Ultrasonic Frame of Reference for the Downward Displacement of the Posterior and Anterior Leaflets of the Tricuspid Valve in Children
Introduction
In downward displacement of the tricuspid valve [1], displacement of the septal and posterior valves is most common; however, the anterior tricuspid valve can also be moved downward [2]. During ultrasound, the root of the mitral valve in the apical fourchamber view of Ebstein malformation can be used as a reference structure for the downward movement deformity of the tricuspid septal valve [3]: however, there is a lack of reference structures for the downward movement deformity of the posterior and anterior tricuspid valves. Thus, the aim of this study was to evaluate the tricuspid annulus and inferior margin of the coronary sinus were as reference structures for posterior tricuspid valve downward movement. In addition, we aimed to evaluate two-chamber and four-chamber view tricuspid annulus as reference structures for anterior valve downward movement malformation, as well as exploring the reference structure for evaluating the degree of posterior and anterior tricuspid valve downward displacement.
Methods
Selection and Description of Patients
From May 2005 to April 2019, all children with tricuspid valve downward displacement diagnosed by echocardiography in our hospital were selected as study participants. Exclude children with unclear diagnosis. Of them, 18 were male and 24 female patients, aged between 7 months and 15.9 years, with a median age of 3 years and 10 months. Of the 42 total patients selected, 40 also exhibited atrial septal defect. Among them, two cases were further complicated with ventricular septal defect, one with pulmonary valve stenosis, one with ventricular septal defect and pulmonary valve stenosis, and one with single atrium and pulmonary valve stenosis. Two cases were not complicated with any congenital heart disease deformities. These complications are summarized in Table 1.
Table 1: Clinical Information.
Note: ASD: atrial septal defect; VSD: ventricular septal defect; PS: stenosis of pulmonary valve; SA: single atrium
Research Methods
Research Methods
Note: RV right ventricle; RA right atrium
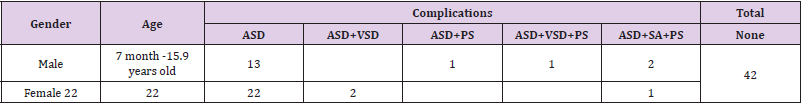
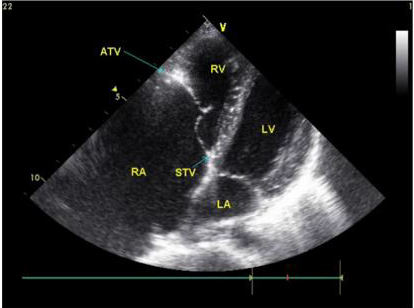
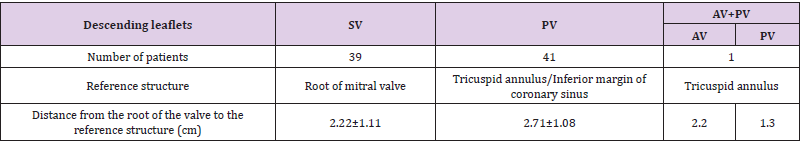
Figure 1: The apical four-chamber view showing that the arrow points to the front of the tricuspid valve annulus. A is the attachment point of the anterior tricuspid valve on the annulus. In the picture, the anterior tricuspid valve is attached to the anterior part of the tricuspid annulus, and the position is normal.
Table 2: Number of patients with different leaflets moving.
Note: SV: Septal valve; PV: Posterior valve; AV: Anterior valve.
Ethical approval was granted by the medical ethical committee of The First Affiliated Hospital of Gannan Medical University with the following reference number: LLSC-202105401. All study participants provided oral informed consent. The tricuspid septal and anterior valves were displayed by echocardiography in the apical four-chamber section, using the ultrasonic examination instrument Philips EPIQ7C and GE VIVID7 (Philips, Amsterdam, Netherlands), with a probe frequency of 3–8 MHz. The descending degree of the tricuspid septal valve was evaluated according to the position of the anterior mitral valve attached to the intracardiac septum, and the size of the atriated right ventricle and right ventricular cavity was observed. The apical four-chamber probe was then rotated about 45° clockwise to make the left atrium, left ventricle, and interventricular septum disappear gradually, exposing the right atrium, right ventricle, and right ventricular posterior wall. The shape, activity and position of the anterior valve of the anterior wall of the right ventricle and the posterior valve of the posterior wall of the right ventricle were observed, the tricuspid annulus and coronary sinus were displayed, and the distance between the attachment point of the posterior tricuspid valve, the inferior edge of the tricuspid annulus, and the inferior edge of the coronary sinus was measured. The apical four-chamber and right cardiac two-chamber views were used to evaluate the downward movement of the anterior tricuspid valve using the tricuspid annulus as the reference structure (Figure 1). The location of tricuspid regurgitation was revealed by color doppler ultrasound (Table 2).
