Ovarian Failure with Absent Uterus in A Rare Mosaic Turner’s Syndrome (45, X/47, XXX)
Introduction
Turner’s syndrome (TS) is one of the most common sex chromosomal disorder, affecting one in 2000 live-born females [1]. Forty-five% of patients were associated with the classical monosomic form (45, XO), while the remaining are various mosaic forms [2-4]. The severity of clinical manifestation is in part related to the type of chromosomal abnormalities, the time at which chromosomal disjunction occurred and the proportion of compromised cells in each tissue [5]. The development of uterus, fallopian tubes, and vagina are usually normal [4-5]. We report a rare case of a 14-year-old girl who presented with short stature. She was found to have phenotypic features of turner syndrome, and ovarian failure with absent Mullerian structures with Karyotyping of 45XO/47XXX.
Case Report: A 14-years-old female presented to the pediatric endocrine clinic, King Khalid University Hospital, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia with short stature and stunted growth. She was the product of preterm delivery of a 35 weeks gestation with birth weight of 1.8kg. Her parents are not consanguineous and all of her siblings are healthy individuals.
At that time, her height was 114cm (far below the 3rd centile for normal population growth chart). Her weight was 25kg (on the 3rd centile). She was found to have phenotypic features of turner syndrome in the form of short stature, short fourth metacarpal bone, ptosis, shield chest, webbed neck and cubitus valgus. Her breast and pubic hair development were Tanner’s stage I at age of 10 years then progressed to tanner 3 over the last 4 years. her external genital is of normal female phenotype. Examination of the cardiovascular, respiratory, and neurological systems was normal. Laboratory investigations revealed normal hematological and biochemical parameters. She was investigated with a provisional diagnosis of Turner syndrome. Thyroid panel was normal, Lipid profile was normal and celiac antibodies were within normal rang. Ovarian failure is reflected in the form of marked elevations in serum follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) 41.86IU/L, luteinizing hormone (LH) 16.25IU/L with low ESTARDIOL 18.35nmol/l and TESTOSTERN 0.09nmol/l.
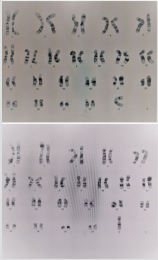
Echocardiography was normal. Chromosomal analysis (Figure 1): identification of the Karyotyping was made by G-banding or Q-banding method. The karyotype of all of the 45 cultured peripheral lymphocytes using a high-resolution technique revealed 45 chromosomes with one X chromosome missing (45, X monosomy). fluorescent in-situ hybridization (FISH) in peripheral blood lymphocytes was carried out using the CEPX (DXZ1) and Y (SRY) DNA Probe panel (Abbott USA) to screen for the copy number of chromosomes X and Y and the presence of the SRY gene region. A total of 500 interphase nuclei were scored for each chromosome signal pattern suggests the presence of two clones (45X/ 47XXX). Clone with monosomy for chromosome X which is consistent with Turner’s syndrome in 88% of scored nuclei. Clone with three copies of X chromosome in 12 % of scored nuclei. No detected SRY gene. Her pelvic ultrasound revealed uterus, and cervix (Figure 2). These findings were confirmed by MRI of the pelvis (Figure 3). Other organs like kidneys, pancreas, liver, and adrenals were normal.
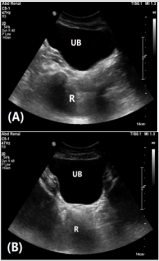
Figure 2: Ultrasound pelvis in mid-sagittal (A) and axial (B) planes demonstrating absent uterus and ovaries. Urinary bladder (UB) and rectum (R).
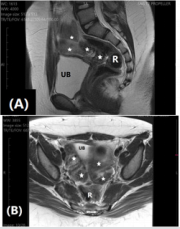
Figure 3: MRI pelvis in mid-sagittal.
A. and axial
B. planes demonstrating absent uterus and ovaries with bowel loops (stars) filling the space between urinary bladder (UB) and rectum (R).
Discussion
Turner syndrome (TS) is one of the most common sex chromosomal disorders, affecting 1 in 2000 live births females. It is characterized by short stature, cubits valgus, webbed neck, nail dysplasia, shield-like chest, widely placed nipples, lymphedema of hands and feet, low set ears, genus valgus, horse-shoe kidney, and congenital heart disease and the most common of which is coarctation of aorta Other clinical features include streak ovaries that leads to primary amenorrhea or premature ovarian failure. The ovaries usually develop normally at first, but the egg cells die prematurely and most of the ovarian tissue degenerates. Premature ovarian failure is confirmed by failure in the progress of puberty and primary amenorrhea which was supported by hormonal studies of low estradiol and very high gonadotrophins levels and was confirmed by ultrasonography (US) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) [1-7]. Ultrasonography and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) have been shown to be useful in the evaluation of pediatric patients with Turner’s syndrome [8-10].
Conclusion
Ultrasonography and MRI of pelvis are necessary tools in the assessment of patients with Turner’s syndrome.
Acknowledgment
The authors would like to than Mr. Abdulrahman N. AL-Jurayyan for his help in preparing this manuscript.
For more Articles: https://biomedres01.blogspot.com/



No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.