Enhancing Patient Outcomes with Clinical Nutrition: The Effects of Supplementation in Orthopedics
Introduction
Each year more than half of people over the age of 18 in the
US will develop a musculoskeletal injury that lasts more than 3
months. This is roughly 18% of all clinical visits and represents
enormous costs, ~5.7% of US GDP and 216 million lost workdays
[1]. Tens of millions of patients each year turn to orthopedic
surgeons and physical therapists to treat their injuries and return
to normal function as quickly as possible. There is an urgent need
to utilize all of the latest techniques, tools and technologies to
improve outcomes and enhance patient recovery to lower the cost
burden on the health system and improve economic output due to
lost workdays. New innovations continue to enhance the field of
musculoskeletal injury treatment and management. One area that
is showing considerable promise is in targeted nutrition.
Nutrition and Healing
Science is increasingly showing just how critical nutrition is to
healing and recovery. As we know during a state of trauma, such as
injury or surgery, the body’s nutritional needs increase:
a) The body enters a higher metabolic state and requires more
energy
b) Trauma and lack of use leads to muscle atrophy, which prolongs
recovery
c) The immune system is weakened due to stress and shock
d) Risk of wound infection is increased
e) Persistent inflammation delays return of function
f) Trauma and physiological stress lead to increased fatigue
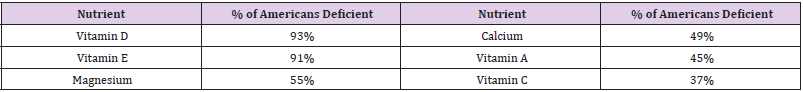
Nutritional deficiencies impede the natural progression of
healing, including elevating the risk of infection and lengthening
recovery periods. A patient that is nutritionally optimized will heal
better and faster and have better long-term outcomes. One that
isn’t will heal more slowly and may have long-term complications.
Unfortunately, most Americans are overfed and undernourished,
meaning most Americans are not at optimal nutritional status
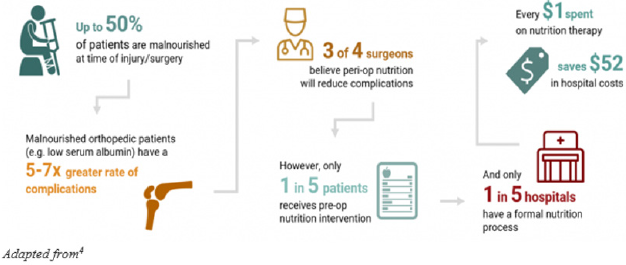
to prevent complications post-trauma. Hospital studies have
shown that as many as 50% of patients are undernourished or
malnourished [2]. These patients face greater complications than
properly nourished patients, including longer hospital stays, greater
risk of infection, and increased mortality. One study, published in
the Journal of Nutrition, studied over 16,000 individuals and found
that many are not meeting the minimum recommended thresholds
for micronutrient intake (Table 1): The combination of increased
baseline nutritional needs post-trauma, from injury or surgery, and
prevalent undernourishment means that most Americans are not
well equipped nutritionally to heal Figure 1.
Clinical Evidence - Nutrition as an Orthopedic Treatment Tool
The science of nutrition in orthopedics is advancing rapidly and
a growing body of clinical trials are demonstrating convincingly that
targeted nutrition can enhance outcomes, both for acute patients
as well as for patients with chronic conditions. Wound healing,
inflammation response, increasing muscle mass and strength,
and decreasing muscle atrophy are crucial recovery objectives for
orthopedic patients, and nutrition has been shown to support these
healing processes. Below we look at a sampling of randomized
trials from a larger set of published clinical trials in orthopedics. A
randomized controlled study by Ekinci et al. [3]. included 75 older
female patients with hip fractures and investigated the effects of
Calcium HMB, vitamin D, and protein supplementation on wound
healing and muscle strength. The study group received an enteral
product containing 3g CaHMB, 1000 IU vitamin D, and 36 g protein,
in addition to standard postoperative nutrition. They found that the
patients on the nutritional supplement product had an acceleration
of wound healing, shortening of immobilization period, and
increased muscle strength without changing body mass index.
