Painful Cutaneous and Subcutaneous Tumors Accompanied with Vascularized Appearance using High-Resolution Ultrasound in Dermatology: The Acronym “England” or “Lend an Egg”
Introduction
The acronym “ENGLAND” or “LEND AN EGG” is often used to recall these painful tumors in dermatology. “ENGLAND” tumors show: eccrine spiradenoma, neuroma, glomus tumor, leiomyoma, angiolipoma, neurilemmoma, and dermatofibroma. “LEND AN EGG” tumors show: leiomyoma, eccrine spiradenoma, neuroma, dermatofibroma, angiolipoma, neurilemmoma, endometrioma, glomus tumor, and granular cell tumor [1]. The acronym “LEND AN EGG” show “ENGLAND” entities associated with endometrioma and granular cell tumor. Dermatologic ultrasound imaging has been rapidly growing in recently years because of the development of high-resolution multifrequency transducers and multichannel color Doppler machines [2]. The international working group, called DERMUS (Dermatologic Ultrasound) was formed and provided the guidelines for performing dermatologic ultrasound examinations [2] and proposed for an assessment training program [2,3]. The minimum frequency recommended for performing dermatologic examinations was 15MHz [2,3]. We usually perform US examinations for dermatologic diseases with a high-resolution, broad-band (5MHz-18MHz) linear transducer (Nobulus Hitachi, Ltd.Tokyo, Japan) and have described some reports [4-9].
Eccrine Spiradenoma: Eccrine spiradenoma are rare benign tumors of the sweat gland, showing hererogeneously hypoechoic with lobular margin on gray-scale US and with increased peripheral portion, with or without blood flow in the central portion on color Doppler US [11]. Real-time Tissue Elastography (RTE) is widely used for diagnosis of breast and thyroid lesions on tissue elasticity. Recently, it has been reported that the usefulness of elastography is described in dermatologic field [7,9]. Sonoelastography evaluation showed a predominantly blue color, suggesting hard tissue component [19].
Histologically, ALM shows a proliferation of smooth muscle cells and vascular channels. Based on the size of the vascular channel and the degree of muscular thickness, ALM have been classified into three histological subtypes: a solid or capillary type, a cavernous type and a venous type. The solid subtype of ALM usually presents as a painful tumor in the limbs and occurs more frequently in females [20].
Recently, we have reported an ALM of the thigh in female with intermittent pain using high-resolution ultrasound including gray-scale US, color Doppler US and Real-Time Tissue Elastography (RTE). Vascular distribution was regarded as central and peripheral pattern on color Doppler US and peripheral flow signals was suggested to be consistent with adjacent vessel as previously described [7].
Angiolipoma: Angiolipomas can be painful and are one of the varieties of lipomas. Fibrin thrombi may be found within capillaries, and the degree of vascular proliferation may or may not be associated with pain. Bang et al reported that most subcutaneous angiolipomas are oval-shaped, have well-defined margins, and hyperechoic appearance on gray-scale US. They also described that color Doppler US findings may help in differentiating angiolipoma from ordinary subcutaneous lipoma. Shin, et al also reported that sonography might help differentiate angiolipoma from superficial lipomas.
Angiolipoma: Angiolipomas can be painful and are one of the varieties of lipomas. Fibrin thrombi may be found within capillaries, and the degree of vascular proliferation may or may not be associated with pain. Bang et al reported that most subcutaneous angiolipomas are oval-shaped, have well-defined margins, and hyperechoic appearance on gray-scale US. They also described that color Doppler US findings may help in differentiating angiolipoma from ordinary subcutaneous lipoma. Shin, et al also reported that sonography might help differentiate angiolipoma from superficial lipomas.
a) On gray-scale US show a well-defined hypoechoic nodule with cystic change and eccentric nerve-tumor position.
b) A few central blood flow signals are depicted on color Doppler US.
c) Power Doppler US show many central vascularity in a mass.
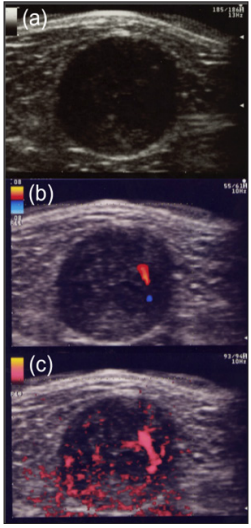 Neurilemmomas or Schwannoma: Neurilemmoma, or schwannomas, occur along the course of a peripheral nerve. They may be tender and firm and have a flash- to pale-pink color. Histologically, S-shaped nuclei, Vero cay bodies are characteristic. Both Antoni A and Antoni B tissue may be present. The nervetumor association and vascularity of the tumors could be useful for differentiation of between schwannoma and neuroma. Schwannoma shows eccentric nerve-tumor position on gray-scale US and vascularity within the tumor on color Doppler US [12]. Tsai et al. reported that color Doppler US shows hyper vascular flow signals in a patient with schwannoma [21]. US findings of pathologically confirmed as a schwannoma in the thigh in a 47-year-old male were present as follows: A well-defined hypoechoic nodule with cystic change and eccentric nerve-tumor position were depicted on grayscale US. Blood flow signals were more detectable on power Doppler US than on color Doppler US (Figure 1a-1c). Photomicrograph shows well-defined ovoid mass with degenerative cystic foci. Less cellular Antony type B area consisting of neuronal spindle cells forming Vero cay bodies was detected (Figure 2a- 2c). Tumors were comprehensively diagnosed as schwannomas in the upper extremity in a 46-year-old female were noted as follows: The tumor presents as well-defined hypoechoic nodule without an obviously nerve-tumor position on gray-scale US. Many central blood flow signals were depicted both on color Doppler US and power Doppler US (Figure 3a-3c). Figure 4 shows magnetic resonance angiography image as vascular tumors, suggesting schwannomas. ALM mimic schwannoma very closely. The features of nerve-tumor association and adjacent vessel could be useful for differentiation of between schwannoma and ALM as previously described [7].
