Clinical and Biological Factors Associated with ISH Amplification in HER2 2+ by IHC in Breast Cancer Patients
Introduction
Epidermal growth factor receptor 2 gene (HER2) is overexpressed in approximately 18% to 20% of primary breast cancers [1] providing a special prognostic and predictive factor. Since 2001, the use of trastuzumab, the first antiHER2 therapy, has shown a significant survival improvement when combined with chemotherapy in the metastatic setting [2] other pivotal trials have confirmed this benefit in early and locally-advanced breast cancer [3-5]. In the last few years new HER-2-targeted drugs such as lapatinib [6] pertuzumab [7] and ado-trastuzumab emtansine (TDM1) [8] have been approved for the treatment of HER2 positive breast cancer. Thus, HER2 status of the patients has been integrated in the clinical practice to guide therapy decisions.
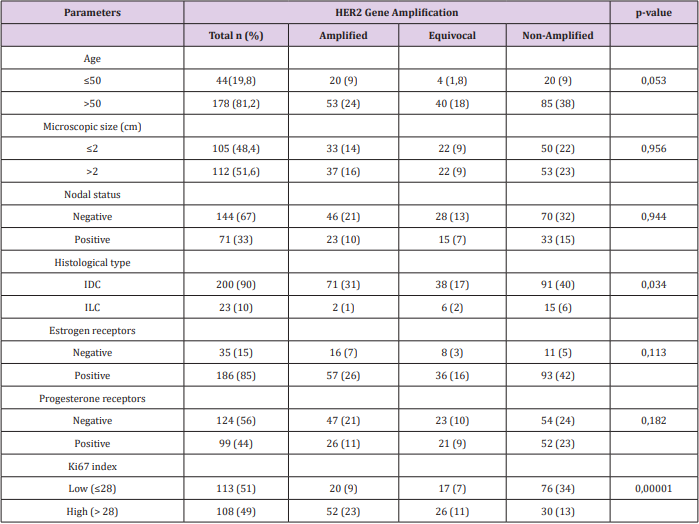
The most widely used guidelines for the diagnosis of HER2 protein overexpression by immunohistochemistry (IHC) are those recommended by the American Society of Clinical Oncology and College of American Pathologists (ASCO/CAP) [9] which categorize the tumor Her2 status: IHC score 0/1+ (IHC-negative), 2+ (IHC equivocal), and 3+ (IHC positive). The IHC-equivocal or borderline 2+ subgroup have ambiguous tumor nature, with a weak HER2 oncoprotein expression. It’s highly crucial for clinicians to determine if these patients are eligible for antiHER2 therapy, so further molecular diagnostic tools are needed to define the Her2 status. In situ hybridization techniques (ISH) are the standard cytogenetic methodology to identify increased number of gene loci (using CEP17 DNA sequence as reference) for accurate HER2 assessment [10]. We analysed a series of 223 patients with IHQ HER2 2+, in which further ISH was performed and correlated with clinicopathological variables that predicting ISH amplification. Main characteristics and its correlation with final ISH results are shown in Table 1. Most of the patients were ER positive (79,8%) and had a high (>20%) proliferative index Ki67 (70%).
Findings
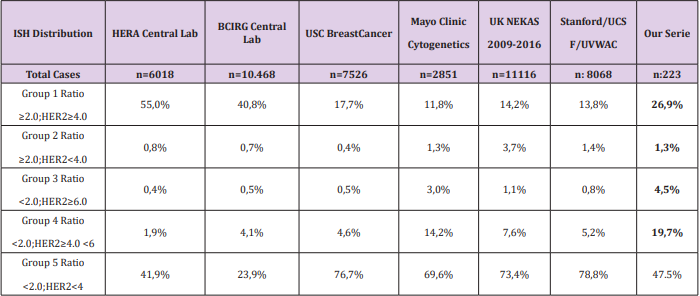
As only patients with HER2 gene amplification have clinical benefit to anti HER2 therapy [11] it is extremely important to define Her2 status in these cases. The ISH techniques show that only 24% of the IHC 2+ tumors have gene amplification [12]. Provided that ISH techniques are complex, we should identify more accurately which cases must be tested by ISH. Many studies have reported that HER-2 overexpression (IHC 3+) or HER-2 gene amplification is associated with high cell differentiation grade, absence of ER or PR expression, DNA aneuploidy, and high Ki-67 [13]. When analyzing factors which could predict HER2 amplification, ER and PR positivity are shown to be related with negative HER-2 status and better prognosis [14]. The most used ASCO guidelines (ASCO/ CAP2013) defines HER2 positivity as: HER2 signal ≥6.0 or ISH ratio >2.0, but the multiple combination possibilities of these two parameters can be categorized in five groups [15].
The results of our cohort of patients are shown in Table 2. The group with HER2 signal ≥4.0 but <6 and ratio <2 is the most controversial and it is defined as equivocal, requiring a new assessment of HER2. In our series, almost 20% of cases are equivocal, considered as a high rate; but still in range of most of the studies [11]. In our cases any variable was found with a predictive value for equivocal ISH result. We found a total of 73 (32%) cases stablished as positive by ISH, which is consistent with other series [11]. A few studies[14] have described the proliferative index Ki67 as the most predictable variable to determine a positive result, with a Odds Ratio (OR) around 3. We performed a logistic regression model to reveal risk factors for HER-2 amplification. The association between clinicopathological variables and HER-2 amplification is shown in Table 1. Cases with high Ki67 had a significantly higher HER-2 amplification than those with low Ki67 (OR =4,318; 95% CI, 2,339-7.971; P<0.000). Unlike other studies, we do not find any correlation between hormonal receptors and ISH status; in contrast with other studies where this correlation is weak compared to that of Ki67. We have generated a risk score that combines the expression of ER and Ki67 with the specific threshold of Her2 positivity. We have found that patients with ER>250 and Ki67<28% show a 19% possibilities to be ISH positive, in contrast to 46% in patients with ER<250 and Ki67>28 (χ2 =23,31, P<0.000).
Conclusion
Accuracy of Her2 status determination in breast cancer is a key point in defining a treatment strategy. However, there are about 20% of cases with equivocal IHC results that require additional techniques such as ISH. A high proportion of these equivocal cases (up to 20%) will require predictive biomarkers. We have found that Ki67 expression correlates to a higher Her2 positivity by ISH, more so if we correlate it with ER expression.
More BJSTR Articles: https://biomedres01.blogspot.com/



No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.