The logistics management of Modular integrated construction (MIC) (Mohamed Hussein, et al. [1]) has always been a major barrier to the wider adoption of (MIC). Nonetheless this challenge can be tackled by the application of lean techniques namely justin- time (JIT). Numerous studies have identified and evaluated the critical factors (CFs) required to implement JIT. The results indicate that all the 42 CFs are important for applying JIT of (Mohamed Hussein, et al. [1]) which seven are highly significant for successfully implementing JIT in (MIC). The results of the randomized trial strongly support (Christopher M, et al. [2]) the efficacy of just-in-time evidence-based reminders as a means of changing clinical practice among home health nurses who are geographically dispersed and spend much of their time in the field. Both the basic and the augmented interventions greatly increased the practice of evidence-based care according to patient records in the areas of patient assessment and instructions about HF disease management. While not all results were statistically significant at (Christopher M, et al. [2]) conventional levels intervention effects were positive in virtually all cases and effect magnitudes frequently were large (Figure 1).
The JIT and stockless approach to provider supplier relationships (Lynch D [3]) has proven to be a win-win proposition for the partners that have implemented it in many manufacturing industries and health care organizations as well. This strategy will fundamentally impact the entire cost structure within the hospital supply distribution chain. The sweeping changes the health care industry experienced during the 1980s are leading creative materiel managers to seize the initiative to improve the current operating (Lynch D [3]) costs of their hospitals. They do not want to be left behind “holding the inventory.” JIT leads to waste reduction improves productivity and (Kaswan S, et al. [4]) provides highquality patient care. The practical implementation of JIT depends on vital factors known as enablers. Grey Relational Analysis (GRA) has been used in the present study to rank enablers and ranks were further validated using the fuzzy technique for (Kaswan S, et al. [4]) order of preference by similarity to ideal solution (TOPSIS) and sensitivity analysis. Clinical nurse educators are expected to (White, et al. [5]) prepare students for the realities of practice while providing meaningful learning experiences.
However, shortened patient stays in the acute care setting often lead to wasted and useless effort for both instructors and students. The application of Just-in-Time principles offers a viable and alternative solution for clinical (White, et al. [5]) practice preparation in today’s rapidly changing healthcare environment. Different organization around the globe are using 5S (Ahsan Siddiqui [6]) and 7 Muda methodology to get benefits for improvement of their health care system. The step-by-step process of 5S and 7 Muda methodology is smart way to start monitor, finish and follow up the broken health system in several countries. Lean management and Lean six sigma methodology has shown promising results to improve the quality of health care system. Lean six sigma methodology works by reducing 8 wastes including overproduction, inventory, waiting, Motion, Transportation, rework, over processing and non-utilized talent. The 5 (Ahsan Siddiqui [6]) principles of lean model include value, value stream, flow, pull and perfection.
Healthcare providers are critical to disaster response (Ahsan Siddiqui [7]) throughout the world. Increasingly, there are government and nongovernment sponsored opportunities for providers to participate in disaster response as members of disaster response teams. Training opportunities on-line and in-person are readily available but not usually for a specific disaster at the time it occurs. Just-in-time disaster specific training prepares providers for imminent deployment for a real-time disaster. Particularly for disaster response (Ahsan Siddiqui [7]) in an austere environment just-in-time disaster specific training optimizes preparation and response.
The Author of this article has chosen the scoping review of the 37 articles and the websites to discuss details about the Just in time methodology. Scoping review focuses more on to discuss the 10 benefits/advantages of the JIT methodology and the 10 steps to perform JIT methodology. The author has chosen subject and words to find out the which organization should use the JIT methodology and some of the disadvantages of the JIT methodology. Articles are specially selected from the PubMed NIH website focusing only on healthcare JIT methodology. Just-in-time (JIT) has been a popular operation strategy partly (Ahsan Siddiqui [8]) because of its success in the Japanese automobile industry. Various benefits such as inventory reduction improved operations efficiency and faster response have been studied widely in previous studies. Therefore, successful implementation of JIT is vital to many companies. The major contribution (Ahsan Siddiqui [8]) of this paper lies in the discussions of the successful factors as a practical guide to implement JIT systems.
