Coats Disease in Young Patient with Congenital Cataracts History
Case Report
He is 14-year-old boy, attended at the Ophthalmology Unit
of High Specialty at Hospital Civil de Guadalajara Fray Antonio
Alcalde since 2013. He had an ophthalmologic precedent of
bilateral congenital cataract, treated with cataract faco aspiration
and capsular bag implantation of intraocular lens (IOL) of both
eyes in the same year, as well as correction of air lenses after the
surgical procedure and visual therapy, with adequate evolution.
Nevertheless, the patient loses his follow up as of 2018. Later,
in May 2021 he requests a new assessment due to progressive
visual loss of the right eye of 5 months of evolution, with no other
association. Left eye reports no symptomatology. Other personal
precedents without significant data.
Ophthalmologic Exploration
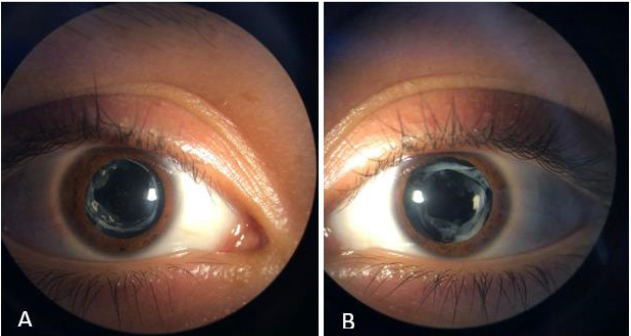
Best corrected VA OD 20/400, OS 20/30. No alterations in OU eyelids and annexes, eucromic conjunctiva, clear cornea, formed anterior chamber, isochoric pupils, nomoreflectic, Pseudofaquia, intraocular lens in capsular bag (Figures 1 and 2).
Figure 1: Clinical picture of IOL in situ, opacity of posterior capsule is observed, as well as fibrosis with free visual axis right eye (A), left eye (B).
Fundoscopy
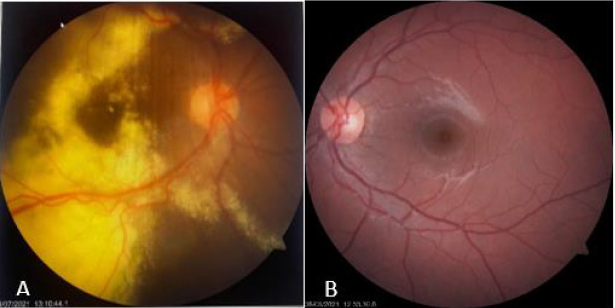
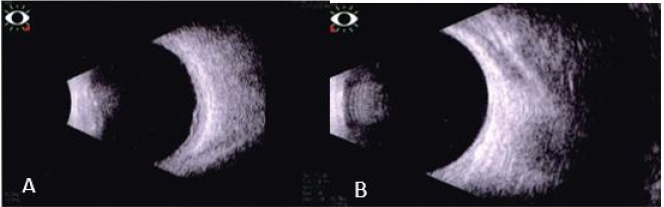
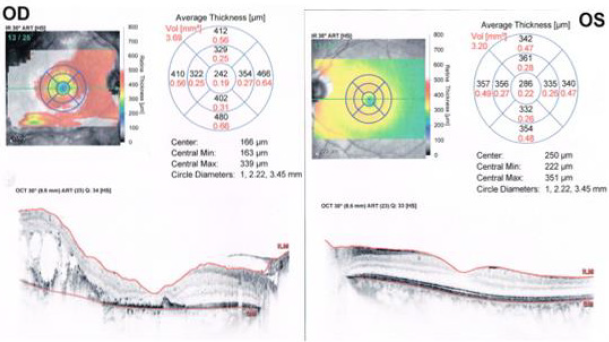
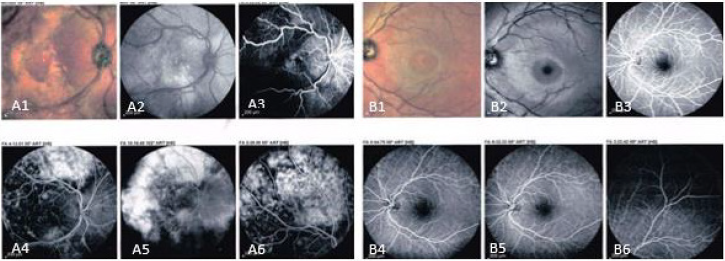
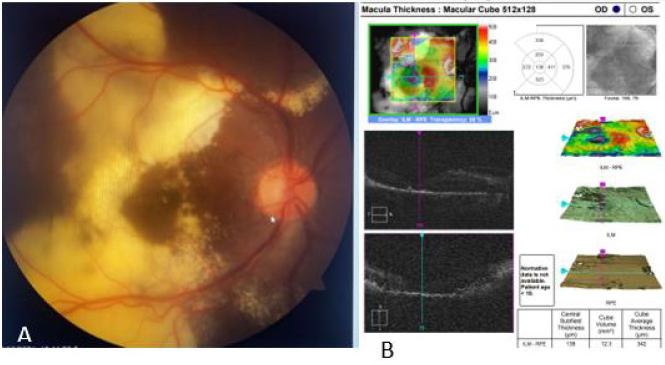
OD clear vitreous, isochoric pupil, normochromic, retina with exudation at inferior and superior temporal arcade level with presence of vascular tortuosity, macular exudates. OS without alterations (Figures 3-5). In ultrasound of OD, we observe normal ocular globe contour, with intraocular lens of posterior chamber, vitreous with small mobile condensations of low reflection, thickened retina due to important cystic edema with macular involvement, thickened choroid secondary edema, irregular papilla. OS is reported without alterations (Figure 4). Macular spectral domain ocular coherence tomography of OD, where 242-micron central foveal thickness is observed, in presence of intra-retinal cysts and sub-retinal fluid.
