Analysis of Relationship between Recovery of Consciousness and Personal Safety after Painless Induced Abortion
Short Communication
In clinical painless induced abortion, it is obligatory that patients who do not suffer any operative pain or special discomfort should regain consciousness completely within a short time after the operation, return to their preoperative state and leave the hospital safely. Intravenous anesthesia using propofol and sufentanil has been widely used in painless induced abortion [1]. It is characterized by precise anesthetic effect, quick onset and quick elimination without significant accumulation. Patients regain consciousness completely and have no memory of the operation. It can inhibit the vagus reflex and eliminate the induced abortion syndrome, has minimal affect on circulation and respiration and is relatively safe [2]. However, dosage is frequently excessive or insufficient. Excessive dosage will delay recovery and insufficient dosage will affect the operation [3]. At present there is still no domestic uniform standard for the retention and in-hospital observation time for patients following induced abortion. In this article we carried out a survey of patient recovery of consciousness following induced abortion to provide criteria for the safe discharge of patients with relationship to their state of wakefulness.
Materials and Methods
There is no uniform standard for in-hospital observation of patients after induced abortion under anesthesia and analgesia using propofol and sufentanil. In this article, we surveyed the recovery of consciousness of patients following induced abortion to provide evidence for clinical use. One hundred and twenty four patients who volunteered for the questionnaire were at ASA I grade, with an average age of 25.8±5.6 years, weight of 58.8±9.6kg and gestation period of 63±11.6 days. With fasting and water deprivation for 12h before operation, the blood pressure (BP), electrocardiogram (ECG) and pulse oxygen saturation (SPO2) was continuously monitored in the operation room. Beginning three min before the operation, atropine 0.5 mg, 0.15ug/kg sufentanil and 2mg/kg propofol was given in succession by intravenous injection within 2 min, respectively. When patient consciousness and eyelash reflex were no longer present, the operation began. BP, heart rate (HR) and SPO2 were recorded before the anesthesia, 1 min, 2 min, 5 min, and 10 min after anesthesia and observations were made to determine any adverse reactions. The doctor filled out the unified tabular questionnaire after questioning patients. Consciousness recovery:
Retrograde Amnesia
Before the operation, patients were shown two pictures of familiar animals (dog and cat) and then asked to distinguish these among five pictures after the operation.
Orientation
Determination was made whether patients could tell the direction indicated by doctors.
Excitability
Whether the patient took the initiative in communicating with medical staff or other patients.
Motor coordination
While standing or walking, whether patient’s step was sure.
Fatigue
Whether the patient had a sense of fatigue or drowsiness. Data was statistically processed by Excel 2003. Measurement data were expressed withx ±SD using t-test.
Results
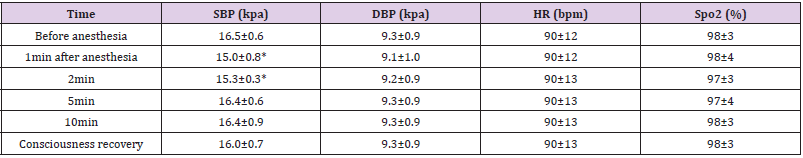
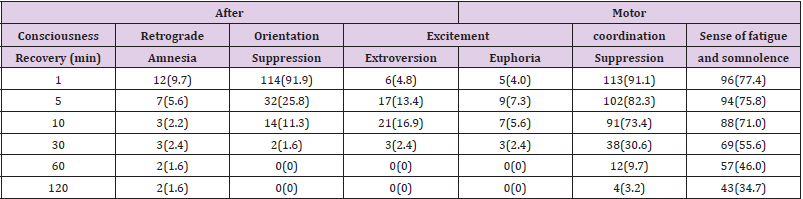
The systolic pressure decreased one and two min after anesthesia, a statistically significant difference compared with that before anesthesia (P <0.05). However, for patients without severe hypotension who needed ephedrine, there was no statistical difference in systolic pressure at other time points compared with that before anesthesia (P <0.05). There was no statistical difference in diastolic pressure, heart rate or blood oxygen saturation before or after anesthesia (P <0.05) Table 1. Eighty-nine (71.8%), 28 (22.6%) and 12 (9.7%) patients had adverse reactions of respiratory depression, injection pain and postoperative nausea, respectively. The respiratory cases showed lower respiratory frequency and apnea with a period of 36±15.8s after intravenous injection of propofol. It took the patients 3.8±1.4min to regain consciousness. Some patients had retrograde amnesia. The orientation suppression and increased excitability lasted 30 min after the operation, while motor coordination suppression and sense of fatigue lasted 2h after the operation Table 2.
