Posterior Brachial Plexus Block with Neurostimulator for Orthopedic Humerus in a Pre-Obese Patient
Introduction
There are several approaches to the brachial plexus. Blockade techniques vary according to surgical site and anesthesiologist’s experience, and may be performed by interscalenic, intersternocleidomastoid, supraclavicular, infraclavicular or axillary approach [1]. Posterior brachial plexus access, also known as cervical paravertebral block, is an alternative. It has been firstly described by Kappis [2] in 1912 and remained forgotten for almost 80 years before Pippa [3] in 1990, rediscovered the technique and applied loss of resistance to locate the plexus, and reintroduced with neurostimulator in 2005 [4]. A study was recently carried out prospective and observational in 50 patients to evaluate the clinical effectiveness of posterior brachial plexus access with a single injection of the combination of lidocaine and enantiomeric excess levobupivacaine with neurostimulator in patients with clavicle, shoulder and proximal beach chair procedures associated with general anesthesia [5]. The result showed an excellent technique providing adequate anesthesia and blocking almost all nerves at the end of surgery, with postoperative analgesia with an average of 18 hours, without any complications. We will present a case of posterior brachial plexus block in a pre-obese patient with a difficult airway.
Case Report
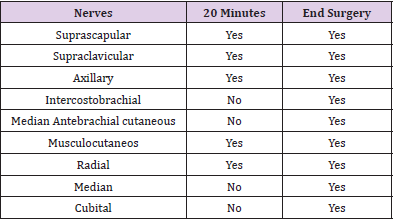
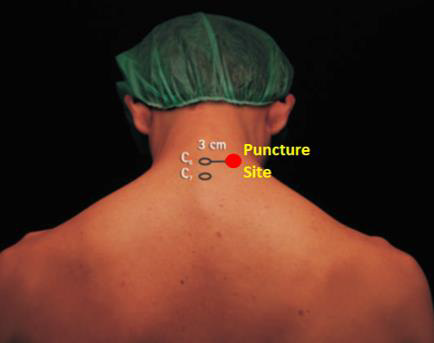
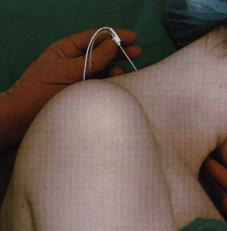
Female patient, 59 years old, 75 kg, 160 cm, and body mass index (BMI) of 29.3 kg/m2. Venoclysis with 18G extracath, monitoring with cardioscope, NIBP, pulse oximetry and capnography. Sedation with 100 μg of fentanyl and 1 mg of midazolam, for placement in the sitting position for blockade. Patient in a sitting position marked the apophyses of C6 and C7 and on the lower border of C6 (Figure 1). After infiltration with 2 ml of lidocaine, an A110 needle was inserted coupled to the neurostimulator with a current of 0.60 mA and a frequency of 2 Hz until obtaining the stimulus of the suprascapular nerve with shoulder elevation. After the introduction of the needle connected to the neurostimulator (Figure 2) and suprascapular motor response, 1 mL of iohexol contrast was injected with 300mg. mL-1, to confirm the location of the needle (Figure 3). Immediately after checking the position of the needle, they were injected 20 mL of 1% lidocaine with epinephrine and 20 mL of enantiomeric excess levobupivacaine with 0.25% epinephrine (S75:R25). Analgesia distribution was evaluated by the pain test with a 27G needle at 20 minutes, with the following nerves blocked: suprascapular, supraclavicular, axillary, radial and musculocutaneous. Due to obesity and the prediction of difficult airway associated with position in a beach chair, general anesthesia was performed with propofol, fentanyl, cisatracurium and sevoflurane. Osteosynthesis of the proximal humerus was performed, lasting 2:20 hours and 500 mL of bleeding (Table 1). The patient did not experience any side effects such as hypotension blood pressure, cardiac dysrhythmias, or other signs and symptoms of accidental intravascular injection, such as dizziness, tinnitus, perioral numbness, metallic taste, irritability, tremors, or convulsion.