OS with central foveal thickness of 286-micron, within normal parameters (Figure 4). In the fluorescein angiography (FA) of OD we observe retinal vessels with dilation and leaks, with telangiectasias in retina surrounded by hard exudates, in peripheric retina with hyperfluorescent zones corresponding with areas of capillary closure. FA of the OS is observed without alterations (Figure 5) In accordance with clinical characteristics of the patient, as well as findings in complementary studies, Coats disease is diagnosed. Treatment with scheme of intra vitreous anti-VEGF (Aflibercept) of OD, and with previous informed acceptance from his parents, first dose was applied on Aug 05, 2021. After three weeks he is evaluated, and patient refers recovery of visual quality. Nevertheless, BCVA of OD didn´t improve further than 20/400. A second dose of anti-VEGF was applied in September 2021. He was evaluated one week later presenting vision improvement, with a BCVA 20/200 and reduction of retinal exudation as shown in Figure 6.
Figure 5: Fundus images, right eye (A1), left eye (B1). Red-free images of the retina, right eye (A2), left eye (B2). Flouoresceine angiography of right eye (A3- A6), left eye (B3- B6).
Discussion
Coats Disease is a retinal vascular disease, characterized
by telangiectasias and vascular leaks that lead to exudation. It is
typically found in young males, between the first and second decade
of life, with a peak of incidence between 5 and 11 years old. In 85-
90% of patients, it is a unilateral affectation. In cases of bilateral
disease, the other eye shows no symptoms with slight telangiectasic
changes in the periphery. There is no preference for race, and is a
sporadic non inherited condition, without systemic association;
the gold standard for the diagnosis of this disease is the eye fundus
clinical exploration through direct ophthalmoscopy [1,2] and as
our patient fitted in the above-mentioned characteristics, the
diagnosis of Coats has reached. However, there are very few reports
regarding the association of this pathology with the presentation
of Congenital cataracts, even less in a bilateral way, as is the case of
our patient [3,4].
The etiology of Coats disease is not completely defined;
however, it is well known that retinal vascular leak is one of the
main pathologic processes found in this disease. Several studies
have been recently found that where an increase of cytokines is
evidenced in the aqueous humor of patients with Coats disease,
mainly the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) of the
aqueous humor was strongly elevated in this entity and had
correlation with the extension of the retinal exudation. Tingy
Liang et al. analyzed the aqueous humor of two groups of patients.
One of them had 36 patients with Coats disease and another one
with 15 patients as a control group with congenital cataract.
Concentrations of 22 different cytokines, of which, concentrations
of 8 cytokines (VEGF, IL-6, IL-8, MCP-1, MIP-1α, IP-10, VCAM-1 e
ICAM-1) were significantly higher in the group of Coats disease,
however, significant differences were observed in bFGF, TNF-a and
IFN-y between the group of Coats disease and the control group,
being this of importance for our patient since he presented both
diseases and thus the use of anti-VEGF drugs for his treatment is
sustained [5].
Broadly speaking, the objective of the treatment for slight and
moderate disease is preservation of the vision and prevention of progression of the disease as retinal detachment and all the
other complications already mentioned. That is why treatment
is focused in ablation of the actual abnormal vasculature of the
retina by means of photocoagulation with laser and cryotherapy.
However, the innovative therapy is the use of intra vitreous VEGF,
which is also recommended as a contributory manner with the
traditional therapies already mentioned, since it seems to reduce
macular edema and exudates, stabilize visual acuity and enhance
regression of abnormal vessels, as observed in our patient, with a
vision improvement and reduction of posterior retinal exudation to
the first dose of intra vitreous anti-VEGF. Even though a complete
regression of the disease is not expected, our objective is to stop
progression and avoid appearance of future complications. [2,6,7].
Even though association of the appearance of cataracts is reported,
after presentation of Coats disease, as mentioned by Daruich A. et
al. [7], inverse association (that means, late presentation of Coats
disease with bilateral congenic cataracts background) without a
syndromic association is very rare.
Conclusion
Coats disease is a pathology that must be found within the
diagnostic suspicion from the general ophthalmologist and the
pediatric ophthalmologist since it is a relatively frequent pathology,
since it can have important implications for the visual quality and
life of the patient; as well as the severity of differential possible
diagnosis as can be the retinoblastoma and, as in our case, always
maintain close ophthalmologic monitoring in patients with
pathologies that are not so frequently associated as Congenital
cataracts, since, as there are no systemic associations found, the
current limited understanding of the exact pathophysiological
mechanisms that produce this disease leaves us with a window
of possibilities in which we can observe clinical presentations as
varied as the case of our patient.
For more Articles on : https://biomedres01.blogspot.com/



No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.