Cardiac Fibroma Revealed at Adulthood….!!
Short Communication
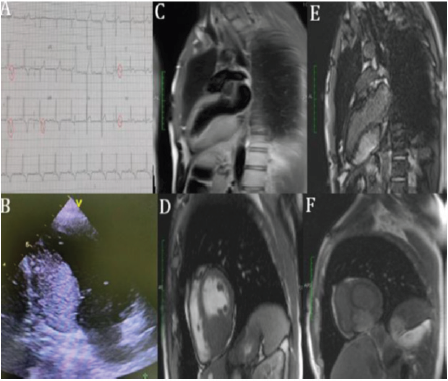
A 37-year-old man without known comorbid conditions or cardiovascular risk factors presented with lipothymia. The neurological and cardiovascular examinations were normal. The brain magnetic resonance imaging was normal. Electrocardiogram (EKG) showed LV hypertrophy with T waves inversion in inferolateral leads (A). 24-hours EKG Holter showed a sinusal rhythm with no further abnormalities. Transthoracic echocardiography (TTE) revealed a left ventricular hypertrophy localized in the inferior wall suggestive of myocardial mass (B) with normal left ventricle ejection fraction. In the subsequent cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) imaging, a 7.6×2.6 cm mass was found. The mass was well demarcated, lined with normal myocardial tissue, hyperintense on T1 weighted images (C), hypointense on T2 weighted images (D), and showed extensive late gadolinium hyperenhancement (E; F). Those CMR findings were consistent with cardiac fibroma. Despite of the known risk for arrhythmias of cardiac fibroma, the decision was made to closely follow this patient without excisional surgery given the normal sinus rhythm, the absence of history of syncope or resuscitated sudden death and the patient preference. Cardiac fibroma is the second most common primary pediatric cardiac tumor after rhabdomyoma. It remains a rare entity, especially in the adult population. Clinical presentation of patients with cardiac fibroma depends on the location and size of the tumor. CMR imaging is an excellent tool for evaluation of patients with suspected cardiac masses as it provides excellent tissue characterization and may give information about the possible etiology of cardiac mass thus foregoing the need for myocardial biopsy (Figure 1).
Figure 1:
a) EKG showing LV hypertrophy (Sokolow index at 39 mm) and T waves inversion in infero-lateral leads
b) TTE 2-chamber view showing the myocardial mass in the inferior wall of the left ventricle
c) T1-weighted imaging 2-chamber view showing a hyperintense cardiac mass
d) T2-weighted imaging short-axis view showing a hypointense cardiac mass. Delayed enhanced imaging (2-chamber view at 2 min)
e) Short axis at 10 min
f) Showing marked late hyperenhancement of the mass with gadolinium, which is a hallmark of cardiac fibroma.



No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.