Pharmacological Evaluation of Gentiana Kurroo Plant Extracts Against Alzheimer’s Disease
Introduction
Alzhemier’s disease (AD) is one of the most common neurodegenerative disease. It is characterized by progressive neuronal loss and accumulation of proteins including extracellular amyloid plaques (Aβ) and intracellular tau tangles (neurofibrillary tangles, NFT) [1]. It is the major cause of dementia affecting millions of elderly people across the world [2]. An estimated 5.7 million Americans suffer from Alzheimer’s dementia. By mid-century, the number of people living with Alzheimer’s dementia in the United States is projected to grow to 13.8 million (Alzheimer’s Association Report). According to World Health Organization (WHO) estimation, 71% of 81.1 million dementia cases will be reported by 2040 [3]. AD mainly targets the brain. It leads to impairment of cognitive function. In AD neurons finally get damaged. Furthermore, the neurons which are responsible to carry out basic bodily functions also get damaged [4]. The etiology of this disease is multifactorial [5]. Many different hypothesis have been given from time to time to elucidate the causative factors of this disease, in order to explain the multifactorial nature of disease, such as cholinergic hypothesis, Aβ hypothesis, tau hypothesis, oxidative stress hypothesis and inflammation hypothesis [6]. Currently only approved treatments by US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), includes five drugs that are used to treat the cognitive manifestations of AD.
Acetylcholiesterae inhibitors AChEIs-rivastigmine (Exelon), galantamine (Razadyne, Reminyl), tacrine (Cognex), and Donepzil (Aricept) and NMDA receptor antagonist-memantine (Namenda) that target symptoms at its best [7]. Reminyl, Exelon and Aricept are effective in the early stages of treatment. Each drug has different mechanism of action and a different way to decrease the breakdown of acetylcholine which is an important neurotransmitter in the brain [8]. In AD there is a decreased level of this neurotransmitter. Memantine (Namenda) is the only drug which is shown to be effective at the later development of the disease [9,10]. To date, established treatments are only symptomatic in nature, trying to counterbalance the neurotransmitter disturbance of the disease. All the treatments suffer from various side effects [11]. Novel strategies have been developed to modify the disease process. In this regard major development is targeted to the Aβ and tau-based therapeutics, which is a major key to unlock this disease soon [12]. New approaches to develop drugs for the treatment of AD that prevent free radical production and hence neurodegeneration, including AGE-inhibitors, antioxidants and anti-inflammatory substances are being emphasized [13]. The development of diseasemodifying drugs for AD is recognized as a worldwide necessity [14].
Natural products and herbal remedies have been a source of many beneficial drugs. About 80% of the world’s population is dependent on plant-based medicines [15]. Herbal mixtures might have advantages as they have multiple target approach as compared with the single target. Herbal therapy can be a novel treatment option for AD. Phytotherapy may be a potential corner stone based on which treatment strategies can be streamlined [16]. There is evidence which suggest that herbs or herbal formulations may provide complementary cognitive benefits to the approved drugs, however due to various methodological limitations, their use alone, it remains inconclusive. As many drugs are available today for treatment of AD, various plant and their extracts are extensively employed in vivo models and AD patients. Herbal extracts produce a diverse range of natural products which includes alkaloids, indoles, phytosterols, isoflavonoids which exhibit complex pharmacological properties [17]. Plants provide wealth of bioactive compounds, which exert a substantial strategy for the treatment of neurological disorders such as Alzheimer’s disease [18]. Plants with traditional knowledge of antioxidant and anti-alzhemeric activity have been studied [19].
