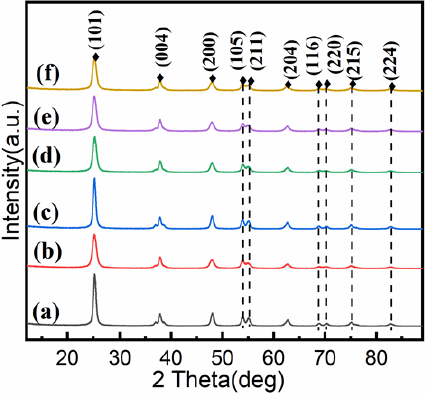
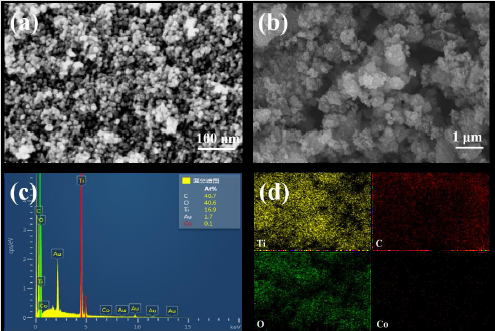
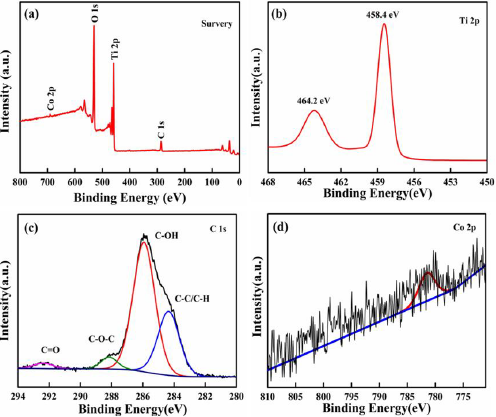
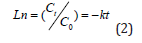Teaching Reform of Obstetrics and Gynecology
Nursing Course in Higher Vocational Colleges Based
on OBE Education Concept from the
Perspective of Big Data
Obstetrics and gynecology nursing is one of the core courses
of nursing specialty in higher vocational colleges. This course is
opened in the third semester, with a total of 3 credits. This course
is a key course for students to master before entering gynecology
and obstetrics clinic. Through the study of this course, students
are required to have solid professional knowledge and proficient
practical skills. Therefore, this course needs to cultivate students’
clinical thinking ability and operation skills through the combination
of theoretical knowledge and practical operation. The course team
analyzed the current situation of the course of Obstetrics and
gynecology nursing in Higher Vocational Colleges by using big
data tools and found that the teaching materials of this course are
relatively backward; The teaching mode is single; The assessment
method is single; Students’ learning initiative is weak; The training
of theoretical knowledge and practical ability. In this regard, our
curriculum group adopted OBE teaching concept to reform the
curriculum through comparison and exploration. OBE (outcomesbased
education) means that the final results of teaching activities
are presented by students’ learning outcomes. Students’ learning
achievement is the maximum ability that students can achieve after
a period of learning. Schools and teachers are required to make
clear the students’ learning achievement, combine the diversified
learning process and hierarchical learning requirements, and let
students complete the challenge of self-realization through the
learning process.
Teachers can feedback and improve the original teaching plan
and teaching implementation by using the results. Secondly, the
ways of enrollment in higher vocational colleges are diversified,
students’ learning background is different, and the use of unified
teaching materials in different learning situations obviously does
not meet the needs of learning situation, which leads to the decline
of students’ learning initiative and enthusiasm. Therefore, starting
from the learning situation, the loose-leaf teaching material is used
to deconstruct the knowledge system and framework, reconstruct
the knowledge chain, reconstruct the teaching module, and teach
at different levels according to the learning situation background.
This course takes the female life cycle as the logic of the course
and reconstructs the knowledge module of the course; Taking
the students as the center, based on the training objectives of the
five major learning areas of OBE, the differentiated teaching is
designed, and the course implementation is carried out in the same
class and heterogeneous way; With students’ learning achievement
as the guidance, multiple assessment methods coexist and
multidimensional assessment is carried out simultaneously; Based
on the learning situation, starting from the needs, project-based
teaching, students are the main body of the course; Integrated
teaching of theory and practice [1,2].