As we enter a new era of technological capacity for (Inbal NS [9]) delivering Just-in-time adaptive intervention (JITAIs). It is critical that researchers develop sophisticated and nuanced health behavior theories capable of guiding the construction of such interventions. Despite the increasing use and appeal of JITAIs, a major gap exists between the growing (Inbal NS [9]) technological capabilities for delivering JITAIs and research on the development and evaluation of these interventions (Figure 2). During the current recession economy around the globe, (Ahsan Siddiqui [10]) it is wise to choose the quality tools such as KAIZEN for the growth of organizations. Toyota motors, BMW Germany, Ford motors USA, other companies are using the KAIZEN tool to organize their organization, reduce the waste and increase the profits.
SWOT tool helps administration to simplify the challenges an organization is facing and would face in the future to write and implement the corrective actions for improvement. SWOT analysis also helps to identify the (Ahsan Siddiqui [10]) 7 Muda wastes of the organization to reduce the wastes to make the organization reliable productive and profitable. Canonical correlation analysis was used to test five hypotheses. (Sadao S, et al. [11]) The results indicated that
a) There was not a significant relationship between the use of JIT practices alone and manufacturing performance,
b) There was a very strong relationship between JIT practices and infrastructure practices
c) The combination of JIT management and infrastructure practice was related to manufacturing performance
d) Infrastructure by itself is sufficient to explain manufacturing performance and
e) Manufacturing performance was [11] related to competitive advantage. The worsening global economy following the burst [12] of the dotcom bubbles in 2001 the financial tsunami in 2008. And the incessant rise in customer demand for better services have all contributed to shrinking profit margins for businesses around the world. One successful solution has been the adoption of Just-in-Time manufacturing systems which involve many functional areas of a firm such as manufacturing, engineering, marketing, and purchasing among others.
Just-in-Time Logistics extends the JIT concept in manufacturing to business logistics an area (Kee h, et al. [13]) that has been observed to account for more than 30 per cent of sales revenue for some firms. The price of alirocumab would have to be reduced (Dhruv S, et al. [14]) considerably to be cost-effective. Because substantial reductions already have occurred, we believe that timely independent cost effectiveness analyses can inform clinical and policy discussions of new drugs as they enter the market. Compared with a statin alone the addition of alirocumab cost $308 000 (UI, $197 000 to $678 000) per QALY. Compared with the combination of statin and ezetimibe replacing ezetimibe with alirocumab cost $997 000 (UI, $254 000 to dominated) per QALY. (Dhruv S, et al [14]) Incremental cost effectiveness ratio in 2018 U.S. dollars per quality-adjusted life-year (QALY) gained. JIT is a philosophy that can be applied to inventory (Kinney Bill C, et al. [15]) management operations to reduce waste achieve cost savings maximize space and improve quality of care. In the healthcare environment a prime vendor program is essential to a successful JIT program.
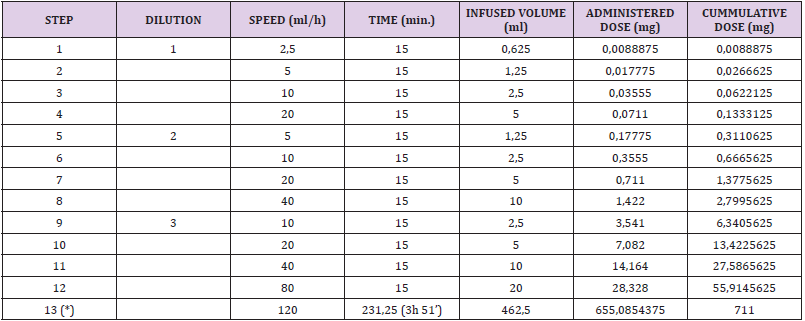
With the advent of a prime vendor program at Naval Hospital, Oakland, the advantages offered by JIT become available. JIT is an innovative approach to inventory management that has been successfully applied in the healthcare industry. The authors examine JIT and how (Bill C, et al [15]) this philosophy can further the goals of the prime vendor program and increase quality of care (Figure 3) (Tables 1-4).
