Road traffic injuries (RTIs) are a public health burden globally. The number of deaths due to road accidents worldwide is exceptionally high, with an estimated 1.35 million deaths and 20 - 50 million injuries each year (World Health Organization (WHO). 2020b). Road traffic is among the leading causes of mortalities due to injuries for all age groups, especially among children and youth and young adults aged 5 to 29 (World Health Organization (WHO). 2018). Globally, road injuries were responsible for more than 55 million years of life lost, 7 million years lived with disability, and 64 million disability-adjusted life years in total, with corresponding age-standardized rates of 745, 126, and 871 per 100,000 population, respectively James SL, et al. [1]. The two most common road traffic injuries are head and spinal cord injuries, which are the leading cause of death and trauma for motorcycle users (World Health Organization (WHO). 2018). Such injuries may result in an enormous economic burden and use extensive portions of a countries health expenditure (World Health Organization (WHO). 2013b, 2018). The risk of encountering RTIs among middle and low-income countries (LMICs) is three times higher than in higherincome countries (World Health Organization (WHO). 2020b).
Motorcycles are the most widely used transport in Viet Nam, accounting for more than 90% of total personal transport registrations (World Health Organization (WHO). 2013a). The average rate of annual road traffic injury mortality was reported approximately 18 per 100,000 population before 2007 (Health Environment Management Agency, Ministry of Health. 2011). In response to the rising burden due to RTIs, the Viet Nam government enacted a comprehensive helmet use legislation for motorcyclists in June 2007 (Government of the Socialist Republic of Viet Nam (GOV). 2007). This legislation included obligatory helmet-wearing rules to all two-wheeled and three-wheeled vehicles on all roads, with heavy fines for non-users, and increased enforcement Passmore, JW et al. [2]. The helmet use rate in Viet Nam immediately escalated from 40% in 2007 to over 95% in the following year and has remained steadily above 90% since then (World Health Organization (WHO). 2020a). The introduction of mandatory helmet-wearing legislation in Viet Nam was anticipated to have averted 2,200 deaths and 29,000 head injuries in the year 2008 Olson Z, et al. [3]. The helmetwearing law is useful, especially among less wealthy families.
Many countries have presented similar successful results of putting helmet-wearing laws into practice, resulting in head injuries dropping by 33% in Taiwan and 41% in Thailand after implementing such laws Chiu, WT, et al. [4,5]. Similar studies have examined the effectiveness of helmet law enactment on traffic mortality in Viet Nam. At the national level, traffic deaths related to motorcyclists, and total traffic deaths, in the year following the introduction of the helmet law in Viet Nam dropped by 36% and 18%, respectively Passmore, JW et al. [2,6]. The study by Phung et al. across all provinces in Viet Nam revealed that many areas experienced a significant decrease in potential years of life lost (PYLL) of more than 80% due to RTIs, and the summary post law PYLL stopped increasing six months of implementation helmet laws Phung D, et al. [7]. Another study in an outlying district of a large city in Viet Nam found that motorcycle-related injuries and deaths during the post-law period decreased significantly, by 47% and 31%, respectively Ha NT, et al. [8]. Although the efficacy of helmet laws was demonstrated in reducing road injuries and deaths at the national level, evidence in remote areas is still needed. This study aimed to evaluate the impact of mandatory helmet legislation on the potential change of mortality in Lang Son province, a large mountainous region in northern Viet Nam. This province has an area of 8.310,09 km2 with five national highways (Lang Son Provincial Statistics Office. 2019). Before 2007, the government implemented legislation and enforced motorcycle helmet use, but the helmet use rate stayed low as of 2005 Dinh VH, et al. [9].
Data Sources and Data Items
To obtain the traffic-related fatalities, all deaths in Lang Son Province between January 2005 and December 2018 (missing data 2009-2010) were listed based on an official form referred to as the A6. Form A6 is collected according to decision No. 2554/2002/ QD-BYT of the Ministry of Health to register all causes of deaths in the community. Thereby, the registration process was reviewed monthly for each fatal case by the commune health stations (a total of 200 communes). The completeness, sensitivity, and specificity of the A6 system were reported as 93.9%, 75.4%, and 98.4%, respectively Stevenson M, et al. 2012. Based on form A6, all accidentrelated deaths were identified. To evaluate the completeness and the accuracy of the list, all accidents related deaths were compared with the register at the Center of Disease Control of Lang Son Province.
To improve the accuracy in identifying the cause of death, each case was reviewed by trained researchers to confirm any underlying causes of death. All cases with unclear causes were listed and then feedback to the corresponding commune health centers to clarify and confirm the cause of death. If a decision was not obtained, trained researchers would call the deceased’s relatives to identify the underlying cause of death. All underlying causes of death were coded following ICD-10. Then, traffic-related fatalities were extracted based on ICD-10 codes (V01-V89). Additionally, the deceased’s information of age, gender, date of death, and the average population of their commune in the corresponding year was collected based on designed data collection forms. Guidelines on how to determine the underlying cause of death and methods to collect data were sent to each commune health station, annually, for data collection.