Results
Note: ATV the anterior tricuspid leaflet; STV the septal tricuspid leaflet; RV right ventricle; RA right atrium; LV left ventricle; LA left atrium
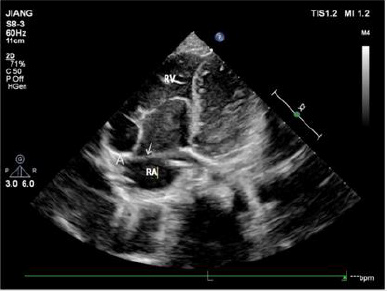
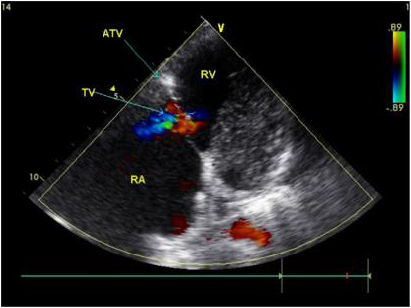
Figure 2: The apical four-chamber view showing that the position of the septal leaflet of the tricuspid valve is significantly lower than the root of the mitral valve during systole.
Note: ATV the anterior tricuspid leaflet; STV the septal tricuspid leaflet; RV right ventricle; RA right atrium; LV left ventricle; LA left atrium.
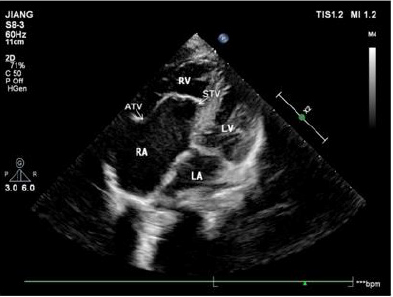
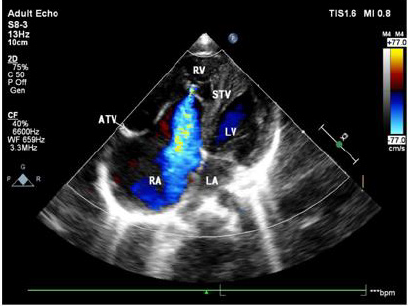
Figure 3: The apical four-chamber view showing that the position of the septal leaflet of tricuspid valve is significantly lower than the root of the mitral valve during diastole.
In 42 patients with Ebstein malformation, the septal and posterior valves moved downward simultaneously in 39 patients; the simple septal valve moved downward in one case; the posterior and anterior valve moved downward at the same time in one case; and the septal, posterior, and anterior valves moved downward simultaneously in one case. Aside from two patients with tricuspid septal and posterior valve downward movement and partial slight downward movement of anterior valve, ultrasound was consistent with the results of operation. Ultrasound showed downward displacement of the tricuspid septal valve in 41 patients (Figures 2 & 3). Aside from two patients in which downward movement of the tricuspid septal valve was so severe that the distance between the tricuspid valve and the root of the mitral valve could not be measured, the attachment point of the tricuspid septal valve was 2.22 ±1.11 cm from the root of the mitral valve in 39 patients.
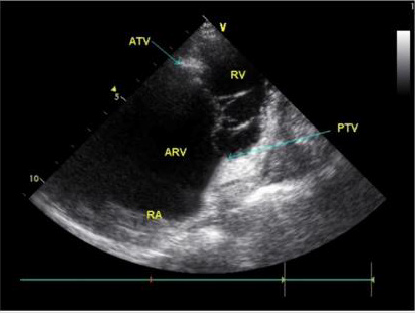
Note: PTV posterior tricuspid leaflet; ATV anterior tricuspid leafle;ARV atrialized right ventricle ;RV right ventricle ;RA right atrium
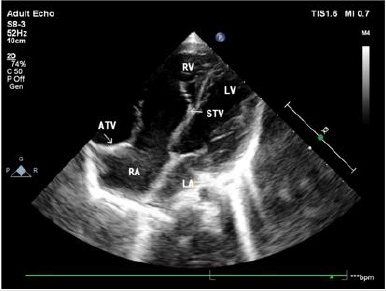
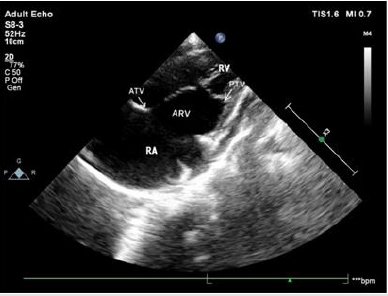
Figure 4: Apical right heart two-chamber view showing that the posterior tricuspid leaflet moves down from the tricuspid annulus and lower edge of the coronary sinus to the apex. The position of the anterior tricuspid leaflet is normal, and the leaflet is elongated.