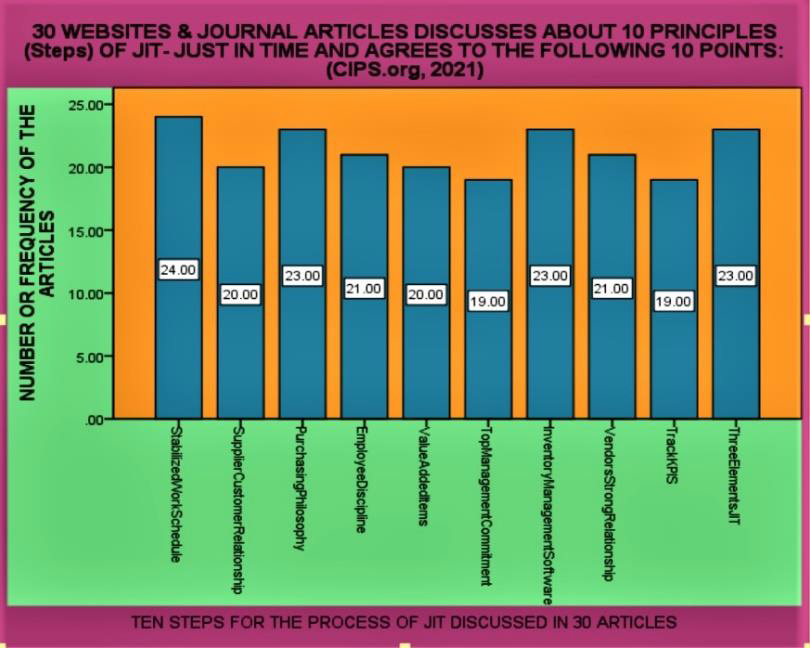
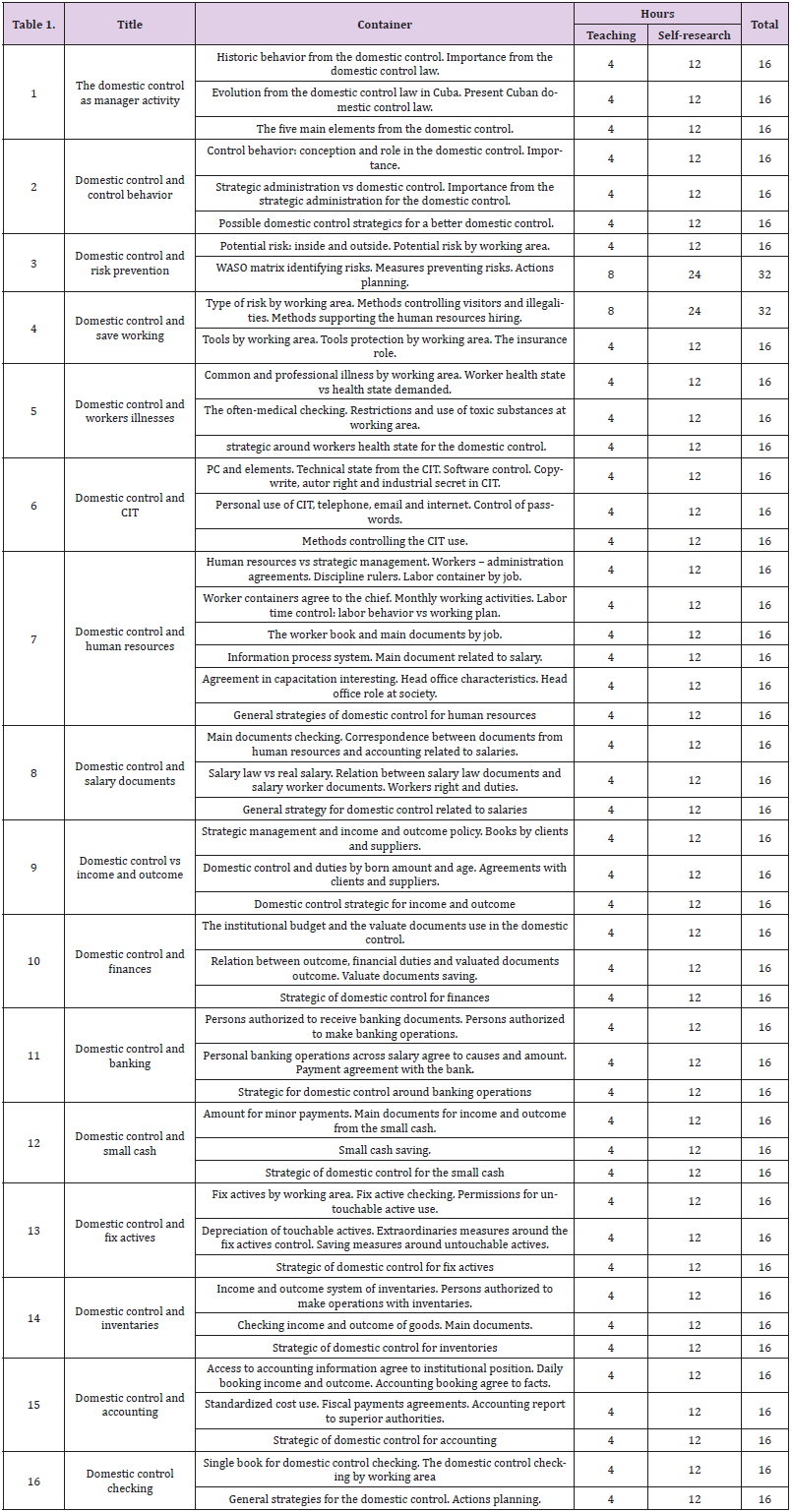
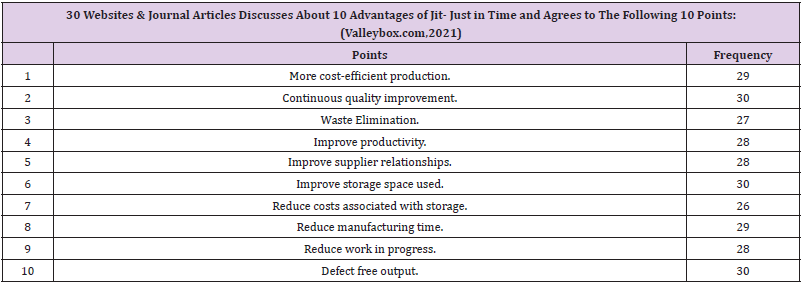
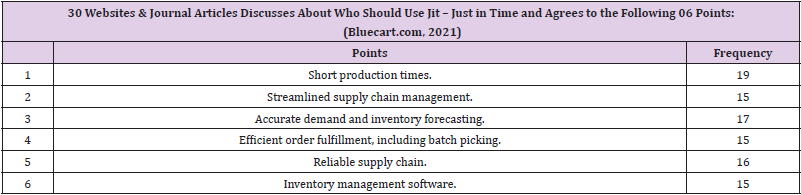
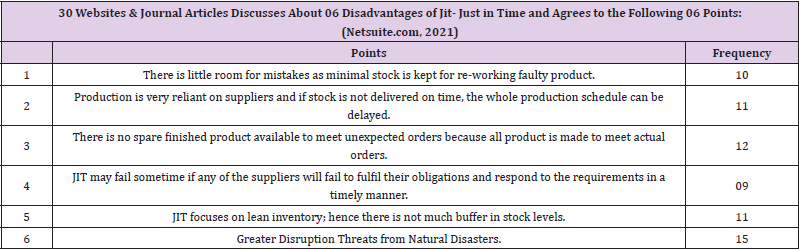
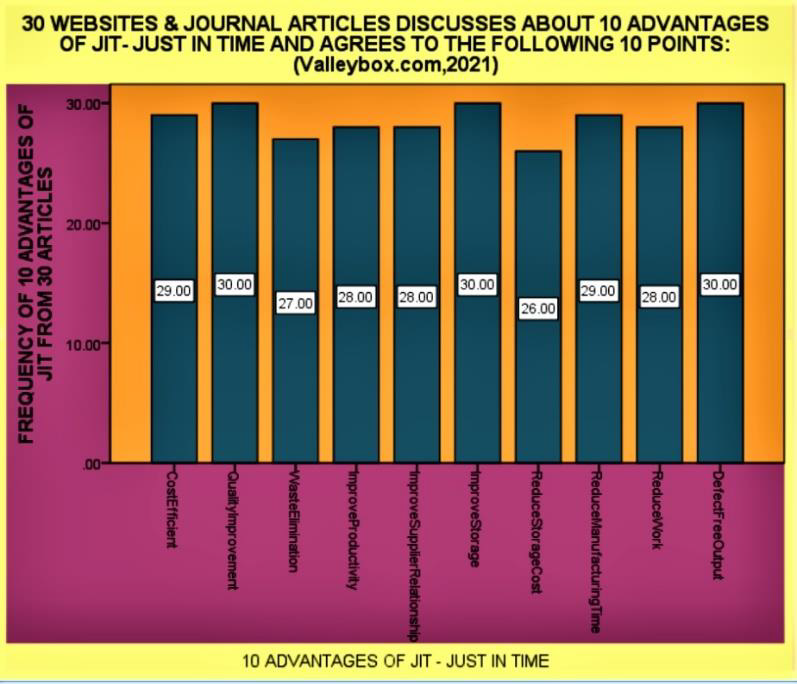
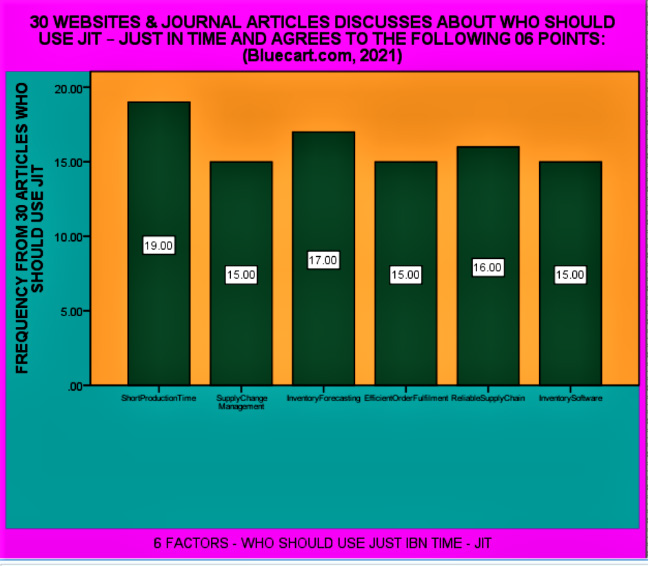
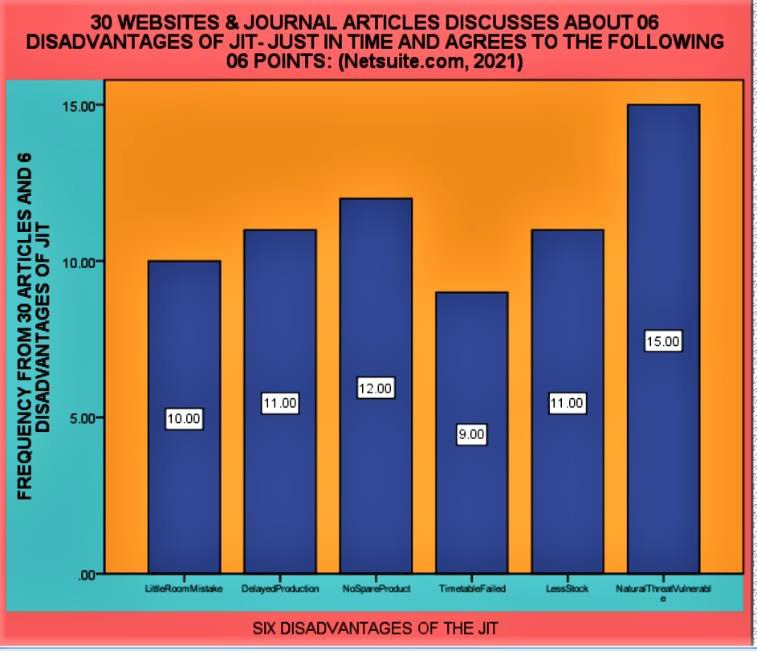
There are four tables providing details about the 10 steps of the JIT methodology and its benefits/advantages. Remaining two tables provide the details about who should use the JIT methodology and its disadvantages. Author has provided the data analysis and diagrammatic presentation by using SPSS software. Four diagrams show the bar charts and the frequencies of the 30 articles of the steps, advantages, disadvantages and who should use the JIT methodology. Just-in-time (JIT) a management concept which requires (Whitson Daniel [16]) the delivery of a service or a product only upon demand can be used by hospitals as a tool for minimizing expenditures in logistics. This system offers a variety of benefits such as continuity in process flows minimization of works-in- process and finished goods inventory and the removal of bottlenecks in the production line.
