The Potential Efficacy of Broussonetia Kazinoki Stem Extract to Show Antioxidant Property or Suppress Collagenase Activity
Introduction
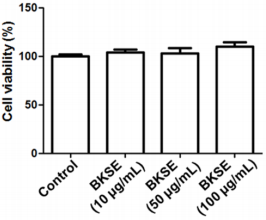
Broussonetia Kazinoki (Siebold) is a kind of tree belonging to the Rosaceae family. It grows mainly in the mountain side of the shore but has been cultivated many times in recent years. The bark is the material that makes the paper, and the fruit and stem are used as a medicinal material, and the young leaves are eaten [1-4]. According to the ancient Chinese medicine book, the leaves of B. kazinoki are effective in the treatment of edema, and the stems of B. kazinoki can be used for the treatment of symptoms such as rubella and poor urination. In this study, we report novel efficacy of B. kazinoki stem extract (BKSE) to show antioxidant property or inhibit collagenase activity. Antioxidants are a very important means of protecting the living body by eliminating the toxic effects of active oxygen [5]. If the living body cannot adequately remove active oxygen due to lack of antioxidants, various diseases and aging progress rapidly. Antioxidant enzymes naturally present in the human body include superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione and peroxidase [5]. First, we investigated whether BKSE displays a cytotoxic effect on human kidney epithelial cells (HEK-293T). Cytotoxic effect by BKSE on HEK-293T cells was not observed, suggesting that BKSE does not have a negative effect on human cells (Figure 1). The DPPH (1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl) radical scavenging assay provides an easy and rapid way to evaluate potential antioxidants. Our DPPH radical scavenging assay suggests that BKSE has an excellent effect on removing DPPH free radicals (Figure 2). Therefore, our results suggest that BKSE has excellent antioxidant activity.
Figure 1: HEK-293T cells were treated with BKSE (0– 100μg/mL), and cell viability at 24h was determined using the MTS colorimetric assay. Error bars represent SD from three biological replicates.
Figure 2: DPPH radical scavenging assay using BKSE (5.5mg/mL). Ascorbic acid was used as a positive control. Error bars represent SD from three technical replicates.
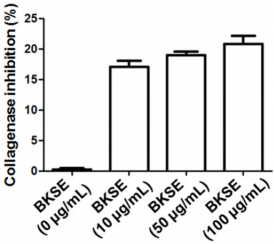
Collagenase is an enzyme of the matrix metalloproteinase family that breaks down collagen and destroys extracellular matrix [6]. Collagen is an abundant structural protein present in animals. Collagenase has a direct effect on skin elasticity and wrinkles through the breakdown of collagen that makes up the skin cell connective tissue. We investigated whether BKSE inhibits collagenase activity. The results showed that BKSE is able to effectively inhibit collagenase activity (Figure 3). BKSE can inhibit the activity of collagenase to properly maintain the collagen content of the skin, thereby adding the elasticity of the skin. Therefore, this work suggests that BKSE can be used as a natural product to prevent wrinkle formation in the skin. In conclusion, BKSE shows excellent antioxidant activity and inhibits collagenase activity. These results indicate that BKSE might be used a raw material for cosmetics to suppress skin wrinkles.
Figure 3: BKSE inhibits collagenase activity in vitro. Collagenase inhibition activity assay was performed using Enzchek collagenase assay kit following the manufacturer’s instruction. Error bars represent SE from three technical replicates.
Materials and Methods
MTS (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-5-(3-carboxymethoxyphenyl)- 2-(4-sulfophenyl)-2H tetrazolium) assay in HEK-293T cells. The B. kazinoki stem was dried and extracted using EtOH (70 %) for 24 hours. The MTS assay was performed as described previously [7]. Briefly, the cells were seeded in a 96-well (2 × 104 cells/well) and treated with different doses of BKSE for 24 h. After incubation, 20μL of the MTS working solution (2 mg/mL in PBS) was added to each well and incubated at 37°C for 4h. Absorbance at 490nm was measured using a microplate reader (PerkinElmer) and cell viability was determined as the percentage of MTS reduction, assuming the absorbance of control cells as 100%.
DPPH Radical Scavenging Assay
DPPH radical scavenging assay was performed as described previously with minor modifications [7]. Briefly, the reaction mixture contained 100μL of BKSE and 0.1 mM DPPH solution. The mixture was incubated for 30 min at 37°C, and then the activity was measured spectrophotometrically at 517nm. The blank was 100 % (v/v) ethanol. DPPH scavenging effect was calculated using the following equation:
DPPH scavenging effect (%) = {(A0-A)/A0} X 100.
Where A0 is the absorbance of negative control (0.1 mM DPPH solution) and A is the absorbance in presence of BKSE.
Collagenase Inhibition Activity Assay
Collagenase inhibition activity assay was performed using EnzChek Collagenase Assay Kit (Molecular Probes) following the manufacturer’s instruction.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Ministry of Trade, Industry & Energy (MOTIE), Korea Institute for Advancement of Technology (KIAT) through the Encouragement Program for The Industries of Economic Cooperation Region.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
For more Articles: https://biomedres01.blogspot.com/




No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.