Epidemiological, Characteristics and Outcomes of Road Traffic Accident Among Patients in Emergency Units
Introduction
Traffic accidents are one of the most unfortunate reasons that
claim dozens of lives every day around the world, in addition to
the occurrence of many injuries and serious damage to the means
of transportation, despite the increase in awareness campaigns in
global traffic weeks, and throughout the year as well, and the causes
of traffic accidents are many [1-3]. There is a continuous increase in
the number of victims due to traffic accidents; In 2016, the number
of deaths resulting from car accidents reached 1.35 million people
around the world, but this percentage is considered constant
with the increase in population numbers around the world, and
the increase in the number of cars, and this indicates the efforts
made to maintain the safety of road users, which led to a lack of
It gets worse, knowing that one of the sustainable development
goals, which is to reduce the death rates from accidents by 50% by 2020,
has not yet been achieved [4-6]. Life and death; the care
of the injured is a very delicate matter; If it is done wrong, it may
lead to the death of the injured, or aggravate his injury, and this
can be avoided by registering in specialized training programs in
ambulance, and caring for the injured from accidents [7-8].
The continent of Africa is the highest in recording death
rates from accidents, and the ages of deaths resulting from traffic
accidents range between young people and children from 5 to 29
years old, while males cause road accidents at a higher rate than
females, accounting for 73% of deaths that result from accidents
[9-10]. Therefore, the RTA occurred among the youngest under
the age of 25 years [11]. Traffic accidents leave a lot of damage,
whether economic, social, or human, and these accidents have
several consequences and many costs, and these costs, for example:
treatment of the injured, the length of their care, and the loss of
the production process due to injury [12-13]. In addition to the
loss of welfare and material losses service to the injured, rescue
operations, police work, investigations into the cause of the
accident, and in addition to these losses, the costs and damages
resulting from accidents are also borne by the families of the
victims and injured [14]. While the costs of accidents in developing
countries are estimated at 65 billion dollars annually; that is, it
exceeds the amounts provided annually for development aid, and it
must be said that all efforts made for maintain the safety of drivers
while driving on the roads have not achieved the required results
[15].
Adolescents, especially those ages between 16 to 19 years,
should be educated and given sufficient experience and the
necessary skill to take responsibility for driving and to keep them
safe on the roads because of its great role in avoiding accidents
[16]. Statistics indicate that the aforementioned age group is the
most likely to die as a result of car accidents, and they cause four
times more horrific accidents than the age group between 25 to
69 years [17]. Technology plays an important role in preventing
car accidents, reducing the risk of injury, and maintaining the
safety of both drivers and pedestrians, such as: sending warning
signals before a collision occurs, enabling the driver to avoid an
accident, facilitating the detection of blind spots on the vehicle, and
improving brake systems [18]. Therefore, the driver must choose
a car with high safety specifications, and advanced technology
to improve safety while driving and, asking about the vehicle’s
specifications before purchasing it [19]. This study aimed to
identify the epidemiological, characteristics and outcomes of Road
Traffic accident among patients in emergency unit during the study
period.
Methodology
A retrospective cross sectional study was conducted among
198471 patients with road traffic injuries were registered on
fifteen provinces in Iraq. The data reported on the present study
were collected between January 2020 and December 2020. Data
were collected including medical history, patient symptoms,
clinical signs and the radiological findings. Data onto patients
were recorded including cause and location of injury, frequency
and type of injury (frequency of soft tissue injuries and bone
fractures), as well as age and gender distribution. Duration of
recovery and associated complication was also recorded. Road
traffic injuries were classified into [20], soft-tissue injuries,
fractures and injuries of organs. Soft-tissue injuries were classified
into abrasion, contusion and laceration. Fractures were classified
into; skull (fissure and depressed fractures) and long bones. The
Glasgow Coma Scale was used to assess the severity of brain injury.
A conservative or operative intervention done for all the cases was
also recorded. Traffic accidents are classified according to the E
code of the International Classification of Diseases (ICD).