Some of the areas wherein the JIT system (Whitson Daniel [16]) can be applied include central supply materials management and pharmacy nursing units and physician practices. During the time of recession and economic instability (Ahsan AS [17]) most of the organizations are looking to save money. The seven quality tools and other 29 administrative quality tools help the organizations to identify the problem, its root cause analysis and implement the corrective action to obtain the best possible result. By the literature review of the PESTEL/PESTLE analysis tool it helps the organization to focus on 6 important factors to grow the business. 6 important factors include political focus on health care, (Ahsan AS [18]) economic challenges, social factors, technological factors, legal factors, and the environmental factors. The present work provides important difficult and easy (Kaswan MS, et al. [19]) to implement JIT elements in healthcare services.
Besides this work justifies the application of decision-making tool (AHP, BWM) for the prioritization of JIT elements in the health care sector. This work also facilitates the proper management of inventory items together with the reduction in various Lean wastes with the proper implementation (Kaswan MS, et al. [19]) of JIT in healthcare. The reduction in various associated wastes leads to cleaner surrounding and lesser environmental degradation. This study examines the transformation of manufacturing industry (Krishnamurthy A [20]) to Just in Time (JIT) manufacturing and mass customization. The main objective is to identify strategies that will accelerate the realization of information technology enabled on demand services. Manufacturing and service systems are compared in terms of the similarities and differences with respect to issues related to their design planning and performance evaluation. These comparisons show that problems related to portfolio optimization workforce optimization and resources allocation are important in both manufacturing and (Krishnamurthy A [20]) service systems suggesting that the similarities be exploited to develop strategies for on demand services.
A new form of relational exchange commonly referred (Gary LF, et al. [21]) to as the “just-in-time” (JIT) exchange relationship has been adopted and implemented by many original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) and suppliers of component parts-materials during the past several years. The authors attempt to expand understanding of
a) How JIT exchanges compare with other forms of exchange between suppliers of component parts-materials and OEMs,
b) What conditions are most conducive to the initiation of JIT exchanges and
c) What key factors (Gary LF, et al. [21]) are likely to influence the success or failure of initiated JIT exchanges. We conclude that in a hospital with a sophisticated material (Epstein R, et al. [22]) management information system OR managers will probably achieve greater cost reductions from focusing on negotiating less expensive purchase prices for items than on trying to link the OR information system with the hospital’s material management information system to achieve just-intime inventory control.
