Antimicrobial Peptide Brevinin-2isb, New Drug Candidates Enhance the Innate Immune Response and Cured Caenorhabditis Elegans With Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA)
Introduction
Antibacterial peptides(AMPs),which in organisms that defend the body against exogenous pathogen. AMPs are an important part of the body’s immune system, and generally composed of 10-50 amino acid [1]. In recent years, drug resistance has become a research focus in the subject area. Traditional antibiotics such as penicillin are expected to change to new antibacterial peptide drugs [2]. Some AMPs are supposed to solve the problem of drug resistance by pathogenic bacteria [3]. Brevinin-2 is firstly separated from the Japanese bog frog skin [4]. By Dec 31st, 2017, there had been 86 peptides of Brevinin-2 family in Antimicrobial Peptide Database (APD) [5]. the primary structure of Brevinin-2 family has a big difference in its family members. From the Brevinin-2 peptides of the pool frog and belly frog, the gram-negative bacterium Escherichia coli bacteria has inhibitor activity (MIC<10 mmol/L), the gram-positive bacteria Staphylococcus aureus and Candida albicans fungus has inhibitory activity [6-8]. Compared to the Brevinin-1 family, the hemolysis activity of Brevinin-2 family is weak. So Brevinin-2 family as an antibacterial drug candidate spotential [9]. The immune response of C. elegances mediated through the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (PMK-1),transforming growth factorβ(TGF-β), and the DAF-2/DAF-16insulin-like and ZIP-2 pathways (17–20). Recently, antimicrobial peptide Brevinin-2ISb was demonstrated to protect C. elegans. In the present study, we tested the effects of on host immunity and MRSA pathogenicity using the C. elegans infection model with ATCC33591. We further examined the effect of Brevinin-2 family, especially for Brevinin-2ISb has the predominantonhost immunity. Moreover, we a number of mutant lines of C. elegans were utilized to determine the role of various signaling pathways in the Brevinin-2ISb related immune response.
Methods and Results
Determinate Motor Ability of C. elegans
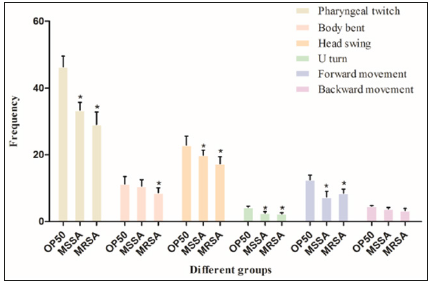
To study the effect of MRSA on nematode movement, Stage L4 larvae were compared among the control group (OP50),the experimental group (MRSA), and the methicillin sensitive Staphylococcus aureus (MSSA) control group on NGM medium. We suggest that MRSA has multiple drug resistance characteristics similar to non-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, such as MSSA. After 3 min, the pharyngeal twitch, head swings, body bending, u turn, forward and backward movement were recorded as athletic ability index. The experiment was repeated 20 times every 30 seconds for statistical analysis. The C. elegans were extracted from NGM medium after 3 min, and placed with OP50 on as and surface. The trajectory of the nematode was clearly visible as a sine curve. In the presence of MSSA, nematode movements were limited to a certain extent; the number of pharyngeal twitches, u turn, and forward movements were significantly decreased. In the presence of MRSA, the trajectory of C. elegans irregular sine curve peaks decreased. Motor ability was significantly reduced, with the exception of backward movement. Both kinds of S. aureushad an obvious effect on the movement abilities of C. elegans, especially MRSA (Figure 1). Each experiment was repeated three times.
Effects of Brevinin-2isb on the Longevity of Nematodes
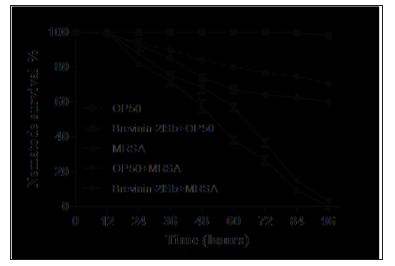
The longevity of nematode is a main basis for the study of aging process. The effects of minimum inhibitory concentration Brevinin- 2ISb on the longevity of nematode were compared. Brevinin-2 ISb was dissolved in NGM plate and survival data were obtained at 12, 24, 36, 48,60,72,84 and 96 hours respectively. The survival rate of OP50 nematode in control group was compared. Survival curves of nematodes were plotted for the whole life cycle (Figure 2). The results showed that the minimum inhibitory concentration Brevinin-2ISb could make the survival curves of nematodes move up. Compared with the control group (OP50), the average and maximum longevity of nematodes in Brevinin-2ISb group were significantly prolonged, and the average longevity of nematodes in Brevinin-2ISb group was higher (more than 20%) than that in the control group. Each experiment was repeated three times.
Figure 1: Motor ability of C. elegans in different groups.
Note: From left to right: number of pharyngeal twitch, body bent, head swing, u turn, forward, and backward movements. Compared with group OP50* means p<0.05
Figure 2: The survival of Caenorhabditis elegans (C.elegans) assessed. Staphylococcu saureus strain Brevinin-2ISb and Staphylococcus aureusstrain ATCC33591 (MRSA) were compared to Escherichia coli(OP50) as a control group.
Brevinin-2isb Protect C. elegans from MRSA Infection
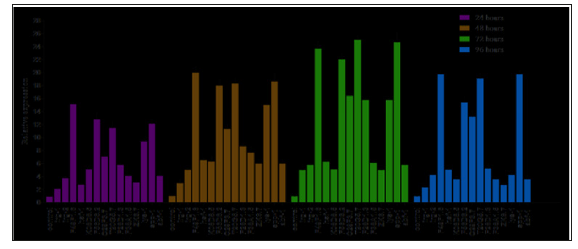
To verify the anti-infective therapeutic potential of Brevinin- 2ISb, a screening in 12-well plates was performed with MRSA–C. elegans. Brevinin-2ISb were screened and demonstrated increased survival rates of MRSA-infected nematodes (Figure 3). Brevinin- 2ISb peptides contributed to a survival rate of more than 60% and increased the survival rate after 96 h compared to control group. The living worms were fed on E. coli OP50 during the assay. Brevinin-2ISb antimicrobial peptides identified above significantly affected nematode survival (Figure 4).
Figure 3: The survival of MRSA-infected C. elegansassessed by liquid-based assayusing Brevinin-2 family peptides.
Figure 4: The relative gene expression of immune response genes in C. elegans after treatment with four Brevinin-2 family peptides. Compared with control group OP50, all treatment groups p<0.05 or p<0.001.


No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.