This study also found a reduced dependence to bed and related
complications after an orthopedic operation [4,5]. A study by Negro et
al. found that twice daily consumption of a mix containing
Essential Amino Acids (EAA), creatine, vitamin D and Muscle Restore
Complex® (MRC®: Alpha Lipoic Acid (ALA), Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10),
resveratrol) for 12 weeks may aid in sarcopenia prevention without
physical exercise by improving muscle aging-related outcomes,
such as muscle mass, muscle strength and muscle power. In this
study 38 healthy elderly subjects were randomized and allocated
into the supplement or placebo group. Significant improvements
were found in the supplement group compared to placebo in
vitamin D blood levels, Legs Fat Free Mass, Appendicular Lean
Mass, Maximal Voluntary Contraction, and Peak Power [6]. Dreyer
et al. found in a double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized trial
on patients undergoing total knee arthroplasty (TKA), that EAA
supplementation is safe and reduced the loss of muscle volume
in older adults recovering from TKA [7]. These studies emphasize
the importance of targeted nutritional supplements for muscle
preservation and return to function - critical in any patient with a
surgery that results in significant muscle atrophy such as ACL.
Certain key ingredients are crucial to include to help support
recovery. Liberman et al. found that thirteen weeks of nutritional
supplementation with Vitamin D and leucine-enriched whey protein
may attenuate the progression of chronic low- grade inflammatory
profile in older sarcopenic persons with mobility limitations [8].
Another key study by Kim et al. found that in surgical patients, the
addition of glutamine supplementation reduced infection rates and
shortened the length of hospital stay. Glutamine also decreased the
production of pro-inflammatory cytokines in this population [9].
By lowering inflammation, the healing process is greatly enhanced.
β-hydroxy β-methylbutyrate (HMB) has been shown in many
studies to promote wound healing and diminish muscle wasting
Flakoll et al. found that elderly women treated with a nutritional
supplement containing HMB, arginine, and lysine for 12 weeks
had increased muscle mass and maximum strength [10]. HMB is
also utilized and useful in combination therapies. This doubleblind
controlled 12- month study by Rathmacher et al. found that
HMB in combination with Vitamin D had a significant benefit on
lean body mass and showed improvement in knee extension peak
torque even with no exercise. Overall, their findings showed that
even without exercise, the HMB+ Vitamin D supplemented group
showed significant increases in functional outputs than those in
controls [11]. Interestingly, HMB has also been shown to increase
anabolic signaling [12].
Conclusions
A very significant proportion of the orthopedic patient
population is nutritionally compromised and during trauma the
body’s nutritional needs increase above baseline. Clinical studies
are increasingly demonstrating that a patient’s nutritional status
can directly impact outcomes and that modification through
supplementation can enhance outcomes. The American Physical
Therapy Association (APTA) has recognized the important role
of nutrition in patient care and treatment and put it in scope of
practice. APTA states: “Nutrition is part of the professional scope
of practice for physical therapists”; further they state: “it is the role
of the physical therapist to screen for and provide information on
diet and nutritional issues to patients, clients, and the community
within the scope of physical therapist practice.” (House of Delegates
P06-15-22-17).” There remains work to be done to quantify the
economic impact and savings to the healthcare system, but we
suspect it is considerable. For example, large retrospective studies
done by Novartis and Eli Lilly of more than 130 thousand patients
shows that severe muscle atrophy and weakness (MAW) is common
in joint replacement patients and that complications related to
MAW cost roughly $10K per patient to treat13. Similarly, according
to a study published by Mackenzie et al. [13]. in the Journal of
Orthopedic Sports Medicine, revision costs in ACL patients range
roughly in the $9K range [14]. Considering the sheer volume of
orthopedic injuries and surgeries, we can extrapolate that there
is billions of dollars of cost in the healthcare system that can be
addressed through nutritional supplementation and optimization.In summary, an increasing body of science suggests that
targeted supplementation should be utilized in patient care. By
doing so, we can improve patient outcomes and reduce healthcare
costs.
For more Articles on : https://biomedres01.blogspot.com/

No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.