Review of the COVID-19 Pandemic on the Urology Literature
Introduction
The COVID-19 pandemic has changed not only our daily lives, but the very practice of medicine as we once knew it. On March 11, 2020, the World Health Organization declared COVID-19 a global pandemic. Since then, our lives have changed in ways we could have never imagined. COVID-19 has become a staple of our daily conversations with family, friends, patients, and particularly fellow colleagues in medicine. During the pandemic, the lives of healthcare workers have changed significantly, both in terms of clinical work and research. There has also been an increased interest in reviewing, studying and analyzing bibliometric trends to characterize and understand the academic literature and how it affects clinical practice [1,2]. Bibliometric instruments have been applied for analyses of the urologic literature [3,4]. Given the immense impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on medical care, investigators from many other specialties have sought to characterize the influence of the pandemic on their respective literature. Preliminary reports have documented a substantial number of peer-reviewed publications pertaining to the COVID-19 pandemic and have noted that these publications have garnered more attention compared to other articles published concomitantly [5]. Our objective in this study was to classify the effect of the COVID-19 pandemic on the urologic literature. We hypothesized that similar trends would be observed in the urological literature with articles related to the COVID-19 pandemic.
Materials and Methods
Using the Journal Citation Reports, the 15 urology journals with the highest impact factors in 2019 were identified [6,7]. These journals were subsequently queried in an Advanced PubMed search to identify all articles published in 2020. This search identified 5,614 articles. The Altmetric Attention score (AAS) for each article was collected using the Altmetric Bookmarklet tool. AAS is a wellestablished metric of article dissemination and influence taking into account article mentions across various social media outlets, the news, and research outlets. The number of subsequent citations was obtained using the National Institute of Health iCite tool [8]. All queries were performed in February 2021. Articles were screened to be subsequently divided into two cohorts, those related to the COVID-19 pandemic and those not related, by searching titles for the following terms: “COVID”, “SARS”, “pandemic”, “corona”, “COVID-19”, “2019 nCoV”, “2019 novel coronavirus”, or “SARS-CoV-2”. Two hundred and sixteen (3.8%) articles met these criteria. Kruskal- Wallis tests were used to compare AAS and citations for COVID-19 versus non-COVID-19 articles. Mann-Whitney and Chi-squared tests were used to assess continuous and categorical variables, respectively. Furthermore, for articles related to COVID-19, AAS and citations were compared by type of article, sub-specialty of urology, and quarter of the year (Q) in which the article was published. Analyses were performed using R Statistical Software (version 4.0.2; R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria) and p-value of <0.05 was considered significant.
Results
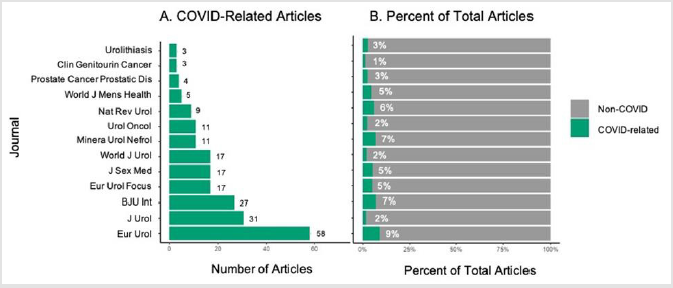
Two hundred and sixteen (3.8%) articles were related to the COVID-19 pandemic based on the aforementioned identifiers which is a comparable proportion to other specialties [5]. All 15 journals published articles pertaining to the COVID-19 pandemic and European Urology published the highest proportion of COVIDrelated articles (9.1% vs. 3.1% all other journals, p<0.001, Figure 1). A total of 29 countries were represented in authorship, with the most common being the United States (26%), Italy (23%), and the United Kingdom (10%). The median number of authors and institutions per article was five and three, respectively. Notably, there were 21 first authors who published more than one article and their contributions accounted for 22% of the COVID-19-related literature in urology. Sixty-three percent of articles discussed the effects of COVID-19 on the field of urology overall, whereas the remainder discussed implications for specific urological subspecialties: 21% oncology, 11% men’s health, 4% endourology, 1% female reconstruction, and 0.5% pediatric urology.
Figure 1:Total number of COVID-19 related articles and percent of total articles published by the Top 15 Urology journals in 2020.