By definition, this category includes all accidents involving at
least one vehicle for any kind. The definition used in the present
study embraces also pedestrians injured in an accident not
involving another person or vehicle, e.g. an injury caused by slipping
or stumbling [21]. Objective measures of injury severity -the injury
severity score (ISS) and the 1990 revision of the abbreviated injury
scale (AIS-90) was determined. The AIS is a scale for categorizing
injury type and severity. The body is divided into six regions (i.e.,
head or neck, face, chest, abdomen, extremities, and external)
in which injuries are graded from 1 (minor) to 6 (clinically
untreatable). The maximal AIS (MAIS), which is the highest single
AIS code in a patient with multiple injuries, was determined. The
ISS, which is useful for assessing the severity of multiple injuries,
is the sum of the squares of the highest AIS coded in each of much
three most severely injured body regions [22]. Statistical analyses
performed included descriptive analysis, chi square test, Fisher’s
exact test, and Mann-Whitney’s U test. This was followed by logistic
regression analyses to determine the impact on the main causes of
craniofacial injuries. The SPSS Version 16.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL)
and Epi Info™ Version 3.5 were used for statistical analyses.
Results
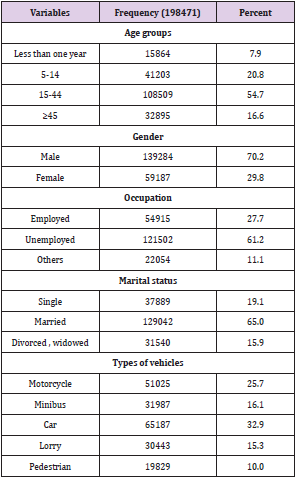
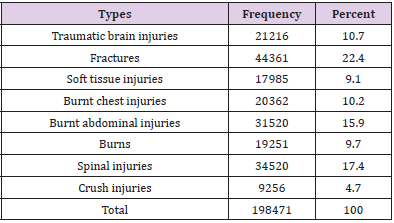
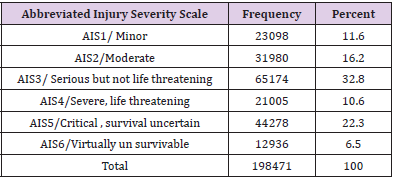
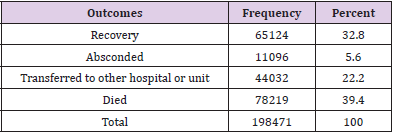
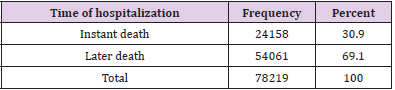
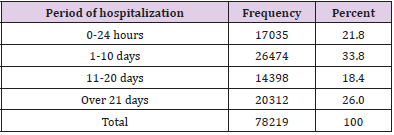
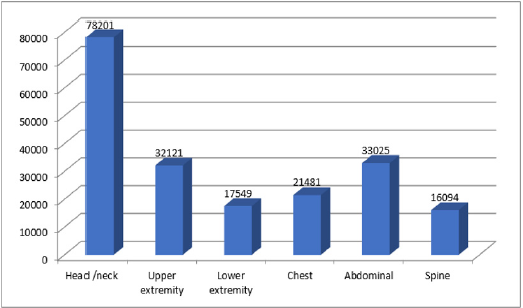
Out of 198471 of RTA patients, half of them 54.7% occurred in the age group 15 to 44 years old and 20.8 % in the age 4 to 14 years old. Male cases 70.2% were more than 29.8% female cases. 61.2% were unemployed and 65% were married. Car constitutes the large victim group of road traffic accident fatalities and injuries (32.9%), followed by motorcycle (25.7%), 16.1% by minibus and 15.3% by lorry (Table1). In Table 2 shows that the highest frequency 22.4% of them had fractures ;followed by 17.4% had spinal injuries, 15.9% had burnt abdominal injuries, 10.7% and 10.2% had TBJ and burnt chest injuries respectively. In Figure 1 shows the highest frequency (39.4%) 78201/198471 had injury in head and neck rejoin followed by (16.6%) 33025/198471 in abdominal rejoin and (16.2%) 32121/198471 in upper extremity rejoin. The studied cases were divided into six groups according to abbreviated injury severity scale (AIS), the highest number of patients scored AIS 3(32.8%) and the least number (6.5%) scored AIS 6 (Table 3). According to outcome of studied cases involved in road traffic accidents,32.8% discharged after recovery , 5.6% absconded,22.2% transferred to other hospital or unit and , 39.4% died (Table 4). Out of 78219 victims, 24158cases (30.9%) died instantly and 54061 (69.1) % died after a period of hospitalization (Table 5). Out of the hospitalized victims, 21.8% died in the first 24 h, 33.8% died in a period of 1–10 days, 18. 4% died in 11–20 days, and 26% died in more than 21 days (Table 6).