After decurarization and extubation, the blocked nerves were investigated and all: suprascapular, supraclavicular, axillary, intercostobrachial, muscular skin of the arm, radial, musculocutaneous, median, and ulnar were blocked, with total motor block of the upper limb. In PACU and your room the patient did not report dyspnea and cyanosis that could represent secondary unilateral diaphragmatic paralysis phrenic nerve block, and she did not have Horner’s syndrome or recurrent laryngeal nerve palsy. No complications were observed at the puncture site. In the PACU, the patient used a food supplement (200 mL of Fresubin Jucy®) and was released into the room without intravenous hydration. The duration of analgesia was 20 hours, not requiring opioid supplementation. Released for residence at 12 hours the following day.
Discussion
In a recent study with 50 patients, using posterior brachial plexus access with neurostimulator and a mixture of 2% lidocaine with 0.5% levobupivacaine (S75:R25), 100% adequate anesthesia was obtained, with motor blockade at the end of the surgery in all patients with no block failure occurring [5]. All patients were operated in the seating position associated with general anesthesia. In the present case report, posterior access with neurostimulator and A100 needle was used and the same association of lidocaine and enantiomeric excess levobupivacaine with 0.25% associated with general anesthesia due to obesity and the prediction of difficult airway. At the end of the surgery, the entire brachial plexus had complete motor block and analgesia lasted 20 hours. The administration of the 20 mL association of 1% lidocaine with 20 mL of 0.25% levobupivacaine (S75:R25) provided a rapid onset of action (3.5 minutes) with mean duration of 18-hour analgesia, varying from 12 to 26 hours, without need for opioids, being considered adequate and long-lasting, allowing for early hospital discharge in less than 24 hours for some patients [5]. The administration of the same mixture and solution presented a duration of analgesia of 20 hours, without the need for the use of opioids. The posterior approach to the brachial plexus can be performed either in the sitting position [5] or in the lateral decubitus position [6]. In our initial study in 2005, access to the brachial plexus in lateral decubitus was used [6]. Subsequently, with the increase in the obese population worldwide, we began to use the sitting position for greater patient comfort [5]. In the present case, due to obesity, a posterior approach to the brachial plexus was used in the sitting position.
In recent years, the prevalence of obesity has increased significantly worldwide. However, obesity per se should not dissuade patients from undergoing shoulder surgery under interscalene block [7]. Interscalene brachial plexus block is associated with greater reductions in FVC and FEV1 in obese participants undergoing shoulder surgery compared to normal weight participants [8]. No time (30 minutes x PACU) nor position (sitting x supine) affected this relationship [8]. Despite these changes, obesity was not associated with increased symptoms or clinical respiratory events. In the present case, no postoperative clinical changes were observed in the PACU. Phrenic nerve paralysis is a common complication in interscalene brachial plexus block. This complication is often ignored by most anesthesiologists because no clinical symptoms occur in patients who have no underlying lung disease. In patients with a BMI≥30 kg/m2 undergoing arthroscopic shoulder surgery, diaphragmatic paralysis is associated with dyspnea, occurrence of episodes of hypoxia and failure of the outpatient procedure [9]. Interscalene block with high volume and also, in smaller extension, low interscalene block volume were found to be responsible for diaphragmatic paralysis [9]. The patient in this case had a BMI=29.3 kg/m2, a little lower than that recommended by other papers, and likewise, no clinical change in respiratory parameters was observed.
Conclusion
In obese patients who have difficulty performing the block in lateral decubitus, the use of the posterior access to the brachial plexus and in the sitting position is comfortable and safe for the patient. This case report showed that posterior brachial plexus block with the use of neurostimulator, in hospitals where the use of ultrasound is not routine, proved to be a comfortable technique for the patient in the sitting position, easy to perform (spinous processes easily identifiable), and associated with general anesthesia for a patient in a beach chair, proved to be safe and effective. The use of local anesthetic (S75:R25) provided analgesia for 20 hours without side effects due to excessive use of opioids, such as nausea and vomiting, respiratory depression and intense itching.
For more Articles on: https://biomedres01.blogspot.com/




No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.