Spontaneous Fracture of an Angle-Supported Anterior Chamber Polymethylmethacrylate Intraocular Lens: A Case Report
Introduction
Angle-supported, Kelman-type anterior chamber intraocular lenses (acIOL) are implanted for correction of aphakia in eyes with insufficient capsular bag support, e.g. following complicated cataract surgery [1,2]. Typical complications associated with this acIOL type are bullous keratopathy (BK), secondary glaucoma and cystoid macular edema [3,4]. Another very rare complication is spontaneous in vivo fracture of the acIOL. Up to date, 4 cases describing spontaneous fracture of older acIOL versions, e.g. semiflexible acIOL with a closed-loop design, have been reported. Purpose of the present report is to describe a rare case of spontaneous in vivo fracture of a modern, all-PMMA, Kelman-type acIOL.
Case Report
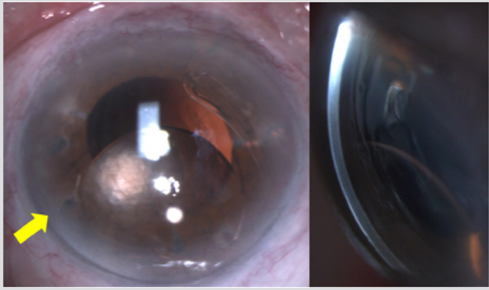
An 86-year-old otherwise healthy man presented due to visual deterioration of the right eye (OD) over the last 10 days. He reported undergoing phacoemulsification with implantation of an acIOL in the same eye 6 years ago while not recalling any ocular trauma in the recent past. He had also undergone phacoemulsification with posterior chamber IOL implantation in the left eye (OS) 5 years ago. At presentation, best-corrected visual acuity (BCVA) was 0.2 OD and 0.8 OS and intraocular pressure was 21 mmHg OD and 15 mmHg OS. Slit-lamp examination revealed a dislocation of the acIOL towards the inferior angle of the anterior chamber. Strikingly, the distal part of the inferior haptic appeared anterior to the decentered optic (Figure 1). The respective inferior haptic loop was not visible at its entire length as it was obscured by the corneoscleral limbus. Finally, a mild anterior chamber reaction was present while the cornea did not show any signs of edema. Central corneal thickness was 567μm OD and 566 μm OS and the corneal endothelial cell density was 1130 cells/mm2 OD and 1335 cells/mm2 OS measured with specular microscopy (Tomey EM-3000, Tokyo, Japan).
Figure 1: Slit-lamp photograph of the right eye depicting the inferiorly decentered acIOL (a) en face aspect and (b) lateral view. Please note the absence of significant corneal edema despite the contact between acIOL optic and corneal endothelium.
Funduscopy was unremarkable in both eyes. In order to avoid endothelial cell loss and corneal endothelial decompensation, exchange of the dislocated IOL was performed on the following day. Pilocarpin 2% eye drops were given twice daily and the patient was instructed to keep 45 degrees seating position until surgery so as to avoid dislocation of the acIOL into the vitreous cavity. The acIOL exchange was performed under subtenon’s block. After creating a 6mm-limbal tunnel incision at 12.00 limbus position, the anterior chamber was filled with viscoelastic and the acIOL was delivered with McPherson forceps. Interestingly, upon explantation of the acIOL became evident that the distal loop was fractured, and the fragment remained in the inferior angle. Subsequently, the latter was also removed and another Kelman-type acIOL (MTA3U0, Alcon, USA) was inserted into the anterior chamber and the tunnel was sutured with interrupted Nylon 10-0 sutures. The postoperative regimen included chloramphenicol/dexamethasone eye drops every three hours for the first 5 days, then 4 times a day for one week and finally twice a day for three weeks. On the first postoperative week, BCVA OD was 0.6 and intraocular pressure was 15 mmHg (Figure 2). The new acIOL was well-positioned in the anterior chamber and no iritis was present.
Figure 2: Photo of the intraocular lens fragments after explanation. Note that the fracture point is located at the proximal part of the lens loop.
Discussion
This is to our knowledge the first report of a spontaneous, in vivo fracture of a last-generation, angle-supported Kelman-type acIOL. Although the precise mechanism cannot be determined, possible explanations are the presence of a manufacturing defect, corrosion of the IOL material and surgical handling causing micro-fissures to the IOL material during cataract surgery. Previous reports on spontaneous in vivo fractures of acIOLs refer to older versions of angle-supported IOLs. Maguen et al. first reported in 1985 fracture of a haptic of a semiflexible Kelman acIOL [5]. Park et al. described in 1987 a fracture at two sites of the haptic of a PMMA, semiflexible, closed-loop acIOL [6]. Later, Craig et al. reported in 1989 a break at the optic-loop junction of an one-piece Cilco Simcoe-type-C-loop acIOL [7] and Weickert et al. in 1992 an acIOL fracture also being localized at the optic-to-haptic junction [8]. Interestingly, an in vivo fracture of a Kelman-type acIOL following blunt ocular trauma has been reported in only three cases [9,10]. The authors suggest that the force applied during a blunt trauma may lead to fracture at the weakest point of the IOL, i.e. the optic–haptic junction, especially on a basis of progressive corrosion of the IOL material.
It has also been described that rarely an acIOL may be fractured even after a Nd:YAG laser iridotomy [11]. Respectively, only 8 cases describing spontaneous fractures of posterior chamber IOL (pcIOL) have been reported. As the latter comprise the vast majority of implanted IOLs, spontaneous fractures of pcIOLs are also considered as extremely rare [12-19]. The authors proposed as causative factors a manufacturing defect, time-dependent corrosion or microdefects of the IOL material induced during the IOL implantation. Additional factors such as blunt trauma or capsular bag contraction could trigger a fracture on a basis of a damaged IOL material [19]. In conclusion, a rare case of spontaneous in vivo fracture of a modern, all-PMMA, Kelman-type acIOL is described, despite the progress in materials and manufacturing of last generation acIOLs. Thus, further improvement of IOL technology could reduce the risk for late fractures. Additionally, although acIOLs are made of rigid PMMA material, careful handling of the implant during catarac
t surgery may be advised in order to avoid mechanical microdefects of the acIOL. Finally, ophthalmologists should always have in mind that although infrequent a spontaneous fracture of an IOL is a possible diagnosis when a pseudophakic patient complaints about deterioration of vision.
For more Articles: https://biomedres01.blogspot.com/




No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.