Ethnomedicine is a promising field of research in Kashmir, as varied medicinal and aromatic plants including those used in curing various diseases, are grown in Kashmir. Gentiana kurroo belonging to family Gentianaceae and is a critically endangered (CR) medicinal plant species. It is endemic to the northwestern Himalayas. The rootstock of the plant is used in various ailments like fevers and urinary disorders. It is also used as a bitter tonic, antiperiodic, expectorant, antibilious, astringent, stomachic, antihelminthic, blood purifier, and carminative [20]. Several researchers have carried out experimental work to validate the folkloric use of the medicinal plant for different ailments like antibacterial, antioxidant, anti-arthritic, anti-inflammatory, analgesic activities and antidiabetic activity [21]. Present pharmacological study was to prove the activity of Gentiana kurroo extracts on Alzhemier’s diseases. Results of various studies had shown that positive effect to treat the disease.
Materials and Methods
In this study, analytical grade chemicals were used and procured from standard commercial sources. Chloroform, sulphuric acid, ferric chloride, sodium hydroxide and Glacial acetic acid were purchased from Central Drug House (CDH). Picric acid, Methanol, Ethanol, Ascorbic acid, were obtained from Merk. Hydrochloric acid, Hexane and ethyl acetate were purchased from Rankem.
Plant Material and Samples Preparation
Gentiana kurroo was collected from Khrew, Kashmir and identified in the Centre of Plant Taxonomy (COPT) under Vocher No. 2466-KASH. The whole plant material was collected, dried and pulverized into coarse powder and extracted successively using hexane, ethyl acetate, methanol, ethanol respectively by soxhlet extraction. The solvents could evaporate in a rotary evaporator at 40 ºC-45 ºC, and the extracts obtained were stored in a refrigerator at 4 ºC. The plant extracts were solubilised in their respective solvents. The entire study was conducted using single batch of each plant extract to avoid batch-to-batch variation and maximize the product constancy.
Phytochemical Screening
Qualitative analysis of different phyto constituents in different plant extracts was done by various reported and standard methods [22].
Effect of GKME on Scopolamine-Induced Memory Impairment in the Elevated Plus Maze (EPM) Test
Experimental Animals
Animals: Swiss albino mice weighing 25-35g were used in this study. Animals were housed in plastic cages in groups. They had free access to food and water, and they were kept in a regulated environment (23ºC, 40–60% humidity). Experiments were carried out between 9:00 am and 5:00 pm, in an experimental room with in the animal facility. All animal procedures were conducted in strict under the rules of ethical committee. The study was approved by the Ethical Committee of Kashmir University under Registration No. KU/2015/09, dated 21-08-2015.
Acute Safety of Plant Extracts
The effect of plant extracts on general behavior and safety was evaluated in mice according to Organization of Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) Guideline No. 425. Mice of either sex (three females and three males) were administered with single doses of 2000 mg/kg of GKME orally by gavage. The animals were observed continuously for 4 hours after dosing, for any toxic symptoms. The number of survivors was noted after 24 hours and the animals were kept under observation for further 13 days. Any changes in general behavior, weight, mortality or other physiological activities were observed.
Dosage and Treatment
Animals were divided into four groups each of six animals.
a) Group I: Control group oral administered by CMC (Carboxy methyl cellulose).
b) Group II: Animals oral administered by scopolamine hydro Chloride which is dissolved CMC (Negative control).
c) Group III: Animals oral administered by Donepzil.
d) Group IV: Animals oral administered by extract which is dissolved in CMC (100mg/kg) and Alzheimer’s induced with Scopolamine
e) Group IV: Animals oral administered by extract which is dissolved in CMC (200mg/kg) and Alzheimer’s induced with Scopolamine.
