Epidemiological and Cytological Aspects of Cervical Dystrophies in Senegal Using Cervico-Uterine Smears
Introduction
The cervico-uterine smear or cervical smear is a collection of
cells from the cervix in order to detect at an early stage any cellular
abnormality that may suggest the presence of precancerous or
cancerous lesions of the cervix as well as lesions of dystrophy [1].
Dystrophy is an abnormality of cell growth, which is distinct from
the metaplastic phenomenon and dysplasia. It consists of mild and
limited morphological abnormalities, thought to be of inflammatory
or hormonal origin. These abnormalities must be considered
according to the context in which they are observed (ectopy
metaplasia, atrophy, treatment, irrigative states, and infections) [2].
Methods
It was a retrospective study from August 1, 2014 to June 1, 2016 carried out at the Aristide LE DANTEC hospital in the laboratory of clinical cytology and reproductive biology. The technique used to detect dystrophy lesions was the cervico-vaginal smear
Patients
The study involved 2391 cases of significant cervico-uterine smears in women from various health facilities in the country and sometimes in the sub region. Women in their menstrual period and women in advanced pregnancy were excluded.
Cervico-uterine Sampling
The cervico uterine sampling made in the laboratory of clinical cytology and reproductive biology at Aristide LE DANTEC hospital of Dakar was carried out according to the following procedure: registration of the patient on arrival, the patient was registered in a register with an identifying number, second name, first name, age, and origin and billing number. After this step, a receipt with the registration number was given to the patient to be presented on the day the results are to be retrieved; and interrogation was carried out based on the survey form.
Papanicolaou Coloration
The slides are then dried and stained using the Papanicolaou method.
Interpretation
Satisfactory smears are smears with an abundant epithelial cell population (covering 20% of the slide) of intact morphology, corresponding to squamous (ectocervix), glandular (end cervix) or metaplastic cells without inflammatory reaction or excessive bleeding. These are smears that cannot be reliably analyzed for the following reasons: paucicellar swabs; dense inflammatory or hemorrhagic lesions masking the epithelial elements.
Ethical Consideration
The study protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee of the faculty of medicine, pharmacy and odontology in Cheikh Anta Diop University, Dakar, Senegal. A written informed consent was taken from all participants.
Statistical Analysis
The data was stored and analyzed on the Excel software.
Results
Age
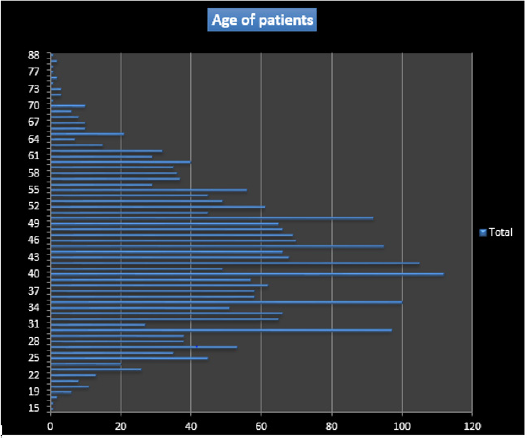
The mean age of the patients was 47.72 years with a standard deviation of 11.37 years. The most represented age (mode) was 40 years (Figure 1).
Reason of Sending
Routine check-ups with no apparent clinical manifestations represented 43.16% of patients. The other requests were due to various clinical manifestations: metrorrhagia, primary or secondary amenorrhea, pelvic pain, and dysmenorrhea.
Types of Dystrophies
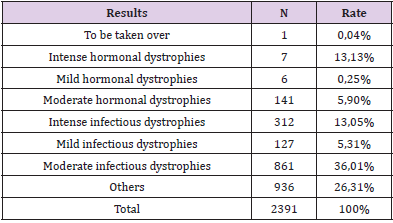
Multiple dystrophic lesions (60.85%) were found of infectious (mild, moderate and intense) and hormonal type. Infectious dystrophies accounted for 54.37%. The infections encountered were bacterial, parasitic (chlamydial), fungal or viral (herpetic) (Table 1).
Discussion
Epidemiological Data
Systematic analysis of the results of our study provided us with
important information on the epidemiological data of cervicouterine
smears in Senegal. Indeed, after 22 months of collection,
the mean age of the patients in our series was 47.72 years with
extremes between 15 and 88 years. In Ethiopia, Mesele and his team
found the same average age in 2010 (47.7 years), after 6 months of
study [3]. This age generally corresponds to the period of genital
activity in most women. Epidemiological studies have shown a
strong correlation between sexual age and certain HPV infections
[4] and patients were sometimes referred by various public (more
than 65%) and private health facilities. This can be explained by
the rather accessible cost of this examination in our center (less
than 10 euros) compared to private structures that perform this
same examination. Our countries have very little universal health
coverage, unlike several countries in the North where adherence
to screening is higher but limited in some areas by disparities [5].
Our patients lived mostly on the outskirts of Dakar, 53.47%. The
departments of Pikine and Guédiawaye are home to more than 50%
of Dakar’s population [6]. We therefore believe that increasing the
number of public screening facilities in the Dakar suburbs would
surely increase adherence to systematic screening.
Asymptomatic subjects referred for routine screening
represented 43,.17%. These results are in contrast to those
obtained by Diallo and his team, who showed 20 years ago that in
the absence of functional urogenital signs, women rarely consulted
Senegalese health facilities for early detection of cervical lesions
[7]. In France, the high health authority recommends systematic
screening for precancerous and cancerous cervical lesions by
cervico-uterine smears every three years in women aged 25 to 65
[8]. We note that education, information and communication about
cervico uterine diseases are fundamental in their prevention.
The Dystrophic Smears
Dystrophic smears with an inflammatory background were founded in 60.73% of patients, 54.37% of which were infectious. Infections are of several types (viral, bacterial, parasitic and mycotic), sometimes intertwined. Cervicitis and cervico-vaginitis are very frequent in developing countries and are characterized by desquamation and ulceration of the surface epithelium with infiltration of neutrophils [9]. A study conducted in the same department found a rate of dystrophy almost similar: 61.33%. The frequency of infections in our countries is explained by several factors including polygamy, poverty and ignorance.
Conclusion
Cervical dystrophy lesions are benign lesions that could, by
their persistence, lead to low-grade epithelial lesions.
For more Articles on : https://biomedres01.blogspot.com/

No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.