In the course of teaching reform, how to reconstruct the
teaching system, optimize the teaching content, improve the
teaching methods, standardize the teaching process and improve
the teaching evaluation as the main content, it is imperative for
us to implement the teaching reform and practice of big data
application technology course, and cultivate the compound talents
with practical ability and technological innovation ability.
Construction of DQP Academic Framework Under OBE
Teaching Concept
In 1981, American scholar Spady first put forward the concept of
achievement-oriented education, and gradually formed a complete
education system. The theoretical connotation is that students are
the main body, and the ultimate learning achievement of students
is the goal. From the setting of teaching objectives to curriculum
design, curriculum implementation, curriculum evaluation are all
result oriented, and then every link of curriculum implementation
is deduced from the results. The DQP model is based on students’
learning outcomes. The main structure of DQP is composed of
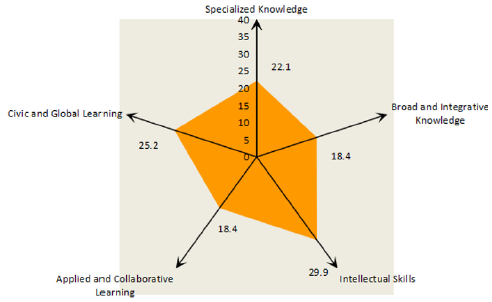
five institution specific areas and three academic levels, namely:
professional knowledge, extensive and integrated knowledge,
intellectual skills, applied and collaborative learning, citizen and
global learning. Among the five learning areas, “extensive and
integrated knowledge”, “application and collaborative learning”,
“citizen and global learning” are the three areas emphasized in
general education to achieve the teaching effect“Professional
knowledge and intellectual skills are the two fields that put more
emphasis on the requirements of students’ professional knowledge
and skills. According to the theory of DQP, the five learning areas
in the same level of academic structure combine the differences
among different students, which can truly and uniformly reflect
the ability evaluation standard. The three academic levels include
associate degree, bachelor’s degree and master’s degree.
The differences in different academic levels mainly reflect the
progressive relationship between the reference points of learning
achievement requirements in the five major learning fields: the
learning achievement requirements of all bachelor’s levels include
the learning achievements of associate degree, and the learning
achievements of all master’s levels also include the learning
achievements of bachelor and associate degree. The requirements
of learning outcomes at each level show the further challenges
and skills that students need to deal with when they move from
one degree to a higher degree. Through the spider web diagram of
the five major learning fields, the unity of the evaluation of each
educational level is intuitively reflected; The hierarchy of ability
requirements; Comprehensive knowledge support and achievement
embodiment [3] Figure 1. Taking the knowledge structure of
the five learning fields as the framework template, students can
change from “understanding, mastering and memorizing” in the
previous curriculum standards to curriculum norms, including the
process comprehensive assessment of “being able to say, be able
to do, be able to solve, etc. “For example, DQP puts forward that
“in a special field or a relatively common field of art and science,
when doing a project, writing an article or program, or performing a
performance, we can effectively find the information we need,
classify the collected information, evaluate the usefulness of the
information, and properly quote or apply the useful information to
the project Article or scheme, performance “.
For example, in order to cultivate students’ creative ability,
teachers can carry out evidence-based analysis of clinical operation
guidelines in the practical training of Obstetrics and gynecology
nursing, let students divergent thinking, find evidence through
empirical research to support existing views or improve existing
views, innovate existing equipment, etc. We should cultivate and
incubate valuable research to promote the progress of teachers
and students. Students and teachers design together, verify the
results together, learn together and grow together [4]. The form of
curriculum assessment is not only reflected in knowledge memory
and knowledge accumulation, but also focuses on the practicality
of knowledge. At the same time, it combines the application and
innovation of knowledge, which is well in line with the call of
the country for innovation and entrepreneurship. Through the
learning process of peer-to-peer curriculum, diversified curriculum
achievements are reflected, and students’ learning process and
skills are deposited in the display of learning achievements, which
can be measured, evaluated, further corrected and improved. Verify
the learning effect of students and reflect the teaching effect of
teachers, so as to reverse design the course and further implement
the classroom reform and optimization [5].