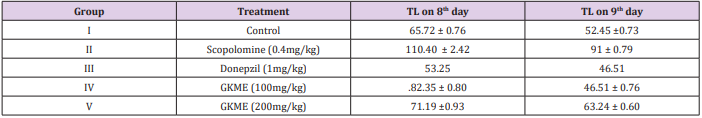
Elevated plus-maze served as the exteroceptive behavioral model to evaluate memory in mice. The procedures, technique and endpoint for testing memory were followed as per the parameters described by the investigators working in the area of psychopharmacology. The elevated plus maze for mice consisted of two open arms (16cm×5cm) and two covered arms (16cm×5cm×12cm) extend from a central platform (5cm×5cm), and the maze was elevated to a height of 25cm from the floor. On the first day (i.e. eighth day of drug treatment), each mouse was placed at the end of open arm, facing away from the central platform. Transfer latency (TL) was defined as the time (in seconds) taken by the animal to move from the open arm in to one of the covered arm with all its four legs. TL was recorded on the first day (training session) for each animal. The mouse could explore the maze for another 2 minutes and then returned to its home cage. Retention of this learned task (memory) was examined 24 hours after the first day trial (i.e. ninth day, 24 hours after last dose). Donepzil was used as positive control.
Statistical Analysis
All the experiments were performed in triplicates and the mean values ± standard deviations (SD) are represented. Statistical differences between control and target groups for all experiments were determined using the analyses of variance (ANOVA). Statistical differences were considered significant at ‘p’ value less than 0.05.
Results
Phytochemical Screening of Gentiana Kurroo Extracts
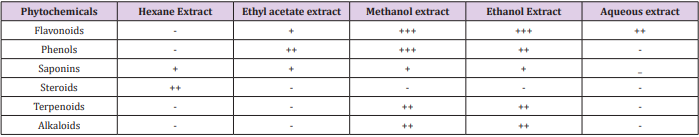
Gentiana kurroo also contained maximum phyto constituents in polar solvent extracts, as shown in Table 1. The results show the presence of maximum content of flavonoids in methanol and ethanol extracts followed by aqueous and ethyl acetate extracts. Maximum content of phenols was present in methanol extract followed by ethanol and ethyl acetate extracts. Saponins were present in all the extracts except aqueous extract. Hexane extract contained maximum amount of steroids whereas aqueous extract tested negative for steroids whereas rest of the extracts were negative for steroids. Terpenoids were found to be present in maximum amounts in methanol and ethanol extracts whereas other extract did not show the presence of terpenoids.
Acute Toxicity Study
The effect of plant extracts on general behavior and safety was evaluated in mice. Mice of either sex (three females and three males) were administered with single doses of 2000 mg/kg of GKME orally by gavage. The animals were observed continuously for 4 hours after dosing, for any toxic symptoms. The number of survivors was noted after 24 hours and the animals were kept under observation for further 13 days. Any changes in general behavior, weight, mortality or other physiological activities were observed. In acute toxicity study, no adverse effects or mortality were observed after administration of single dose of 2000mg/kg body weight of GKME No adverse effects or mortality were observed after administration of single dose of 2000mg/kg body weight of GKME. No behavioral changes were observed in mice during the entire period of experiment. However, taking into consideration the efficacy of any drug, lower doses up to 200mg/kg body weight were selected for further in vivo studies.
Acute Toxicity Study
The effect of plant extracts on general behavior and safety was evaluated in mice. Mice of either sex (three females and three males) were administered with single doses of 2000 mg/kg of GKME orally by gavage. The animals were observed continuously for 4 hours after dosing, for any toxic symptoms. The number of survivors was noted after 24 hours and the animals were kept under observation for further 13 days. Any changes in general behavior, weight, mortality or other physiological activities were observed. In acute toxicity study, no adverse effects or mortality were observed after administration of single dose of 2000mg/kg body weight of GKME No adverse effects or mortality were observed after administration of single dose of 2000mg/kg body weight of GKME. No behavioral changes were observed in mice during the entire period of experiment. However, taking into consideration the efficacy of any drug, lower doses up to 200mg/kg body weight were selected for further in vivo studies.