Because expensive items typically have different models and sizes each of which is used by a hospital less often than this for almost all items there will be (Epstein R, et al. [22]) no benefit to making daily adjustments to the order volume based on booked cases. There are two keys to JIT supplier logistics that is taking control (Harry G [23]) of inbound deliveries and establishing quick feed-back loops. Various models have been proposed to investigate the improvement and learning processes the JIT system seeks to foster. To maximize the probability of success of a JIT program it is also necessary to put proper incentive systems in place that encourage employees and management to implement the desired changes and to redefine areas of responsibility throughout the organization. The extension of JIT across firms thus creates (Harry G [23]) mutual dependencies between supplier and customer and hence incentives to cooperate to resolve problems and increase efficiency (Figures 4-6).
The analysis was conducted in a systematic manner and (Gary Jarrett [24]) compared the anticipated benefits with benefits validated in other industries from the implementation of JIT. In this particular study the cost and benefit outcomes achieved from a health care JIT implementation were compared with those achieved by the manufacturing service and retail industries. Chiefly, it was found that the health service market must be restructured to encourage greater price competition among priorities. A new standardization process (Gary Jarrett [24]) should eliminate duplication of products and realize substantial savings. Nurse executives need to review what is working in (Jacobs SM, et al. [25]) other industries to see if similar techniques and philosophies can help the healthcare industry. The authors review the manufacturing philosophy supporting the just-in-time JIT method and apply some of its (Jacobs SM, et al. [25]) principles to healthcare to improve operations and operating margins.
Describes one approach to meeting the health‐care cost reduction (Heinbuch SE [26]) challenge through the hospital materials management function. Highlights the value of taking a proactive stance to meet the challenge, transferring technology across industry sectors such as employing a just‐in‐time inventory management system in clinical areas of hospital materials (Heinbuch SE [26]) management and adopting a win‐win managerial philosophy. Features a case study to demonstrate the ideas in practice. With the implementation of the recent Healthcare Reform Act (Bhushan K [27]) and the increased scrutiny on the soaring costs of healthcare medical plans are looking for ways to optimize workflows and reduce costs. Titan Healthcare is a large non-profit integrated healthcare company located in Arizona New Mexico, Nevada, Colorado, and Texas. They provide health insurance coverage and a broad range of comprehensive health care.
From a pharmacy inventory (Bhushan K [27]) perspective expectation for the system is to significantly reduce inventory costs and increase service levels to their members. With the recent public focus on health care reform hospitals (Yitteck Walker [28]) are under more pressure than ever to be more cost efficient. In order to accomplish these hospitals must explore new business models that will help them reduce costs while at the same time increasing productivity. The just-in-time (JIT) inventory system is selected in this project as a potential cost saving strategy for hospitals. This project explores the feasibility of adopting a JIT inventory system (Yitteck Walker [28]) in a hospital setting through a detailed review and comparison of 20 articles. Lean management aims to add value to the patient (Tomasz K [29]) and the healthcare unit by eliminating superfluous and non-value adding activities. The purpose of the article is to discuss the implementation of lean management/lean healthcare solutions to the healthcare units thanks to the use of a value-adding Just-in-Time (JIT) method in hospital inventory management. The article is based on [29-39] an up-to-date subject literature and was conducted by means of desk research analysis.
To conclude, just in time methodology (JIT) is a lean methodology to provide economic comfort to the organization. JIT has proven that it could save lot of wastes for the organization and provided affective savings for the organization. The method to get the benefit is to order only what is needed and do not waste the time and money in inventory stocks. Toyota motors, Apple, McDonald and others are successful organizations taking huge benefits from the JIT methodology from decades. Small businesses should practice JIT methodology, which is convenient to use and sensible, easy to implement in the organizations.
For more Articles on: https://biomedres01.blogspot.com/