Neurilemmomas or Schwannoma: Neurilemmoma, or schwannomas, occur along the course of a peripheral nerve. They may be tender and firm and have a flash- to pale-pink color. Histologically, S-shaped nuclei, Vero cay bodies are characteristic. Both Antoni A and Antoni B tissue may be present. The nervetumor association and vascularity of the tumors could be useful for differentiation of between schwannoma and neuroma. Schwannoma shows eccentric nerve-tumor position on gray-scale US and vascularity within the tumor on color Doppler US [12]. Tsai et al. reported that color Doppler US shows hyper vascular flow signals in a patient with schwannoma [21]. US findings of pathologically confirmed as a schwannoma in the thigh in a 47-year-old male were present as follows: A well-defined hypoechoic nodule with cystic change and eccentric nerve-tumor position were depicted on grayscale US. Blood flow signals were more detectable on power Doppler US than on color Doppler US (Figure 1a-1c). Photomicrograph shows well-defined ovoid mass with degenerative cystic foci. Less cellular Antony type B area consisting of neuronal spindle cells forming Vero cay bodies was detected (Figure 2a- 2c). Tumors were comprehensively diagnosed as schwannomas in the upper extremity in a 46-year-old female were noted as follows: The tumor presents as well-defined hypoechoic nodule without an obviously nerve-tumor position on gray-scale US. Many central blood flow signals were depicted both on color Doppler US and power Doppler US (Figure 3a-3c). Figure 4 shows magnetic resonance angiography image as vascular tumors, suggesting schwannomas. ALM mimic schwannoma very closely. The features of nerve-tumor association and adjacent vessel could be useful for differentiation of between schwannoma and ALM as previously described [7].a) Photomicrograph shows well-defined ovoid mass with degenerative cystic foci (hematoxylin and eosin, original magnification x40).
b) Photomicrograph shows less cellular Antony type B (hematoxylin and eosin, original magnification x100).
c) Less cellular Antony type B area consisting of neuronal spindle cells forming Vero cay bodies is detected (hematoxylin and eosin, original magnification x200).
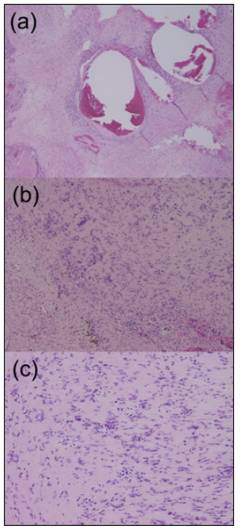 Figure 3: Schwannomas comprehensively diagnosed as a schwannoma in the upper extremity in a 46-year-old female.
Figure 3: Schwannomas comprehensively diagnosed as a schwannoma in the upper extremity in a 46-year-old female.a) The tumor presents as well-defined hypoechoic nodule without an obviously nerve-tumor position on gray-scale US.
b) Many central blood flow signals are depicted on color Doppler US.
c) Power Doppler show central hyper vascular flow signals.
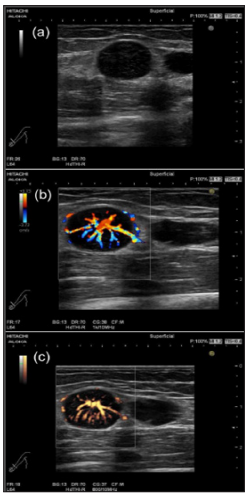 Figure 4: Schwannomas comprehensively diagnosed as a schwannoma in the upper extremity in a 46-year-old female. Magnetic resonance angiography image shows vascular tumors.
Figure 4: Schwannomas comprehensively diagnosed as a schwannoma in the upper extremity in a 46-year-old female. Magnetic resonance angiography image shows vascular tumors.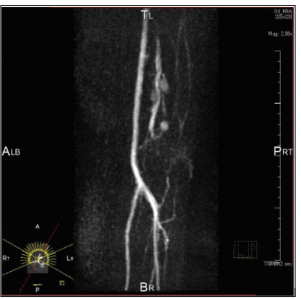 Dermatofibroma: Although most dermatofibromas are asymptomatic, some are tender. Characteristic epidermal hyperplasia may overlie the tumor, and lipid and hemosiderin may be present in the dermis. Jin, et al. reported that a patient with dermatofibroma showed a well-defined margin and hypoechogenic in the dermis-to-subcutaneous fat layer with increased vascular flow. The acronym “LEND AN EGG” show “ENGLAND” entities associated with endometrioma and granular cell tumor.
Dermatofibroma: Although most dermatofibromas are asymptomatic, some are tender. Characteristic epidermal hyperplasia may overlie the tumor, and lipid and hemosiderin may be present in the dermis. Jin, et al. reported that a patient with dermatofibroma showed a well-defined margin and hypoechogenic in the dermis-to-subcutaneous fat layer with increased vascular flow. The acronym “LEND AN EGG” show “ENGLAND” entities associated with endometrioma and granular cell tumor.A. All painful cutaneous and subcutaneous tumors in dermatology used the acronym “ENGLAND” especially, angioleiomyoma, eccrine siradenoma, schwannoma and glomus tumor show vascularized appearances on high-resolution color Doppler US.
B. The classification of the vascular distribution is contributed to the differentiating between schwannoma and angioleiomyoma.
More BJSTR Articles : https://biomedres01.blogspot.com



No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.