Assessment of Cytotoxic Activity of Calotropis Procera’s Extracts Using Artemia Salina Assay
Introduction
In modern era, the medicinal plants have been gradually
replaced by synthetic drugs. But of recent, it is being realized that
several diseases were found to develop drug resistance to synthetic
drugs and also responsible for many of adverse effects. The present
study concentrates on the cytotoxic activity of the folklore claimed
plant Calotropis procera using brine shrimp lethality bioassay which
is based on the ability to kill cultured brine shrimp (Artemia salina).
Artemia salina the brine shrimp is an invertebrate component of the
fauna of salina aquatic and marine ecosystem. It plays an important
role in the energy flow of the food chain [1]. Calotropis procera
was formerly placed in the family Asclepiadaceae (the milkweed
family), which is now considered a subfamily of the Apocynaceae.
Materials and Methods
Collection of Plant Samples
Apparently healthy plant namely C. procera were collected from Ado-Ekiti, Ekiti State Nigeria.
Preparations of Plant Extracts
The plant parts leaves and stem were air-dried for 5 weeks at room temperature (25 + 2 0 C) and then ground to powder with a mechanical grinder (Thomas Wiley machine, model 5 USA). Powders (200g) of each plant were extracted with 1litre of sterile aqueous water, ethanol, methanol and acetone separately at room temperature (25 + 2 0 C). They were labeled as crude extracts.
Cytotoxicity Assay
This assay is carried out by using Brine Shrimp (Artemia salina L.) model [2]. Brine shrimp eggs were collected and placed in one side of a small tank divided by a net containing brine salt solution at a temperature around 370 C equipped with constant oxygen supply by using an air pump for hatching. The method of Artemia Salina was used to analyze the cytotoxicity assay, whereby the concentration of the extracts were varied as follows; 10, 100, 1000µg/ml. The positive control and the negative control were (DMSO4 ) and (brine solution without extracts) respectively.
Results
Cytotoxicity Assay of The Active Extracts of Calotropis Procera Leaf and Stem
The number of shrimps that were able to survive after 24 hours and 48 hours were enumerated.
Cytotoxicity Assay of The Active Extracts of Calotropis Procera Leaf and Stem After 24 Hours
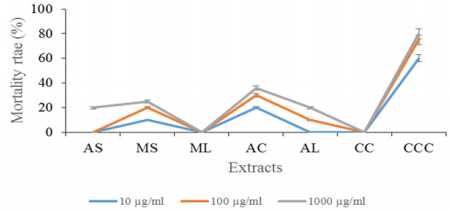
Acetone extract had the highest mortality rate, followed by the methanol stem and aqueous stem extracts whereas there was no death of the brine shrimp in methanol leaf extract (Figure 1).
Figure 1: Mortality rate of Brine shrimp exposed to extracts of Calotropis procera at different concentration after 24 hours.
Key: AS-Aqueous Stem, MS- Methanol Stem, ML- Methanol Leaf, AC- Acetone Leaf, CC- Negative Control And CCC- Positive Control.
Cytotoxicity Assay of The Active Extracts of Calotropis Procera Leaf and Stem After 48 Hours
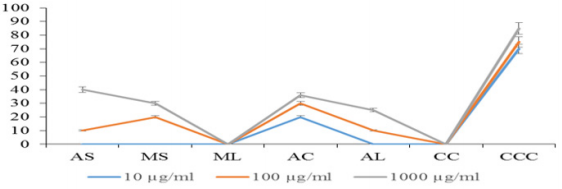
At 48 hours, the mortality rate increases in all the extracts except methanol leaf extract that had no death of the brine shrimp even at 24 hours (Figure 2).
Figure 2: Mortality rate of Brine shrimp exposed to extracts of Calotropis procera at different concentration after 48 hours.
Key: AS-Aqueous Stem, MS- Methanol Stem, ML- Methanol Leaf, AC- Acetone Leaf, CC- Negative Control And CCC- Positive Control.
The Lethality Dose (LD50) Values (µg/Ml) Of Active Extracts
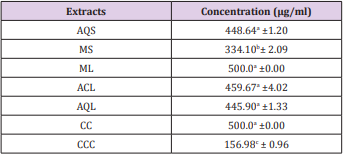
The lethality dose showed that the CC (positive control) which is brine solution without extracts; had the highest mortality rate which gave the lowest value of LD50 (Table 1).
Table 1: The lethality dose (LD50) values (µg/ml) of various extracts required to killed 50% brine shrimp after 24 hrs.
Key: AQS-Aqueous Stem, MS- Methanol Stem, ML- Methanol Leaf, ACL- Acetone Leaf, AQL- Aqueous Leaf
CC- Negative Control And CCC- Positive Control.
The Lethality Dose (LD50) Values (µg/Ml) Of Active Extracts
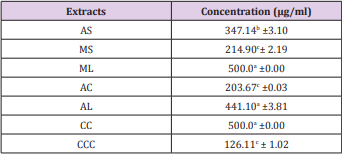
The result showed that the CCC (positive control: brine solution without extracts); with the highest mortality rate had the lowest value of LD50 (Table 2).
Table 2: The lethality dose (LD50) values (µg/ml) of various extracts required to killed 50% brine shrimp after 48 hrs.
KEY:
AS: Aqueous Stem
MS: Methanol Stem
ML: Methano Leaf
AC: Acetone Leaf
AL: Aqueous Leaf
CC: Negative Control; just the brine solution without extract
CCC: Positive Control; brine solution with 2ml of 5% DMSO4
Discussion
This assay plays an important role in the energy flow of the
food chain and it can be used in the laboratory bioassay in order
to determine the toxicity by the estimation of the medium lethality
concentration LC50 [3] Mortality increased gradually with the
increase in concentration of the test samples. This difference
in the toxicity results may be probably due to the chemical
complexity of the crude extracts which seemed to be essential for
the bioavailability of the active constituents of the examined plant
[4]. There was a gradual increase in the percentage of the mortality
rate with the increase in concentration of the extract; this finding
is in support with Ramachandran et al. The brine shrimp lethality
bioassay represents a rapid, in expensive and simple bioassay for
testing plant extracts bioactivity which in most cases correlates
reasonably well with cytotoxic and anticancer properties [5].
Generally, it can be concluded that the extracts contain potent
cytotoxic compounds except the methanol leaf extract.
For more Articles on : https://biomedres01.blogspot.com/



No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.