggregates, before the rinsing process, with X4 magnification (left) and x10 magnification (right).
Besides, no evidence for cell distribution, i.e. heterogeneity around the probe (not emitting, sham) was observed. Such was not the case in the combined CNTs/RF samples (Figure 6). Several CNTs aggregates were still present whereas more numerous and of smaller size, in an area close to the extremity of the probe. This feature was not reasonable to quantify - a factor of 2 to 5 ? - due to the important heterogeneity in the half centimeter around the probe wall. However, a true “no cell area” was truly present in the several millimeters around the probe. Furthermore, linear arrangements of CNTs were observed (Figure 6) in the closest vicinity of the antennas (wires inside the probe while aligned along its main axis) , this revealing true interactions between CNTs and RF and/or ultrasound coming from the piezo.
Figure 6: CNTs + RF group after 72h exposure time showing a cell depleted area close to the probe extremity; longitudinal CNTs orientation in the CNTS+RF group after 72h exposure time before rinsing resulting homogenization.
The aim of the preliminary work was to evaluate the effects of a co-exposition from carbon nanotubes and electromagnetic field on an in vitro glioma model. The Sham / Field group cell count showed a limited decrease of the C6 cells population compared to the Sham / Sham group and a similar survival rate between the two groups, 99% and 100% respectively. Compared to Kirson’s results several differences arise (9,11) :in the present work, the frequency was fixed at 100 kHz while Kirson’s group used a 100-300 kHz frequency system, with an emitting power twice as ours. The Sham / CNTs group cell count showed a 25% decrease of the C6 cells population compared to the Sham / Sham group with a 97% survival rate. CNTs alone have a strong effect on C6 cells. This could be related to their own direct or indirect toxicity related with the ability of CNTs to trap growing factors in a culture medium [18-21]. The most interesting results were to find a synergic effect of the CNTs with the electromagnetic field. The Nano + RF cell count showed decrease to 51% of the C6 cells population compared to the Sham / Sham group with a 95% survival rate. As an hypothesis, the SWCNTs could induce an increase of the local field’s strength and a disruption of the field direction. According to the mechanism of action of TTFields described by Kirson, TTField efficacy must be a function of the angle between the field and axis of division of the cells; when the two are parallel it has a maximal effect and when one is perpendicular to the other, it has a minimal effect [11].
In our case, the carbon nanotubes could solve this problem as they might cause a local reorientation of the field, overcoming the previous problem. In addition, the effect of the piezoelectric component might be useful to open the blood-brain-barrier and increase the dispersion of the CNTs into the tumor after a local injection using the convective infusion technique [23]. The results showed a strong effect associated with an important decrease of the C6 population subjected to the double exposure. However, the survival rate of the cells is still high and this combination tends to prove that the effect of the co-exposition is not on the destruction of the cells herself but by an inhibition of the cell proliferation [11].
At this step it is not possible to ensure any specific effect due to the several bias of the study. First of all, the studied population of cell wasn’t enough to draw conclusion. More experimentation should be performed in order to obtain a strong statistical analysis. In addition, most of the dead cells are eliminated during the rising process because they can’t bind the flask anymore once they lost their structure. In order to include these cells into the final calculation, centrifugation of the rising solvent might be a good idea to retrieve dead cells. Another possibility would be gel phase culture and direct final count by optical density lecture , for instance. Besides, the specific effect of each component separately or combined with one or all the others should be addressed, for instance separate piezo and RF contribution and association with CNTs. Finally, the particle exposure could also be improved.
The particle size distribution showed that the dispersion of the carbon nanotubes was neither homogenous not ideally dispersed. Due to their strong hydrophobic properties, CNTs bind each other and form large aggregates. This could diminish the efficacy of the CNTs on the cells and hide a potential effect. The CNTs concentration used here (50µg/ml) may be at the origin of the problem and using a lower concentration could increase the dispersion of the carbon nanotubes. This concentration was chosen based on the previous studies on the CNTs toxicity [18,21,27]. The CNTs concentration isn’t the only parameter that could affect the results. The previous pictures were obtained using a phase contrast technique that could not distinguish apoptotic cells and necrotic cells (especially at the beginning of an apoptotic process).
Flow cytometry imaging could solve this problem, with a Hoechst stain to visualize the cell nucleus or even a fluorescent stain using PKH [28,29]. From a mechanistic point of view, different cell types should be tested to ensure (or not) the existence of aspecific mechanisms at mitotic bundle destructuration, as mentioned by Kirson. From this , and by designing the probe small enough to be implanted in living systems, in vivo experimentation procedures would be envisaged. These different points are presently addressed, and we plan to set up a “matches-sized” probe, including a coaxial catheter for direct perfusion of CNTs or charged drugs. Hence other drugs could be carried by the convective infusion system and the combination with a special drug carried by CNTs [30]. The idea of an intra tumoral catheter including an RF emitter allowing the distribution of chemotherapy or carbon nanotubes using the convective infusion technique seems promising. This thematic actually plans to in vivo animal experimentations procedure where other questions such as possible blood-brain-barrier opening and safety evaluation of such therapy.
The Effectiveness of Polarized Polychromatic NonCoherent (BIOPTRON) Light in the Management of Acute Lateral Elbow Tendinopathy: A Case Report-https://biomedres01.blogspot.com/2021/02/the-effectiveness-of-polarized.html
More BJSTR Articles : https://biomedres01.blogspot.com
More BJSTR Articles : https://biomedres01.blogspot.com
Hematopoietic Elements in Osteoarthritic Femurs Compared to Normal Bone Marrow as Evaluated by Immunohistochemistry Introduction Affecting...