Through peer-to-peer learning process, diversified curriculum
achievements are reflected, and students’ learning process and skills
are deposited in the display of learning achievements. Through data
comparison and analysis, students’ learning achievements can be
measured, evaluated, and further corrected and improved. With the
development and improvement of information technology, people’s
learning methods and behavior habits have been gradually changed.
The traditional teaching mode has been unable to meet the current
teaching needs. Under the perspective of “Internet plus big data”,
students have more learning means and various learning channels.
Nowadays, most of the students in Higher Vocational Colleges grow
up in the period of rapid development of information technology.
They have a natural curiosity about new things and ideas. Their
thinking mode and learning state are very different from those of
the past. Through big data technology, students can search most of
the content on the Internet. To a certain extent, it has changed the
students’ learning style, and also provided some new ideas for the
curriculum teaching reform in higher vocational colleges. Only by
adopting the methods that students can accept, can the curriculum
teaching be effectively changed. Through the analysis of statistical
data to understand the teaching effect, verify the learning effect of
students.
So as to feedback the teaching quality of teachers. Through the
analysis and comparison of classroom data, we can reverse design
the curriculum and further implement the classroom reform and
optimization.
Curriculum Standard of Obstetrics and Gynecology
Nursing
Teaching Content: According to the female life cycle, this
course is designed into five modules: basic theory 2 class hours,
including female reproductive system anatomy and physiology. 16
hours of gestational care, including pregnancy physiology to start
the journey of life, prenatal examination to explore the secret of
baby growth, prenatal examination to explore the mother’s secret,
abnormal pregnancy to reveal the mother’s troubles. Childbirth
care for 10 hours, including normal childbirth escort, abnormal childbirth race against the clock. 16 credits for gynecological
diseases, including inflammation of reproductive system, tumor
of reproductive system and endocrine diseases. 4 class hours for
women’s health care.
Analysis of Learning Situation: We get a series of data by
using questionnaire survey and other methods, and then use big
data analysis method to get the students’ learning situation of this
course. The specific performance of his learning situation is as
follows. The student group of this course is the new generation after
zero, which belongs to the third semester of nursing sophomore.
This student group not only has the common characteristics
of students of this age group, but also has the specific learning
situation characteristics of students of this major. First of all, the
new generation after 2000 is full of personality and curiosity about
new things. They have strong hands-on ability. They don’t like to be
limited and always have unlimited creativity, but they have certain
shortcomings. For example, they are not willing to repeat learning
and are not willing to train many times. Secondly, the proportion of
male and female in nursing major is very different, female students
account for 80% - 100% of the class on average, and the classroom
activity is relatively low compared with ordinary classroom.
In terms of basic knowledge, students have offered systematic
anatomy, female physiology and other courses when they enter the
course. Because the enthusiasm of students’ repeated learning is
not high, so the mastery of theoretical knowledge is relatively weak.
According to the learning characteristics of students, this course
combs the preview before class through mind map and other ways,
strengthens the review after class, and reviews the old to learn the
new. In terms of basic skills, students have preliminary contact
with nursing and obstetrics and Gynecology related skills, but their
proficiency is not high.
In this regard, this course carries out situational guidance,
optimizes training courses, refines training standards, and
improves students’ enthusiasm through mutual training and
evaluation. At the same time, the learning characteristics of this
course are different from other courses. Because most of the
students in the class are girls, they are very interested in exploring
the secrets of pregnant mothers. It is very important for teachers
to take the students’ interest as the ignition point, to stimulate the
enthusiasm of students’ active exploration of learning, and to let the
students become the main body of the classroom, active learning. In
terms of learning characteristics, students like hands-on operation,
but induction and summary, clinical thinking ability need to be
improved. Through the project-based curriculum module, this
course integrates knowledge and skills into vivid nursing cases
and improves students’ problem-solving ability through case
training. In terms of learning habits, students are willing to try
to use intelligent mobile terminal devices to carry out learning,
prefer personalized learning tasks, make full use of online teaching
resources, carry out hybrid teaching, and respect and promote
students’ personality development by personalized assessment of
learning results. The new generation of post-Zero students have
distinctive personality characteristics, strong innovation ability, but
poor knowledge transfer ability. Therefore, it is necessary to teach
students in accordance with their aptitude, improve classroom
participation, and formulate executable training objectives that
match the learning situation, which is the embodiment of OBE
education concept [6].