Discussion
This study aimed to identify the epidemiological, characteristics
and outcomes of Road Traffic accident among patients in emergency
unit during the study period. The most common age group affected
in this study was 15 to 44 years old (54.7%) and is agreement
with other studies from other countries [23-25]. The ages in this
category are the most active and energetic and the most of them
are car users and, therefore it’s represented the largest number of
injuries and deaths resulting from accidents and, this has an impact
on the economic, social and psychological level as well. Preventive
measures are important to this category and, thus reduce the risks
of exposure to severe danger that has an impact on the body. The
result of accident is either disability or loss of life. Also, adolescents
and young adults have different behavior when driving cars,
including drinking, speeding, neglecting seat belts, risking driving
at night, and racing against young people as a form of betting.
Recent studies conducted in some countries indicate that young
drivers between the ages of 18 and 27 years are more likely to be
killed compared with other age groups, as well as lack of experience
and risk are two factors associated with the occurrence of collision
accidents among adolescents.
In our study, we found that the majority 70.2% of those exposed
to accidents are males, and this is due to the predominance of men.
As some of them become more aggressive in the street, as well as the
dominance of men over the drivers of transport vehicles, because
most of them spend their time outside the home and similar higher
incidence of traffic accidents among males has been found by many
other researchers [26-27]. In this study we found that the majority
of victims of RTA 61.2% were unemployed and this finding in
line with other finding done it in Nepal by Karkee [7], the author
found that the majority of studied samples are unemployed. Most
men prefer self-employment, especially in developing countries
that suffer from unemployment and lack of job opportunities for
their citizens. The higher percentage of victims 65% were married
and compared with other results has done it in Iran by Hamzeh
[4], Africa by Sango [9], Nigeria by Labinjo [13], they reported
the majority of victims are married. Car accident represented the
majority of victims of road traffic accidents (32.9%), the same has
been reported by Downing [28], but Kraus, et al. [29], found in San
Diego that 62% of head injuries were to occupants of vehicles.
The higher percentage of car accident in this study may be
attributed to failure of directing and controlling traffic. The type
of road is also one of the risk factors, especially on external roads,
where there are scarce paths, sidewalks and traffic lights, as well
as lighting, as it poses the greatest danger and causes a high risk of
death, especially at night, in addition to weather factors such as fog
and rain, which cause poor visibility and this leads to the accident
[30-31]. Previous studies indicate that drivers acquire many
dangerous and harmful driving habits, especially in developing
countries, and fail to comply with traffic rules. In some countries,
the seat belt is ignored for the driver of the vehicle and other
protective equipment such as the helmet for motorcyclists [32-33].
On the other hand the most commonly injury in similar studies
was to the head (69.63 %) followed by chest (33.62%) [34]. Out
of 198471 cases, there is 44361 (22.4%) had a fatal skull fracture.
Similar findings were seen in few other studies. Most commonly
found a spinal injury (17.4 %) which is consistent with the findings
by other researchers [35-36].
Pre-hospital mortality was found to be in 24158 cases (30.9%).
The rest (69.1 %) was taken to hospital where later they succumbed
to their injuries. This is nearly consistent with the study conducted
in Iran with higher cases of pre-hospital mortality [37]. The present
study observed that the most frequent lesions were in the head /
neck (39.4%) followed by abdominal injuries (16.6 %) and in upper
extremity (16.2%) and this finding in line with other findings in
Thailand [1], Italy [30], Nepal [23], United Arab Emirate [33], they
reported the head and neck the major lesions by RTA.
Conclusion and Policy Implication
In addition to the fact that road traffic injuries pose a significant
health risk leading to a high rate of morbidity, disability and death,
they have a significant social and economic impact on the victim, his
family, and the nation as a whole. This study shows that most deaths
in traffic accidents, brought to hospital, occur either immediately
or within 24 hours of injury which is very worrying and highlights
the need to take urgent steps to provide care services to them as
quickly as possible. It also shows in our study that head injuries
remain the most common and serious type of trauma seen in our
hospital’s emergency department and that quality neurosurgical
care is essential for these patients. There is an urgent need to
highlight the risk factors, conditions and chain to events that lead
to accidents and it will be very useful for policy-making and health.
In summary, it has been shown in this study that males, of younger
ages, pose a higher risk, mortality and morbidity. Our findings may
be useful for forensic experts, clinicians, and mechanical engineers
looking for new vehicle occupant safety devices.
Deaths, injuries and disability after traffic accidents place a
significant financial burden on the budgets of developing countries
like ours. This problem must be resolved as soon as possible before
causing more deaths in light of studies on the causes and prevention
of traffic accidents and the support of international organizations.
For more
Articles on : https://biomedres01.blogspot.com/



No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.