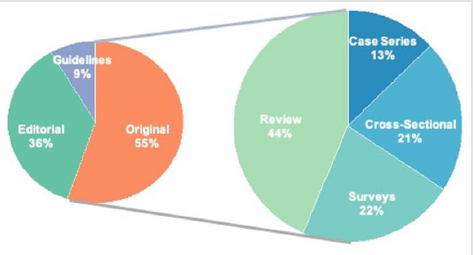
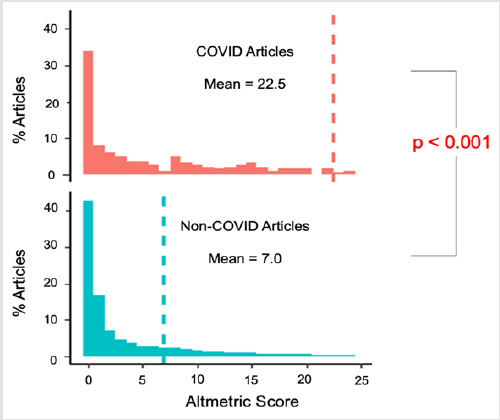
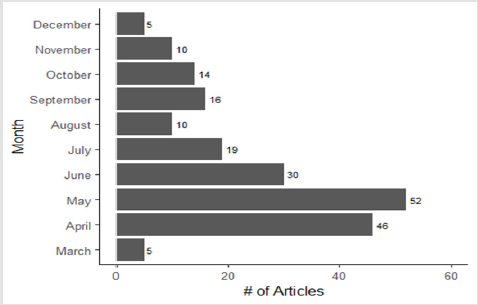
There were 117 (55%) original research articles, 77 (36%) editorials, and 18 (9%) guidelines. Of the original articles, 25 (21%) were cross-sectional studies, 51 (44%) reviews, 26 (22%) surveys, and 15 (13%) case reports (Figure 2). Sixty-two (29%) of COVID-19 related articles had an AAS of zero, indicating that these articles were not disseminated via the web, social media or news outlets. However, the average AAS of COVID-19 articles was significantly higher than non-COVID-19 articles (22.5 vs 7.0, p<0.001) (Figure 3). Among the COVID-19 related articles, original articles had the highest average AAS, followed by guidelines, and editorials (32.4 vs 16.3 vs 9.1, p<0.01). The highest average AAS was observed in Q2 followed by Q1, Q3, and Q4 (30.9 vs 26.6 vs 9.4 vs 7.1 respectively, p<0.05). There was no association between AAS and the urologic subspecialty of the article (p=0.54). COVID-19 articles also had more citations than non-COVID-19 articles (7.5 vs 0.9, p<0.001). Articles published earlier in the year accrued more citations (Q1: 36.0 vs Q2: 10.5 vs Q3: 0.7 vs Q4: 0.45, p<0.001). The median time between submission and publication was 52 days, with editorials having the fastest turnaround times (39 days vs. 63 days for other articles, p=0.075). The month of May had the highest number of articles published at 52, followed by April at 46 (Figure 4). Articles had a median word count of 1,393 and referenced a median of nine sources.
Discussion
This review and analysis indicate that the COVID-19 pandemic has had a profound impact on the urological literature. This is apparent by the number of articles published pertaining to COVID-19 during the pandemic and by the increased influence and impact these articles carried compared to non-COVID-19 related articles published concomitantly. This suggests that urologists utilized the literature as a mechanism for discussion and innovation to address the global pandemic. Early in the pandemic, research predominantly focused on the effects of COVID-19 in their respective communities and its impact on the practice of urology [9,10]. As the pandemic progressed, research became more focused, narrowing in on at-risk patient populations, such as those with renal failure infected with COVID-19 [11]. Nearly a third of all COVID-19 related articles had an AAS of zero, demonstrating that they were not disseminated at all in news outlets or social media. Still, the mean AAS scores of COVID-19 articles were three times that of non-COVID-19 articles.
This suggests a higher level of reader interest at the time of publication for these articles and implies that research related to the pandemic was very a “hot topic.” As expected, the average AAS was highest for original research articles which are typically based on higher levels of evidence with more rigorous study design, followed by guideline statements and editorial commentaries. Notably, Q2 of 2020 had the highest average AAS compared to any other single quarter of the year. A close second was Q1, followed distantly by Q3 and Q4. While COVID-19 was first identified in December 2019, it was not declared a pandemic until March 2020. This timeline coupled with the lag time from submission to publication is likely responsible for this trend. The number of articles on COVID-19 that were published during Q1 (ending March 31, 2020) is impressive and speaks to the speed at which researchers and editors worked to inform the urological community of the many challenges created by this pandemic.
The median time to publication for COVID-19 urology related articles was 52 days. This is markedly faster than the 164 days reported for publications of urology articles prior to COVID-19 [12]. This time acceleration may be due to an increased need for timely COVID-19-related literature to guide clinical practice during the pandemic resulting in many journals prioritizing or fast-tracking COVID-19-related articles. Additionally, the early peak of the pandemic in April and May of 2020 also coincided with the months that had the greatest number of articles published. Of the 29 total countries representing authorship, it is noteworthy that Italy had the second greatest number of publications, second only to the United States. With a population of 60 million, less than one-fifth that of the United States and substantially fewer urologists, the Italian Urologic COVID-19 publication output would be commensurate to that generated in the U.S. . Again, this may be due to a multitude of reasons, but may be attributed to increased research output secondary to the enormous COVID-19 spike Italy experienced in March 2020 [13].
Conclusion
It is clear that urology as a whole united to navigate the hurdles the pandemic created by publishing important articles in a timely fashion. From highlighting the effects of COVID-19 on male fertility, to the experience of urologists on the frontlines of the pandemic in New York City, to studying urological symptoms in COVID-19 patients, the urologic community brought its best to the COVID-19 pandemic [14-16]. While we patiently await our world to return to normalcy, the academic energy generated by our field during the COVID-19 pandemic sheds a beacon of light for better days ahead.
For more Articles on : https://biomedres01.blogspot.com/


No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.