Teaching Objectives
Overall Objective: By using big data analysis tools, we connect
the knowledge points and skills of nursing practical jobs with our
higher vocational obstetrics and gynecology nursing course, to
implement the training program of nursing professionals and the
curriculum standard of Obstetrics and gynecology nursing based on
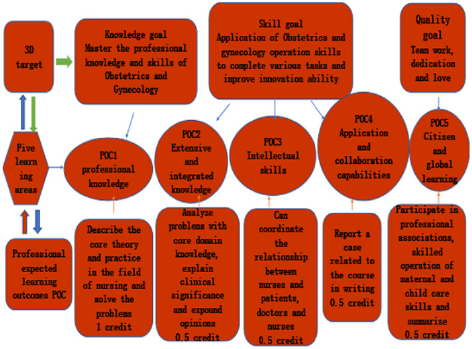
the analysis of learning situation. The curriculum design establishes
a three-dimensional target system of knowledge, skills and quality,
and designs the corresponding program outcome (POC) Figure 2. The
objective of this course is to master the obstetrics and Gynecology
professional knowledge, cultivate professional skills and promote
the ability improvement. The three-dimensional objectives of this
course include knowledge objectives, skill objectives and quality
objectives. The training objectives of each dimension correspond to
and match the relevant learning fields in DQP education framework
structure. Knowledge objectives correspond to one credit of PoC1
professional knowledge in five major learning fields. Students can
describe the core theories and practices in the field of nursing
with relevant terms in the nursing field and solve the nursing
problems in the professional field. The skill objectives correspond
to the knowledge of poc2, poc3 intelligence, poc4 application
and cooperative learning in the five learning fields. Poc2 is 0.5
credits in wide and integrated knowledge. Students can analyze
a controversial problem (such as unprotected delivery, clinical
treatment without payment ability) with knowledge of core areas
learned, explain the clinical significance of the dispute, and explain
their own opinions with the knowledge learned. Poc3 has 0.5
credits of intelligence skills and can use the knowledge learned to
solve and coordinate the relationship between nurses and patients,
medical care and nursing, and propose solutions for specific cases
and revise the implementation plan.
Poc4 application and cooperative learning 0.5 credits, report at
least one case related to the course in writing (such as head basin
incorrect, multiple pregnancy, etc.) to explain how to apply the
knowledge learned to clinical practice and to standardize clinical
evaluation standards. The quality goal is 0.5 credits in poc5 citizens
and global learning fields, that is, through the course learning,
students participate in the relevant professional associations
(including nursing health association and midwifery knowledge
association) to skillfully operate maternal and infant nursing skills,
make oral or written summary (report), and improve coordination
ability, organizational ability and communication ability through
organizational activities [6].
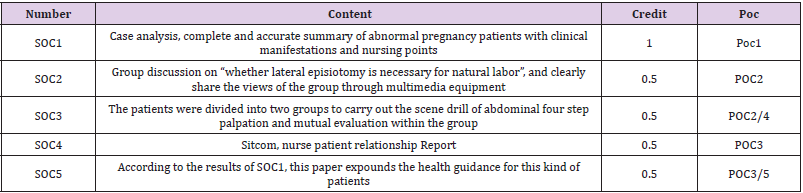
Expected Learning Results of Representative Courses:
According to the characteristics of nursing specialty, we carry
out three-dimensional education of people, and integrate the
cultivation and practice of socialist core values into the teaching
process of each class, so as to keep things fine and silent. Through
the guidance of classroom thinking and politics, we should carry
out labor education, life education, humanistic care, etc. In order
to support and realize the achievement of POC, the corresponding
“subject outcome” (SOC) [7] (Table 1).