Data Analysis
First, the crude death rate per 100,000 person-years was estimated. To estimate the age-standardized mortality rate per 100,000 person-years, we applied the accurate statistical data from the World Health Organization standard population for 2000- 2025. Mortality rates were described by year, sex, and age group to observe the trends and differences. Next, Poisson regression was used to estimate the mortality risk ratios (MRR) and 95% confidence interval (95%CI). The cut point of 0.05 of the p-value was considered statistically significant. The data were calculated using Stata version 13.0 (Stata Corp, College Station, Texas). Additional references can be found in the bibliography in the Appendix.
Mortality Caused by Road Traffic Injuries Total Both Sexes
A total of 1841 deaths were identified by the A6 system, which consisted of 1542 and 299 deaths of men and women, respectively. Lang Son province experienced a crude mortality rate of 20.3 per 100.000 person-years from 2005-2018. All mortality indexes in men were higher than that in women. In terms of age, death cases were most prevalent among those aged under 70 years in both sexes. Overall, the estimated proportion of death cases under 70 years of age was as high as 94%, with 96% in men and 84% in women (Table 1). The overall proportion of deaths in both genders due to road traffic injuries was 3.74% (1,841 cases of road traffic injuries vs. 49,253 total cases). Mortality rates from 2005 to 2018 averaged around an approximate value of 20, with the highest in 2011 and the lowest in 2008.
Combining all death cases from 2005 to 2018, the overall agestandardized mortality rate, according to WHO-ASR, was 20.1 per 100.000 person-years. The number of death cases grew gradually from 2005 (148) to 2007 (164), followed by a sharp decrease in the 2007-2008 period (114). It could be explained by the fact that in 2007, the Vietnamese government passed legislation to force helmet wearing for all users of motorcycles, which was the most widely used personal transport in Viet Nam. However, mortality due to injuries in traffic accidences rose drastically between 2011 and 2013 and varied greatly from 2013 onwards. From 2005 to 2018, the adjusted MRR per year increment demonstrated a slight decline (0.991, 95% CI 0.980, 1.001). This declining trend was, however, non-significant (p = 0.093). The proportion of deaths under 70-year-old was notably high and was consistently above 90% in all years (Table 2).
Mortality Due to Road Traffic Injuries in Men
The estimated proportion of deaths due to road traffic injuries was 4.93% (1,542 cases of road traffic injuries vs. 31,262 total cases) in men. The crude mortality rate varied greatly from a low of 25.2 to as high as 46.4 deaths per 100.000 person-years in 2008 and 2011, respectively. When combining all cases from 2005 to 2018, the age-standardized mortality rate per 100.000 personyears by the WHO-ASR was 33.9. Like the overall trend, male deaths increased from 2005 to 2007 and experienced a sharp decline during the 2007-2008 period, followed by an elevated number of deaths from 2008 onwards. This fluctuation was attributed to the introduction of the helmet-wearing laws in 2007. The per-year increment MRR showed a non-significant declining trend (MRR (95% CI): 0.992 (0.980, 1.003), p=0.158). The proportion of deaths among men under the age of 70 was exceptionally high and was above 95% in almost all the years given (Table 3).
Mortality Due to Road Traffic Injuries in Women
The estimated proportion of deaths due to road traffic injuries was 1.66% (299 cases of road traffic injuries vs. 17,990 total cases) in women. Great variability was noticed within the crude mortality rate and MRR value across different years. However, this change in women was regarded as non-significant (Per-year increment MRR (95% CI): 0.987 (0.961, 1.014), p=0.335), which was similar to the mortality rate in men. After standardizing by age, according to WHO-ASR, the overall mortality rate was 6.7 per 100,000 personyears. Compared with men, the proportion of deaths in women under 70 was lower in general and fluctuated between 74.1 in 2013 and up to 94.1 in 2018 (Table 4).
Age-Specific Mortality Rate
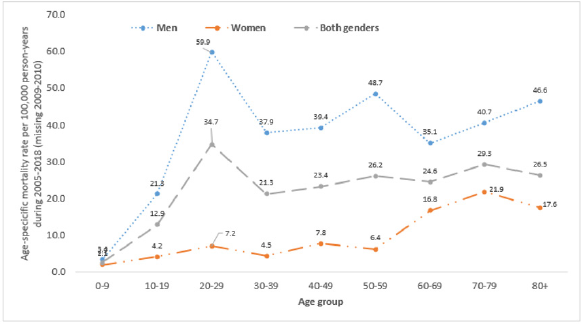
Figure 1 illustrates the trend in the age-strata mortality rate by sex between 2005 and 2018 with the exclusion of 2009-2010 data due to missing reports. Overall, the mortality rate was highest among the 20-29 age group (34.7 deaths per 100.000 personyears), followed by the 70-79 age group (29.3 deaths per 100.000 person-years) and 80+ age group (26.5 deaths per 100.000 personyears). Men accounted for most of the death cases due to injuries by traffic incidences. The death rate in men was highest among the 20-29 age group (59.9 deaths per 100.000 person-years) and remained steadily high (above 30%) from 30-39 age group and older, whereas in females, the rate reached a peak at 70-79 age group (21.9 deaths per 100.000 person-years).
