Histological and Histochemical Methods for Staining of Insulin: A Comparative Analysis
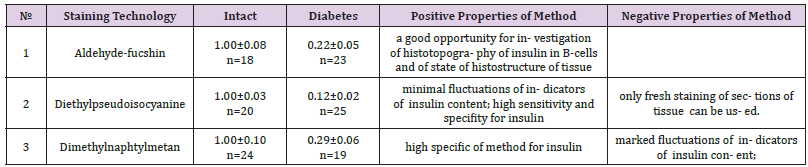
Various histochemical and histological methods are used for analysis of the state of histostructure and of insulin content in pancreatic B-cells. Aim of work: a comparative analysis of the results of using of 3 staining technologies: Aldehyde fucshine, AF, fluorescent diethylpseudoisocyanine method, PS and Dimethylnaphtylmetan, V4 (Victoria 4R, color index 42563). Intensity of fluorescence of A-chair of insulin (PS) measured using of histofluorimetric complex [1]. Calculation of parameter FL= IF1/IF2 where IF2–intensity of fluorescence of intact B-cells (as 1.00) and IF1–B-cells in diabetes. Density of color (AF and V4), parameter DC= DC1/DC2 where DC2-density of color of intact B-cells (as 1.00) and DC1-B-cells in diabetes.
Aldehyde-Fucshine Method
Violet granules in cytoplasm of B-cells correspond to deposited form of insulin [2,3]. Intensity of color of cytoplasm of B-cells directly correspond to insulin content in cytoplasm]. Staining procedures modified by us.
a. Deparaffinization of sections in xylol in 3 portions of xylol;
b. Alcohol 1000-5 min,
c. Alcohol 1000-5 min,
d. Alcohol 800-5 min,
e. Water- 5 min,
f. Oxidation 0,5-2 min oxidation solution: 5 ml of 5% H2SO4+5 ml 2,5% solution of KMnO4+30 ml bidistilled water at +280 elsius -2 min,
g. 2% solution of oxalic acid-rinse until discoloration,
h. Distil. water-5 min,
i. Aldehyde fucshine (“MERCK”; “SERVA”)-5-7 min,
j. Dcidified alcohol 70о №1 – differentiate,,/
k. Acidified alcohol 70о №2 – differentiate,
l. Halmy’s solution-1 min,
m. Distil. water-5 min,
n. Distil. water №2-5 min,
o. Alcohol 1000-5 min,
p. Alcohol 1000 №2-5 min,
q. Xylol - 5 min,
r. Xylol №2 - 5 min,
s. Balm, Result violet color of insulin in B-cells (Figure 1.1) (intact animals; 1.4 in animals with diabetes).
Diethylpseudoisocyanine Fluorescent Method
Schiebler T. and Schiessler S. showed that A chair of oxidized insulin reacted with Diethylpseudoisocyanine chloride with formation of red fluorescent complex which fluoresces in UV light 360-370 nm. We have used modernized method [4,5]. Staining procedures. Preparing of staining solution: 0,4% water solution of Diethylpseudoisocyanine (SERVA, Germany). Staining procedures:
a. Deparaffinization of sections in xylol;
b. Alcohol 900,800,700 1 min in each;
c. Washing in cold water;
d. Oxidation 0,5-2 min; Oxidation solution: 5 ml of 5% H2SO4+5 ml 2,5% solution of KMnO4+30 ml bidistilled water at +280 Celsius;
e. Washing in cold water;
f. 5% solution of oxalic acid -5 sec;
g. Washing in 2 portions of cold water;
h. 0,4% cold solution of Diethylpseudoisocyanine - 20 min in refrigerator at +40Celsius;
i. Washing in cold water 5 min;
j. Store in refrigerator 1,5-3h. Result Intensive red
fluorescence of insulin in B-cells (Figure 1.2) intact animals; 1.5 in animals with diabetes) (Table 1).
Figure 1: Intact animals; 1.6 in animals with diabetes.
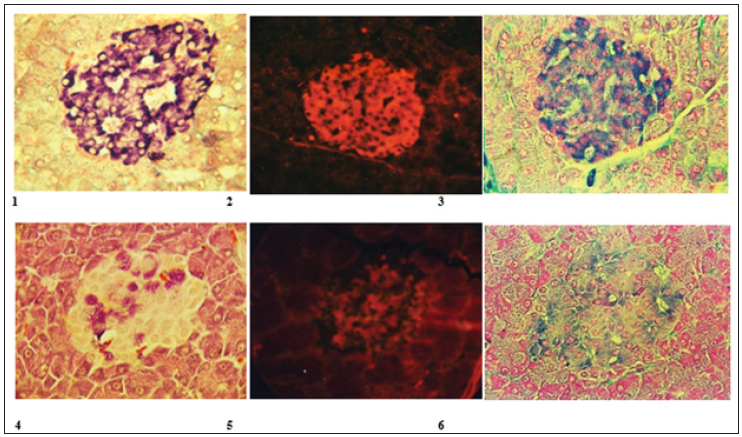
Table 1: Result Intensive red fluorescence of insulin in B-cells (Figure 1.2) intact animals; 1.5 in animals with diabetes).
Victoria Blue 4R Method Staining of Insulin (V4R)
Diphenylnaphthylmetane, colour index 42563; MERCK, Germany; FERAK,Germany). It was showed (8) that V4R aqueous solution interacted with oxidized A-chair of insulin that is accompanied by painting of cytoplasm of В-cells in a blue color proportionally to the amount of insulin [6,7]. Staining procedures:
a. Deparaffinization of sections,
b. Washing in cold water a few min,
c. Oxidation 3-5 min(oxidation solution: 0,3% KMnO4 50 ml+0,3% H24 50 ml; wash sections,
d. Place sections in 2-5% water solution of sodium
bisulphate - 1 min; wash sections,
e. 700 alcohol-1 min,
f. Stain in staining solution (960 alcohol 100 ml+Victoria Blue 4R - 1g) 15 min - 2h; wash sections,
g. Stain on 0,5% water solution of Phloxine 30-120 sec.; wash sections;
h. 5% water solution of phosphor wolframic acid 1-2 min; wash section in water;
i. Stain in 0,5% water solution of Light Green 1-2 min;
j. Dehydratation in 96% alcohol;
k. Balm. Result: blue color of insulin in B-cells; red color of A-cells (Figure 1) (intact animals; 1.6 in animals with diabetes).
The Mechanisms of the Cholinergic Anti-inflammatory Pathway after Acute Intoxication of Organophosphorus Compounds-https://biomedres01.blogspot.com/2020/12/the-mechanisms-of-cholinergic-anti.html
More BJSTR Articles : https://biomedres01.blogspot.com

No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.