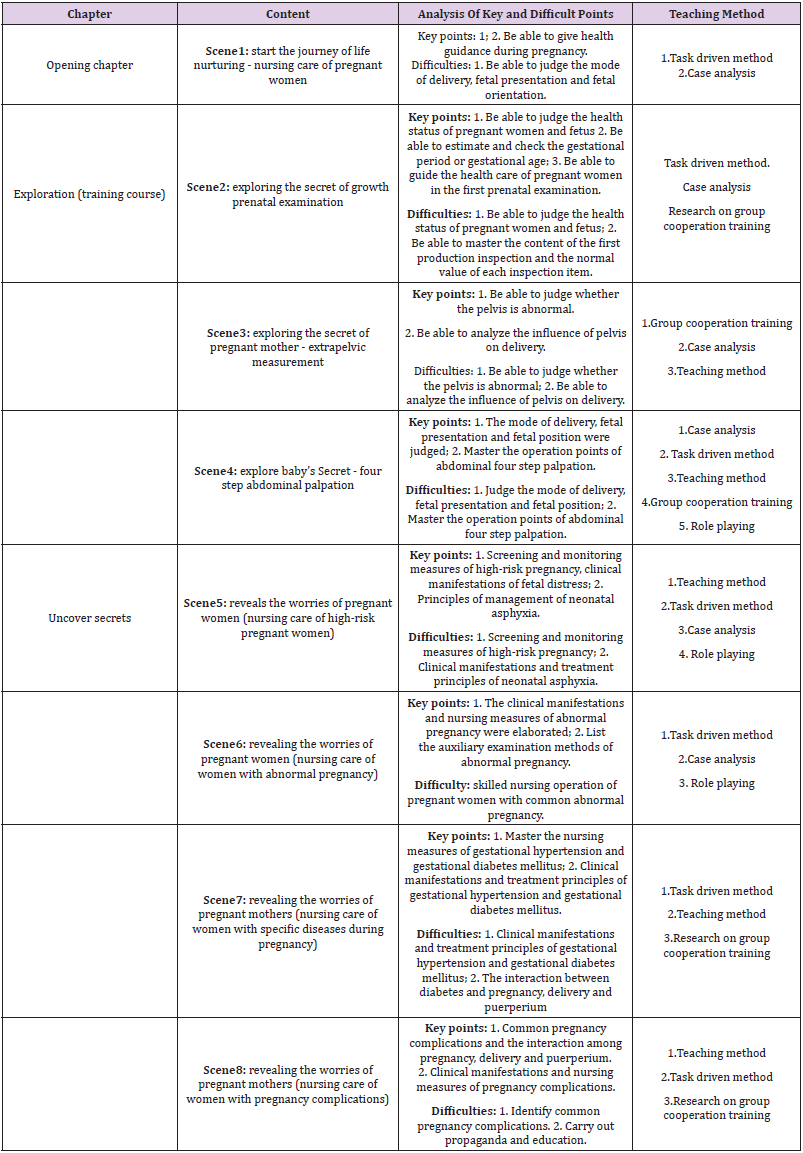
Analysis of Key and Difficult Points and Teaching Strategies:
Based on the background of learning situation analysis, under
the guidance of teaching objectives and professional norms, the
focus of this course is to describe the pathogenesis and symptom
characteristics of Obstetrics and Gynecology related diseases
without error and complete the nursing operation of Obstetrics
and Gynecology related diseases without error. We deconstruct
and reorganize the curriculum according to the female life cycle
and divide the curriculum into five modules. Now take module two
pregnancy care as an example to choose the key and difficult points
and corresponding teaching strategies (Table 2) [8].
Implementation and Effect of Classroom Teaching
Teaching Design Ideas: The teaching design is based on
the analysis of learning situation which is gotten by big data
analysis method, cognitive law of higher vocational students and
industry orientation. 1: integrated teaching, this course adopts
integrated teaching, takes the post demand as the classroom
logic, combines theory with practice, so that students can learn
by doing, practice in learning, and master knowledge and skills.
2: Double subject teaching, course teaching module, on campus
and off campus training, practice together. School learning and
job needs are seamlessly linked. That is: three stages of classroom
teaching, preview before class, knowledge navigation, practice in
class, knowledge consolidation, after class expansion, knowledge
extension, learning for application, improve ability. This model
highlights the progressive cultivation with students as the center,
industry post skills as the basis, students’ learning achievements
as the guidance and ideological and political education as the soul.
This teaching mode realizes “three highs” of teaching effect, that is,
high participation of students, high timeliness of learning process,
and high personalization of learning results [9].
Teaching Implementation Process
Overall Curriculum Implementation: The teaching process
can be divided into three stages: guidance before class, practice
in class and development after class. Based on the teaching plan,
the teaching activities strengthen the communication between
students and teachers by means of information-based teaching.