Effect of GKME on Scopolamine-Induced Memory Impairment in the Elevated Plus Maze (EPM) Test
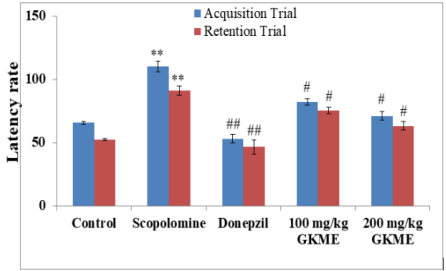
The elevated plus maze for mice consisted of two open arms (16cm×5cm) and two covered arms (16cm×5cm×12cm) extend from a central platform (5cm×5cm), and the maze was elevated to a height of 25cm from the floor. On the first day (i.e. eighth day of drug treatment), each mouse was placed at the end of open arm, facing away from the central platform. Transfer latency (TL) was defined as the time (in seconds) taken by the animal to move from the open arm in to one of the covered arm with all its four legs. TL was recorded on the first day (training session) for each animal. The mouse was allowed to explore the maze for another 2 minutes and then returned to its home cage. Retention of this learned task (memory) was examined 24 hours after the first day trial (i.e. ninth day, 24 hours after last dose). Significant reduction in the TL value of retention indicated improvement in memory. However, this decreased spontaneous alteration behaviour induced by scopolamine was significantly inhibited by GKME at 200 mg/kg (Figure 1 and Table 2).
Figure 1: Effect of GKME on scopolamine-induced memory impairment in rats using the elevated plus maze (EPM) test. Data are expressed as mean latency time (s) ± S.E.M. *Significant difference (** P < 0.05 in comparison to the respective trial of the control group. #Significant difference (#P < 0:05 and ##P < 0:01) in comparison to the scopolamine group.
Discussion
The present study demonstrated memory enhancing potential of GKME against scopolomine induced memory impairments. Scopolamine-induced amnesia has been used extensively to study the effect of compounds with propensity to be developed as therapeutic agents for dementia of AD type. Moreover, the cognitive impairment produced following scopolamine administration resembles the memory impairment seen in AD. Toxicology studies are very important to evaluate the safety of a drug in animals to decide if the drug could be safe for human use or not. Most of the plants and herbs used as food are also used in folk medicine for treatment against various ailments. These herbs are currently one of the main sources of drug discovery, but only few of them have been scientifically investigated for their toxic effects [23]. Acute toxicity studies in animals are important for any intended pharmaceutical use in humans. It is necessary for determining the safe doses. It could also be used to estimate the therapeutic index of drugs [24]. In current study, acute toxicity test was done to check if the administration of the methanol extracts of Gentiana kurroo (GKME) has any adverse effects on any parameter. The results of the study indicate no abnormal symptoms and no death of the tested rats. Change in body weight is regarded as an indicator of adverse effects of any drug [25,26]. The results revealed that single dose administration of GKME did not cause any significant changes in the general behavior and body weight of rats.
Scopolomine also known as levo-duboisine, and hyoscine, is an alkaloid drug with muscarinic antagonist effects. It is basically the secondary metabolite derived from plant from family Solanaceae (nightshade) family of plants. It act as a competitive antagonist at muscarinic acetylcholine receptors, specifically M1 receptor [27]. It is used as a standard drug for inducing amnesia in animals [28]. It affects behaviour, learning and memory. The exteroceptive behavioral model such as elevated plus maze was used to evaluate the learning and memory, whereas scopolamine being the natural ageing inducing amnesia served as interoceptive models [28]. Scopolamine significantly decreased the spontaneous aiteration behavior compared with control group. However this decreased spontaneous alteration behaviour induced by scopolamine was significantly inhibited by GKME.
Conclusion
The effect Gentiana kurroo on scopolamine-induced memory impairment in mice was also studied via the elevated plus maze (EPM) test. The methanol extract of Gentiana kurroo extract when administered orally improved learning and memory of mice. Alzheimer’s disease is a neurodegenerative disorder currently without an effective treatment. Impairment of memory is the initial and most significant symptom of AD. AD is associated with a decline in cognitive abilities. In the present study, Gentiana kurroo extract (100mg/kg and 200mg/kg) administered orally improved learning and memory of mice assessed by the behavioral models like elevated plus maze.
More BJSTR Articles : https://biomedres01.blogspot.com/

No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.