Characterization of Toxic Habits in Patient Geriatrics from a Health Area
Introduction
The older adult in Cuba occupies more than 19%, and it is expected that by 2025, one in four Cubans will be older adults. Of this population only one percent is in institutions, 9% live alone and the rest live with family members [1]. The so-called third age, also known in the terms of old age, late or adulthood, has been addressed in the literature in isolation or as a phase of involution and not as an authentic stage of human development. It is located around the age of sixty, associated with the event of occupational retirement [2].The call third age, bigger or later adulthood, it has been approached in the medical literature in an isolated way and I don’t eat an authentic stage of the human development [3]. Physical rehabilitation consists of restoring the affected function by means of specific interventions, which obey a plan previously established on the basis of the clinical characteristics of the patient in question. Its ultimate goal is the recovery of functions, so that the patient can meet daily demands with a minimum of efficiency [4-6] In spite of the demographic increase and the high degree of population aging that Cuba exhibits, there are not ample references of research in relation to the geriatric study that measure the cognitive and affective state, however, there are statistical data that have been attended and offered monitoring and special treatment of the psychological well-being of the elderly, precisely in these last five years [7-10] The objective of the present investigation was to characterize of toxic habits in patient geriatrics from a health area.
Methods
Theoretical Level
Synthetic Analytical: It made possible the interpretation of each one of the studied texts, to conform the criterion assumed in the epigraphs and paragraphs, as well as to particularize in the data obtained in the surveys to integrate them and to establish the corresponding generalizations.
Inductive-Deductive: It facilitated going from the particular to the general in each of the analyzes carried out in the theoretical study and in the processing of the obtained information.
Generalization: It allowed the establishment of the regularities that were revealed in the study carried out.
Empiric Level
Open Interview: Contributed to identify the toxic habits indicators in the bigger adults.
Individual Clinical Histories: It made it possible to provide information on various personal aspects.
The selection was based on the following approaches:
Inclusion Approaches
a. All the patients of both sexes, older adults between 60 to 80 years of age.
b. Elderly patients who give their consent to participate in the investigation.
Exclusion Approaches
Patients with a psychiatric history whose psychotic level prevents them from cooperating with the study were excluded.
Exits Approaches
Patients that abandon the investigation voluntarily.
Collection of the Information
For the collection of information, a form was designed with the variables that were to be investigated, which included general data, such as age, sex and toxic habits. In addition, the open interview was conducted, with prior informed consent.
Statistical Analysis
Once the information was collected, an automated database was created, supported on Windows Microsoft Excel, from which the frequency distributions for the tables and graphs that summarized the primary data were extracted. Descriptive statistics techniques were applied to obtain absolute frequencies and percentages [12].
Results
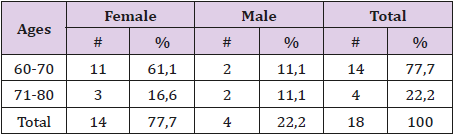
Table No 1: Characterization for Sex and Age
The Table 1 show ages that are located among the 60 years and more, 14 individuals are of the female sex (77,7%) and 4 of the male sex (22,2%). In the analysis of the total of old patients the sex female prevailed with 14 cases (77,7%), the male one represents 4 old men (22,2%), standing out the group of 60-70-year-old ages, for the two groups (77,7%).
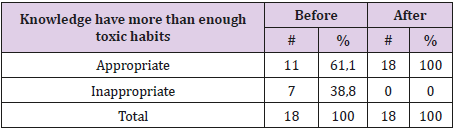
Table No 2: Knowledge Have More Than Enough Harmful Effects of the Toxic Habits
The Table 2 it represents the knowledge it has more than enough effects prejudicial of the toxic habits, you can appreciate that the intervention was valuable, after finishing it, the number of patient with appropriate knowledge increased significantly and even two of them you incorporator to the consultation of Ceasing Tobacco of the rehabilitation Service.
Table 1: Knowledge have more than enough harmful effects of the toxic habits.
Source: Open interview.
Discussion
The aging process brings I get the reduction of the physical capacity and/or the development of an individual’s deterioration cognitive [13]. Nevertheless, diverse pathologies, accidents, history of life, loads genetics and aspects psychologic and social can influence in the speed and severity of such conditions, even in the condition of functional dependence [14]. In connection with the grade of independence, this study coincides with the author Marines Tambura and other [15] where almost 85% of the old men was independent, continued by those with partial dependence (9%). Several works have demonstrated that the depressive symptoms are related with a precarious health and a functional inability, for what is considered as a problem of very important public health and their study is integral part of the investigations about the well-being and the health of people of advanced age [16- 18]. In the literature on the sciences of the health has been picked up that relationship exists between the escolaridad level and the state cognitive of the biggest adults. The old men with low escolaridad grade are hindered the understanding and realization of tasks [19].
The interest for the adjusted lifestyle to the physical sphere, cognitive and affective in the biggest adults they make that by means of pursuit and attendance with the help of the diverse professionals implied with the direct work in rehabilitation achieve an appropriate active or successful aging as primary process that implies gradual and unavoidable changes related with the age, which appear in all the members of a species [17,18]. The aging process is normal, and it happens in spite of the fact that the individual of enjoyment of good health or maintain a healthy lifestyle and I activate. Therefore, it is indispensable for the attention and health integral geriatric to take conscience singular of their own state of health psychologic and social, spiritual and cultural. By way of conclusion, the age is the unavoidable result of the organic and mental deterioration, which becomes visible by the middle of the life and it progresses to a quick rhythm. To age like biological process has extensive social and psychological consequences in today’s world and especially in the county of Villa Clara, where the population’s aging increases, what implies that the biggest adults demand actions integrated with the help of professionals and the intervention of different sectors that cover their diverse biological, psychological and social necessities.
Conclusion
The magnitude of the population’s aging doesn’t have precedents; it is a process without limits in the humanity’s history, the number of grown-ups increases exponentially in complex and uncertain socioeconomic joints. The development of professional competitions that offer attention to the biggest adult to guarantee the quality and the excellence in the attention of health, will allow potencies an appropriate lifestyle and to prevent that becomes a crisis factor for the sanitary structure. The obtained results are notably positive on the cost of their implementation in the current socioeconomic assisting to the focus psychologic and social in health, about the improvement of the lifestyle of this group , as for knowledge that will allow them to modify their state of health and in turn an aging very happened to the minimum of incapacity and this way the development psychologic and social and to prevent that the aging becomes a factor of normative for the sanitary structure and of the social security.
For more Articles: https://biomedres01.blogspot.com/



No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.