Table 1: Changes in Patient Vital Signs before and after Anesthesia ( X ±S).
Note: Compared with that before anesthesia *P<0.05.
Discussion
In this group, patient systolic pressure was significantly decreased one and two min after the administration of drugs, which, however was within the normal range and did not significantly affect their recovery of consciousness, with no need for special treatment. It is common knowledge that an intravenous injection of propofol and sufentanil will cause apnea in most patients and so in administering anesthesia it is necessary to use auxiliary respiratory measures before hypoxia occurs [4,5]. Thus hypoxia had no influence on the recovery of consciousness in this group of cases with a blood oxygen saturation of < 96% [6]. After an intravenous injection of propofol, patients became unconscious with the disappearance of the eyelash reflex and respiration response. The inability to remember the operation is not amnesia. Retrograde amnesia within the initial 5 min following recovery of consciousness might be related to incomplete consciousness [7], but 2h later 1.6% of patients still did not have full preoperative recall, which might be relevant to propofol.
Wang Chunyan [8] thought patients undergoing non-cardiac surgery just after a general anesthesia had cognitive functional disorder. Simon [9] also thought that patients had preoperative retrograde amnesia after propofol anesthesia. As reported in most literature, propofol is not stimulatory [10]. However, it was discovered that in our target group, after regaining consciousness, patients experienced a definite degree of excitability. Different from hallucination or nightmare caused by ketamine, this was a feeling of comfort and pleasure lasting for 5 to 30 min, which expressed itself among some patients who had not liked communicating with others before the operation in that they actively began to talk about how good they felt after the operation. Individual patients displayed initiative in describing their own dreams and a few patients involuntarily swung their legs back and forth, seeming to forget they were in an operating environment. Finco G, et al. [11] also discovered that patients had a sense of well-being after gastroscopy and propofol anesthesia but did not analyze this. Dizziness and disorientation appeared for a certain period of time after the operation, but patients basically recovered within 10 min. This is similar to the observed results of Bouillon T, et al. [12].
But in the present study, we also discovered that the disorientation of a very few patients (1.6%) continued at some level 30 min after operation. The decrease in motor coordination was mainly manifested as wobbling as patients walked immediately after operation. Sometimes patients themselves described this as “weakness of legs.” In our observation, 2 patients nearly fell while walking, which was considered related to propofol and sufentanil. There were also reports of dizziness even with a single use of propofol [13]. As an opioid drug, sufentanil’s above-mentioned side effects were clearly in evidence. Currently there are no unified regulations concerning postoperative management for painless induced abortion using propofol and sufentanil [14].
In most hospitals, patients are kept under observation for 30 min, while some hospitals, especially small hospitals, don’t even have an observation room at all. Although an increase in postoperative excitement is transient, it is inappropriate for patients to leave the hospital too early due to the patient’s decreased safety awareness. Because orientation and motor coordination are affected, patients might fall or even hurt themselves if they began to walk alone immediately after the operation. Generally, patients have a sense of fatigue and some even have drowsiness. In our investigation, it was also discovered that a very few number of patients were not accompanied by family members or even returned home by themselves on bicycle after the operation due to insufficient awareness of the safety issues surrounding painless induced abortion.
The doctor should give patients safety instructions and explain to them preoperative fasting and water deprivation, the need to be accompanied by others and the prohibition against driving. Patients should be accompanied by nurses back to the observation room instead of walking alone immediately after operation. It is advisable that patients without nausea or vomiting after the operation take fluids or soft food, while fluid infusion may be considered for patients with a poor constitution who cannot eat [15]. In our hospital, an observation period of 30 to 120 min is determined based on whether a patient has had nausea, vomiting or dizziness. During this period, fluid infusion and oxygen will lead to a full recovery of patient strength and will avoid the possibility of postoperative orthostatic hypotension caused by preoperative fasting. In view of probable retrograde amnesia after anesthesia, it is necessary to register and check valuables carried by patients before the operation to avoid unnecessary issues later.
Anesthesia affected patient orientation and motor coordination and was probably responsible for a sense of fatigue and increased excitement thus leading to a decrease in patient safety consciousness or awareness. Therefore, it is suggested that patients be forbidden to drive or work high above ground for 24h after the operation. At the same time, patients must be accompanied by others when leaving the hospital. To sum up, it is not appropriate that all patients should be routinely observed for 30 min after painless induced abortion using propofol and sufentanil. The observation period should depend on the varying reactions of patients to the operation and the anesthesia and on whether or not they are accompanied by others to ensure their medical and personnel safety.



No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.