Epicoccum Species as Potent Factories for the Production of Compounds of Industrial, Medical, and Biological Control Applications
Introduction
Discovering new applications for currently known bioactive metabolites and/ or exploring novel biologically active metabolites are of critical need nowadays due to the current increasing dilemma of microbial resistance to available and used antibiotics and therapeutic agents, beside the emergence of new life threatening diseases. These problems have encouraged scientists to look for unconventional sources in order to find novel compounds. Fungi are promising sources for a wide variety of vital metabolites such as alkaloids, flavonoids, phenols, steroids and terpenoids [1-3]. Fungi capacity to synthesize variety of new bioactive metabolites forced researchers to explore these avenues. Epicoccum is an ascomycotic, endophytic fungus that is commonly isolated from different sources in moderate frequencies [4-6]. E. nigrum is famous for its successful applications in the bio-control of many phyto-pathogens [7-13], also for its ability to produce diverse classes of chemically, structurally, and biologically diverse secondary metabolites [13-17]. The aim of this review is to provide information about secondary metabolites of Epicoccum and their promising and current applications. Highlighting the importance of rich sources of biologically active compounds can contribute in encouraging searching for novel sources of potent compounds to face current needs for antimicrobial agents to overcome microbial antibiotic resistance, and to discover drugs for existing life-threating diseases.
Secondary Metabolites of Epicoccum Species
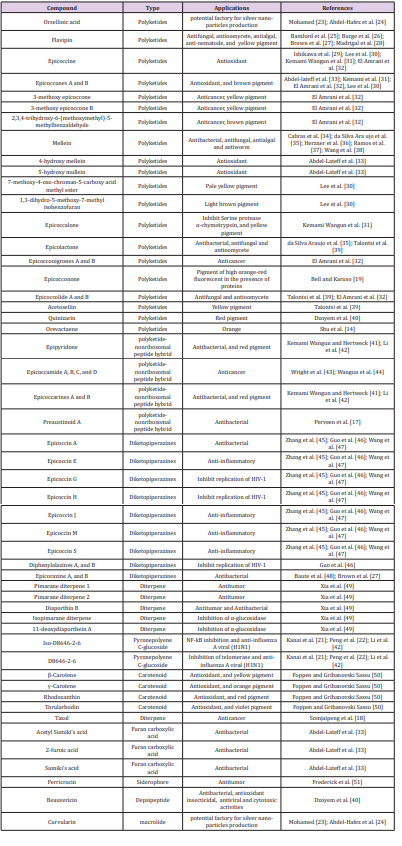
Epicoccum Sp. produces variety of secondary metabolites such as polyketides, polyketide hybrids, diketopiperazines, Siderophores, Carotenoid, and others (Table 1). Majority of these compounds exert promising biological activities such as antioxidant, antimicrobial, anticancer, in addition to potential industrial applications of pigments produced from E. nigrum as a likely safe, nontoxic, and non-pathogenic fungus. Among the important biologically active compounds produced by Epicoccum spp., the anticancer drug, taxol [18]. Also, epicocconone which is known commercially as fluorophore and is used in cell staining and in gel electrophoresis for protein detection [19,20], D8646-2-6 which is a telomerase inhibitor [21,22], in addition to many potential factories for silver nano-particles production such as Orsellinic acid and Curvularin.
Table 1: some secondary metabolites produced by Epicoccum species and their biotechnological applications.
Epicoccum Spp. As Biocontrol Agents
Epicoccum spp. have proven to be a potent biocontrol agents against many phytopathgenic fungi, specially Botrytis cinerea waxflower [23], Claviceps africana in sorghum [24], Pythium spp. infecting cotton [9], Rhizoctonia solani infecting potato plants [25], and Sclerotinia sclerotiorum in sunflower [26], Phytophthora infestans [27], phytoplasma in apple trees [28] and Monilinia spp. in peaches and nectarines [29-33] and against other plant pathogenic fungi [10,11,34,35].The action mechanisms exhibited by E. nigrum as a biocontrol agent varies from reducing host stem disease severity index, and growing along the fungal pathogen hyphae and inducing its lysis [36], or through causing degradation of the pathogen protoplast, malformation in its hyphae, and leakage of cytoplasm [37]. The polyketide, Flavipin, produced by many Epicoccum Sp is the reason causing growth inhibition of numerous phytopathogenic fungi [25,28,38-41]. On the other hand, Epicolactone isolated from E. nigrum has antifungal activity and can induce root growth [42- 57]. All those studies support using Epicoccum species in different host plants as a safe biological control agent and encourage deep investigations for further understanding of the physiological and molecular aspects of this interaction [57-62].
Conclusion
Emerging of microbial resistance, spread of life-threatening diseases, and biological control of pathogens destroying economically important crops, are serious problems that encourage scientists to search for unconventional sources for novel compounds with biological activities. Fungi are promising sources for such compounds due to their ability to produce assortment of secondary metabolites that could be, if truly investigated, the solution for currently serious problems. Epicoccum is one of the pioneer fungi in this field with proven potent ability as promising biotechnological tool to produce industrially, and biologically diverse metabolites.
THI: Is it a Reliable Measure to Assess Cattle Thermal Stress in Silvopastoral Systems in a Subtropical/ Temperate climate?-https://biomedres01.blogspot.com/2021/02/thi-is-it-reliable-measure-to-assess.html
More BJSTR Articles : https://biomedres01.blogspot.com



No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.