The information dissemination is timely and the distance between
teachers and students is shortened. Through the comprehensive
and continuous feedback, the evaluation and implementation of
the whole teaching classroom and course teaching can complete a
complete evaluation and diagnosis closed loop in the three stages
of the teaching process““Learning to practice in class” is carried
out with students as the main body and teachers as the guide.
Each independent classroom is divided into four links of “leading
people, entering and winning” (Table 3). Although this course
focuses on adapting to clinical needs, it is impossible to include a
large amount of knowledge in one class. Therefore, we focus on
each class. Now to explore the baby’s Secret “abdominal four step
palpations” as an example to show the four links. The first key word
of classroom promotion is “lead”, that is, knowledge navigation. In
this link, the teacher leads out the knowledge points of the course
by cases, videos, high-quality questions, etc. The second key word
of classroom promotion is “people”. In this link, the main body of
the classroom is students. The teacher manages the classroom as
a scaffold.
Through the teacher’s demonstration, it shows a complete
operation process or an independent case analysis, so that students
can chain up the knowledge chain from point to area. The third
key word of classroom promotion is “entering”. In this link from
“people” to “entering”, the classroom initiative turns from teachers
to students. Teachers help students to sort out the knowledge
chain through the independent inquiry learning mode, sort out the
knowledge fragments in the classroom, apply the knowledge points
to various clinical situations, think independently and help each
other to improve. Students sort out the knowledge chain, sort out
the operation points and matters, from the simple memory of the
second link to the reappearance and application of the third link
knowledge, students repeat learning, active thinking. The fourth key
word of classroom promotion is “win”. This link is the embodiment
of learning achievements. Through the climbing of learning process,
students and teachers grow together in the classroom, and teaching
and learning are mutually beneficial [10].
Course Fragment Design: Taking the Course of Four Step
Palpation of Abdomen as An Example
The teaching difficulty of this course lies in the operation
method of abdominal four step palpation, and the judgment of
fetal delivery mode, fetal presentation and fetal position. This class
is divided into three stages (diagnosis closed loop) of pre class
guidance, learning practice and after class development, with a
total of 2 class hours. Guidance before class. Before class, teachers
publish the preview materials to the information-based teaching
platform and push them to the wechat end of students’ mobile
phones. The teacher analyzed the preview results, understood that
the students’ judgment on the mode of delivery, fetal presentation
and fetal position was weak, and they had a good grasp of the
purpose of abdominal four step palpation, and finally determined
the teaching plan [11].
After Class Development: After class exercises were pushed
through the teaching platform which si established by big data
system, and the after-class exercises were mainly based on the real
questions of nurses’ qualification examination to prepare for the
students’ nurses’ qualification examination. Answer questions in
WeChat group, shorten the distance between teachers and students,
and break the time and space restrictions of the classroom.
Relevant knowledge is released through the platform of student
associations, and professional associations organize knowledge
and skills competitions.
Teaching Evaluation
The three-dimensional evaluation promotes the effectiveness,
through students’ self-evaluation, students’ mutual evaluation and
teachers’ comments, The big data system is used to collect the above
three-dimensional evaluation information, the three-dimensional
degree can understand the knowledge mastering situation, at the
same time, through role perception and mind map, summarize the
learned knowledge, cultivate students’ ability to build a systematic
and rigorous knowledge structure, and promote students’ learning
effectiveness. The assessment of students’ performance should
change the traditional single assessment method of theoretical
knowledge, pay attention to the comprehensive assessment of
students’ learning attitude, thinking ability, practical ability and
problem-solving ability, and objectively evaluate the students’
learning situation. Curriculum assessment is closely related to
medical practice, and knowledge and skills are consistent with
the national nurse qualification certificate assessment, higher
vocational education personnel training mode and 1 + X certificate
system. The assessment subjects are diversified. The evaluation
data adopts wide-angle evaluation, including students’ selfevaluation,
group mutual evaluation, course teacher’s comments,
and clinical teaching teacher’s comments, striving for multi angle
evaluation and multi angle improvement from knowledge to skills,
skills to ability [12].
Implementation Effect
This teaching mode realizes the “three highs” of teaching effect,
that is, high participation of students, high timeliness of learning
process and high personalization of learning results. Students’
participation is high. The whole classroom teaching is completed
in the environment of integration of theory and practice, which
promotes students’ participation and self-confidence, and improves
their ability of knowledge transfer and application. Compared with
the traditional teaching, the effect of teaching reform is obvious.