This is the first study to assess the impact of helmet legislation on mortality related to RTC in Lang Son, a mountainous province in Viet Nam. Data were derived from the national health report system in this province under the A6 form. The present study indicated a slightly decreasing trend in road traffic mortality, but it was not statistically significant, after implementing the mandatory motorcycle helmet law. Although most deaths were aged under 70 years old, differences in ages were observed between the sexes. This study found that helmet law in 2007 reduced road traffic mortality from 2007 to 2008, which was statistically significant. However, between 2011 and 2018 there was only a slight decline, and it is seen as non-significant statistically. The efficacy of the mandatory helmet laws was far from expectation in the mountainous area of Lang Son, specifically. The introduction of helmet wearing laws has been proven to enhance road safety, according to studies in countries neighboring Viet Nam Chiu WT, et al. [4,5], and largescale studies both at the national Passmore JW, et al. [2,6,7], and provincial level Ha NT, et al. [8]. However, after 2007, the RTIsrelated death number in Lang Son province showed a slight yet non-significant declining trend among male and female road users.
One study by Ha et al. showed that more severe traffic injuries, including head injuries, were documented during the post-law period Ha NT, et al. [8], which raises questions about the quality of helmets used in the examined region. Using cheap helmets with poor quality and incorrect helmet wearing is common in Viet Nam Passmore JW, et al. [2,10]. Self-awareness of helmet use was also likely to be affected by social norms, safety beliefs, education, and awareness of traffic rules, which are distinctive for each geographical region Phung D, et al. [7], Urie Y, et al. 2016. A review study in Greece proved that the major reasons for noncompliance with the wearing of seat belts and helmets were education and culture Chliaoutakis JE, et al. [11]. Another study in Iran indicated that awareness of traffic legislation and enhancement of safety training towards motorcyclists was the key to helmet use Haqverdi MQ, et al. [12]. Additionally, rural areas might have more RTIs and RTIs-related deaths than modernized areas because of many environmental and cultural factors Chliaoutakis JE, et al. [11,13]. The majority of drivers in mountainous areas are unlicensed and underage Jiang B, et al. [13], which was also regarded as a result of a lack of compliance and policing of the laws. Distance from qualified medical emergency centers was another problem in remote areas, resulting in more deaths as traffic injuries were not treated properly and promptly Jiang B, et al. [13].
The present study also shows that fatalities due to road traffic injuries in men were higher than in women, as reported by previous author’s studies Chiu WT, et al. [4,14,15]. Many studies indicated that alcohol use increases risk among drivers Borges G, et al. [16,17]. In particular, alcohol use was a factor because of the drinking culture in Viet Nam Lincoln M [18]. A study in rural areas of the North of Viet Nam reported that the prevalence of alcohol consumption was 66% among men and 5% among women, respectively Kim BG, et al. [19]. This study has revealed that mortality in men was highest among the 20-29 age group as they are likely to have traffic-related habits, such as risky driving behavior and alcohol consumption Papadakaki M, et al. [20]. Nonetheless, the death rates from 30 to 80+ years of age remained consistently high, irrespective of age group. In contrast, RTIs among females were most prevalent towards the later age group of 70-79. The elderly female population is considered as vulnerable road users. They rarely participated in traffic as direct vehicle users due to the inability to operate a vehicle safely, requiring both physical and mental capability for immediate decisions whilst driving Kim SC, et al. [19].
This study has several limitations. First, the quality of data was unable to be validated due to the nature of secondary data, in particular, such as deaths without reporting by deceased’s relatives. However, the A6 system was proven to be highly reliable for road injury studies Stevenson M et al. 2015; Stevenson M et al. 2012. Secondly, the impact of other factors that may influence mortality rates, such as the availability and readiness, and the quality of the health care system, were not considered, which may distort the findings. However, the present study also suggested a hypothesis regarding the impact of mandatory motorcycle helmet laws on the trend of traffic-related mortality in a mountainous area in Viet Nam. Thirdly, missing data from 2009 to 2010 might not reflect the true effectiveness of helmet-wearing laws implemented in 2007.
The RTIs related annual mortality in Lang Son province decreased slightly but was statistically non-significant, indicating that helmet law implementation in 2007 had little impact on the overall death rates in this area. Therefore, further in-depth studies need to be considered to comprehensively assess the impact of helmet law on death-reducing outcomes in mountainous areas, including feasibility, acceptability, and sustainability.
The authors would like to thank the staff of 200 commune health stations for the time and effort they devoted to this study.
There are no conflicts to disclose.
All authors reviewed the manuscript and contributed revision many times. TTTD, LHP, LVN, NVT, and LTN were mainly responsible for drafting, revision, and analytic data. LHP, LVN, and NVT were principally responsible for data collection. TTTD and LTN extracted data and were mainly responsible for managing and analyzing data. All authors approved the version for publication.