Study Regarding the Inhibition of Acetylcholinesterase by Isopropyl 4-Nitrophenyl Methylphosphonate
Introduction
Isopropyl 4-Nitrophenyl Methylphosphonate (NIMP) [1,2], a sarin simulant, was synthesized for testing the AChE inhibition capacity, in order to find it as suitable chemical simulant [3] for sarin (Figures 1 & 2). In vivo pharmacotoxicological experimental study of the above presented chemical compound was performed in order to determine its LD50 value, the degree of cholinesterase inhibition lethal doses appropriate, and the oxime assisted protective ration case of poisoning. To determine the LD50 and index protection defined as the ratio of LD50 the lot poisoning CWA simulant and treated and LD50 the lot intoxicated and untreated, there were used laboratory animals (rats Wistar) distributed in homogenous groups (intoxicated, treated and batch control). Monitoring of animals during the experiment was to record the moment signs of intoxication, mortality recording 60 minutes, 24 hours after poisoning the lots intoxicated and intoxicated and treated, tracking and recording time appearance remission signs of intoxication lots intoxicated and treated. The AChE activity was measured by using the standardised bioanalytical method performed by Eyer & Woreck in 2001. The used specimen was rat heparinised blood collected by venous punction. A UV/VIS Perkin Elmer Spectrometer equipped with soft UV KinLab. Lambda 40 was used as measuring equipment. Experimental data statistical analysis was performed by using Student’s T test and One Way Anova test.
Figure 1: Structures of nerve agent (sarin) and the corresponding simulant (NIMP) used in the biological study.
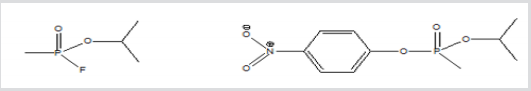
Sarin
Isopropyl 4-nitrophenyl
C4H10FO2P
methylphosphonate
C10H14NO5P, MW 259
MW 140, [107-44-8]
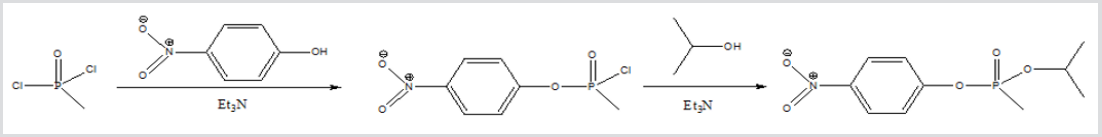
Figure 2: NIMP general synthesis reaction.
Experimental Results
Inhibition of erythrocyte [4] AChE due to the studied compound three doses in the range of logarithmic progression of the points, showed a related to dose pharmacodynamic effect between 53% and 95%, values like those of the reference compound. NIMP doses in the range of LD50 (0.59, 0.47, and 0.31 mg/kg i.p.) leads to 95, 87, and 53% of AChE inhibition, comparable to the AChE inhibition values determined by the appropriate range LD50 of nerve agent correspondent, sarin. The experimental data are presented in the Figure 3. The calculated LD50 values by using our experimental data was 0.45 ± 0.002 mg/ kg i.p. (reference range 0.31 to 0.59 mg/kg i.p.) for NIMP. The regression equation and the correlation coefficient calculation results in NIMP LD50 are presented in the Figure 4. The determination of the protection ratio, linear regression and correlation coefficient are represented in Figure 5 and (Table 1).
Figure 3: Structures of nerve agent (sarin) and the corresponding simulant (NIMP) used in the biological study.
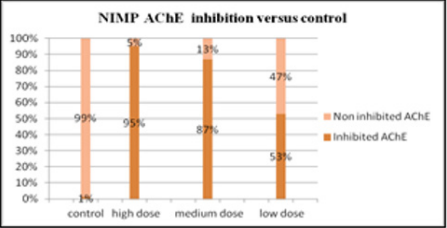
Figure 4: The regression equation and the correlation coefficient calculation results in NIMP LD50; X axislogarithmic values of doses administered 3 groups introduced in the experiment; Y axis- values of the probit corresponding to mortality percentage.
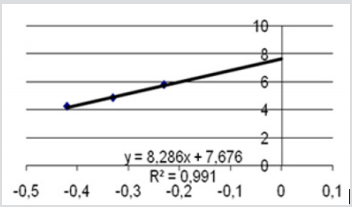
Figure 5: Highlighting experimental data of mortality in calculating the protective ratio in case of NIMP poisoning: 0.45 mg/kg NIMP LD50 doses administrated to the poisoned and untreated study group; 1.125 mg/kg NIMP LD50 doses administrated to the poisoned and oxime assisted study group.
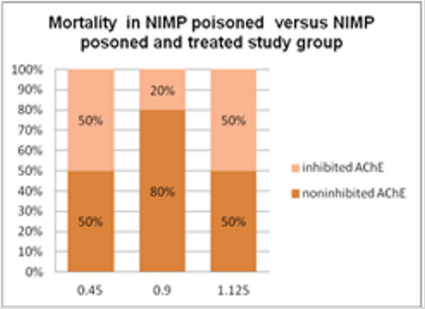
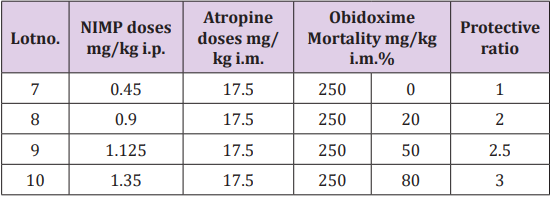
Table 1: Highlighting experimental data of mortality in calculating the protective ratio in case of NIMP poisoning: 0.45 mg/kg NIMP LD50 doses administrated to the poisoned and untreated study group; 1.125 mg/kg NIMP LD50 doses administrated to the poisoned and oxime assisted study group.
Conclusion
The study showed that the percentage of inhibited AChE is comparable with the sarin one. Comparative analysis of LD50 values for NIMP and the correspondent nerve agent, showed lower intrinsec toxicity of the synthesized simulant. The protective ratio of antidote therapy (atropine, obidoxime) in the groups exposed to NIMP was I.P. = 2.5, value comparable with the sarin one. Also, the enzymatic AChE reactivation value was comparable to the relevant reference substance levels. Inhibiting activity of this nerve agent simulant is enough to mimic exposure to real agents, being present all the clinical signs typical of poisoning. As with aging sarin - related acetylcholinesterase, simulants show a slower rate of aging, prolonging survival time and allowing therapeutic window for reactivating oximes. Thus, it can be concluded that the compound studied shows similar pharmacodynamic effects and references due to lower intrinsic toxicity may be suitable as a simulant for research studies in the laboratory activities.
MFC-Based Biosensors Known as an Integrated and Self-Powered System-https://biomedres01.blogspot.com/2021/02/mfc-based-biosensors-known-as.html
More BJSTR Articles : https://biomedres01.blogspot.com



No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.