The efficiency of learning process is high. The teaching process is
streamlined, and the diagnosis closed loop is formed. The efficient
teaching implementation has been achieved, and the basic teaching
objectives have been basically achieved. Learning outcomes are
highly personalized. In and out of class, students are encouraged
to discover and develop their own interests and expertise. Students
actively participate in personalized learning results display and
exchange activities and enhance their learning initiative and
initiative.
Teaching Characteristics and Reflection
Since January 2014, we have been carrying out the practical
research on the curriculum reform of Obstetrics and gynecology
nursing in Higher Vocational Colleges Based on the OBE education
concept from the perspective of big data. We have been deepening
the reform, the teaching effect has been continuously improved,
and the students’ ability has been continuously improved [13].
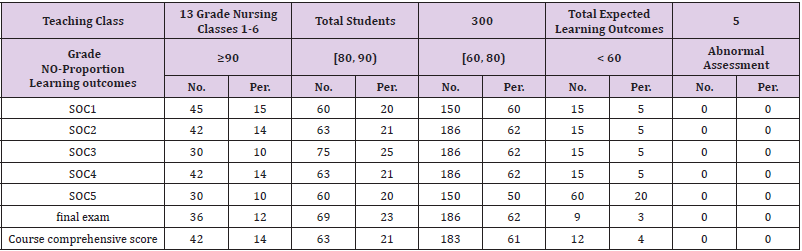
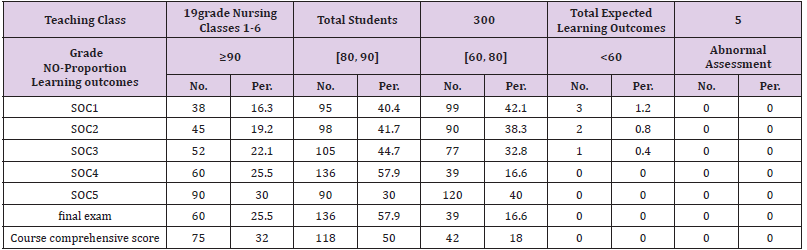
Before the teaching reform, the average score of Obstetrics and
gynecology nursing course was only (73. 94 1 ± After the reform, the
average final score of each semester was (88.72 10.60) ± Through
big data analysis, students’ satisfaction with the course was 90.41
points, which were higher than that before the implementation of the reform. The students’ passing rate of the examination was
significantly improved, and their learning initiative and enthusiasm
were also greatly improved. According to the comparison between
(Table 4) (assessment of Obstetrics and gynecology nursing in June
2014 - before the education reform) and (Table 5) (assessment
of Obstetrics and gynecology nursing in the second semester of
2020-2021 academic year - after the education reform), We get the
following conclusions: from the perspective of big data, based on
the OBE education concept, the practical research on the curriculum
reform of Obstetrics and gynecology nursing in higher vocational
colleges has greatly improved students’ mastery of the knowledge
points and operation skills of Obstetrics and gynecology nursing,
greatly improved their autonomous learning ability, and cultivated
students’ lifelong learning ability.
Especially, From May 2021 to now, during the New Coronavirus
epidemic in Guangzhou, we used the big data system to carry out
online teaching, uploading a large number of teaching video screens,
chapters of the target test questions and comprehensive exercises
to the database, and set the teaching video screen as playback status
in the database, so that students can use fragmented spare time to
learn repeatedly. Master the key and difficult points thoroughly.
The teaching effect is greatly improved. Teachers use the big data
system to arrange a large number of extracurricular research
topics and course papers and require students to use the Internet
and big data to search for information in the system. Students can
make full use of big data system and computer network system for
conscious learning, in-depth learning, and complete course papers
and research topics, which greatly improves students’ scientific
research and innovation ability and cultivates students’ pioneering
spirit. It creates a new mode of Higher Vocational Education from
“teachers want students to learn” to “students are willing to learn”,
which lays a solid foundation for higher vocational education to
cultivate more and better high skilled talents to meet the needs of
society, and makes due contributions to the development of nursing
and Health Management College of Guangdong Lingnan vocational
and technical college, At the same time, it has also explored some
experience reference for the higher vocational colleges of nursing
medicine, which benefit more students, teachers and colleges. Therefore,
from the perspective of big data, the practical research
on curriculum reform of Obstetrics and gynecology nursing in
Higher Vocational Colleges Based on OBE education concept has
created great social benefits.
The starting point of education is not knowledge, but people,
and it is the object of our education.0be teaching concept is
student-centered, based on the learning background to set up
courses, from curriculum design, curriculum implementation,
curriculum evaluation, and through the results of reverse design
courses, modify the classroom implementation, form an effective
classroom teaching closed loop, so as to implement the curriculum
objectives, realize the requirements of five major learning areas of
professional talent training. The curriculum reform of Obstetrics
and gynecology nursing based on OBE education concept is based
on the “123 teaching mode” of work study combination based on
the analysis of learning situation, cognitive law of higher vocational
students and industry orientation. This model highlights the
progressive cultivation with students as the center, industry post
skills as the basis, students’ learning achievements as the guidance
and ideological and political education as the soul. This teaching
mode realizes the “three highs” of teaching effect, that is, high
participation of students, high timeliness of learning process and
high personalization of learning results. The teaching process can
be divided into three stages: guidance before class, practice in class
and development after class. Each teaching link has assessment and
diagnosis, which provides reference data for the next link.
Through the comprehensive continuous evaluation and
feedback, the evaluation implements the whole teaching classroom
and course teaching, so that the three stages of the teaching
process complete a complete evaluation and diagnosis closed loop.
Through knowledge learning, school skills practice, clinical skills
observation and internship, clinical hospital internship progressive
extended learning space, multi angle and multi-level cultivation of
students’ clinical comprehensive quality and nursing professional
quality. From simulated training to feeling the relatively real work
scene, observing the clinical operation process to using skills to
solve practical clinical problems, the separation between classroom
learning and post, progressive extension of learning space and zero
gap connection between major and post have been solved [13].
Education is a subject that is constantly being revised, just like
the endless curriculum reform. The introduction of OBE teaching
concept, through the feedback of learning results to modify the
classroom. In the course reform, we find that the new generation
of students have unlimited potential, unlimited creativity, and
each has its own characteristics. The significance of education is to
respect each individual’s progress and personality. Therefore, we
are still thinking about how to refine the measurement standard
of learning outcomes, further humanize and personalize the
quantitative results, and respect each individual learning process
and output.
Finally, it should return to our teaching goal: from professional
knowledge to methods and abilities, and finally reflect the students’
social adaptability and ability to produce gradient climbing. Any
teaching method is not an isolated way, it needs absorb anything
and everything. Any kind of teaching method is not only suitable
for a course, but also can be copied and improved, and suitable for
more subjects; Any kind of teaching method is not only aimed at
a certain group of people, but it should also be adjusted through
“teaching students in accordance with their aptitude”, so that
more students can use it and produce greater learning influence.
In the theme of education, students should pay attention to their
interests; Starting from the major, students should pay attention to
it; Starting from emotion, arouse students’ resonance [14]. From
the perspective of big data, based on the OBE education concept,
a series of reforms of Obstetrics and gynecology nursing courses
in higher vocational colleges have been carried out for many years.
The practice shows that the knowledge and skills of Obstetrics and
Gynecology Nursing of higher vocational college students have
been improved rapidly, their ability to analyze and solve problems
has been greatly strengthened, their graduates are more popular in
the society, and the popularity and reputation of higher vocational
colleges have been improved, The number of students registered
for Guangdong Lingnan Institute of Technology is also increasing
year by year, forming a virtuous circle, which promotes the further
development of College of nursing and health of Guangdong
Lingnan Institute of Technology.
Therefore, it is very urgent to continue to promote a series of
reform of Obstetrics and gynecology nursing curriculum in Higher
Vocational Colleges Based on OBE education concept from the
perspective of big data, and keep pace with the times, constantly
promote the achievements and experience of teaching reform, and
promote the teaching reform to a deeper and broader direction.
In particular, how to make good use of the Internet for Teaching
Reform [14], how to make better use of big data to carry out indepth
teaching reform research of Obstetrics and gynecology
nursing course in Higher Vocational Colleges Based on OBE
education concept from the perspective of big data are our future
efforts.
For more Articles on : https://biomedres01.blogspot.com/