Note: PTV posterior tricuspid leaflet; ATV anterior tricuspid leaflet; ARV atrialized right ventricle; RV right ventricle; RA right atrium
Figure 5: Right ventricular inflow tract view showing that the posterior tricuspid leaflet moves down from lower edge of the coronary sinus to the apex. The position of the anterior tricuspid leaflet is normal, and the leaflet is elongated.
Note: ATV the anterior tricuspid leaflet; STV the septal tricuspid leaflet; RV right ventricle; RA right atrium; LV left ventricle; LA left atrium
Figure 6: The apical four-chamber view showing that the anterior tricuspid leaflet moves down significantly, and the position of the root of the septal tricuspid leaflet is normal.
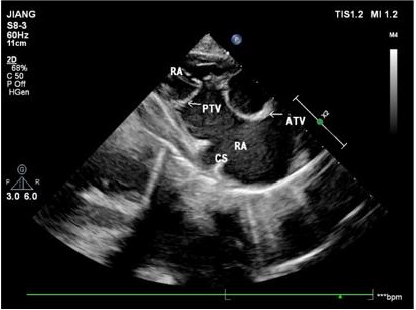
Note: PTV posterior tricuspid leaflet; ATV anterior tricuspid leaflet; ARV atrialized right ventricle; RV right ventricle; RA right atrium
Figure 7: Apical right heart two-chamber view showing downward motility of the anterior tricuspid leaflet and the posterior tricuspid leaflet positions.
Table 3: Distance of downward movement of different valves.
Note: SV: Septal valve; PV: Posterior valve; AV: Anterior valve.
Ultrasound also showed downward movement of the posterior tricuspid valve in 41 patients with reference to the tricuspid annulus or the inferior edge of the coronary sinus in the view of the inflow tract of the right ventricle and the right ventricle (Figures 4 & 5). Aside from the severe downward movement of the posterior tricuspid valve reaching the cardiac apex that could not be measured in three patients, the distance between the root of the posterior tricuspid valve and the inferior edge of the tricuspid annulus or inferior margin of coronary sinus was 2.71 ±1.08 cm in 38 patients. In one patient, downward movement of the anterior and posterior tricuspid valves, was confirmed by both operation and ultrasound. Ultrasound showed that the position of the anterior tricuspid valve had moved downward in the apical four-chamber section (Figure 6), which was 2.2 cm away from the tricuspid annulus, and that the anterior tricuspid valve was attached to the anterior wall of the right ventricle. The two-chamber view of the apical right heart showed the downward movement of the posterior tricuspid valve (Figure 7), and the distance from the tricuspid annulus was 1.3 cm (Table 3).
Note: ATV the anterior tricuspid leaflet; STV the septal tricuspid leaflet; RV right ventricle; RA right atrium
Figure 8: Color Doppler showing that the orifice position of the tricuspid regurgitation (blue shunt) has downward direction, and that the direction of the TR flow has an anterolateral bias in patients with downward displacement of the anterior leaflet in the apical four-chamber view.
Note: ATV the anterior tricuspid leaflet; STV the septal tricuspid leaflet; RV right ventricle; RA right atrium; LV left ventricle; LA left atrium
Figure 9: Color Doppler in the apical four-chamber view showing that the orifice position of the tricuspid regurgitation (blue shunt) has significant downward motility.
The right atrium was significantly enlarged, the atriated right ventricle was located on the anterolateral side, and the anterior lobe of the tricuspid valve was not obviously lengthened. The apical four-chamber section showed that the tricuspid septal valve was in the exact position. Color Doppler confirmed that the position and direction of the tricuspid regurgitation orifice had shifted to the anterolateral side of the anterior tricuspid valve (Figure 8). Color Doppler ultrasound showed that the position of the tricuspid regurgitation orifice was significantly decreased in 42 patients (Figure 9).
Discussion
In the apical four-chamber ultrasound section, the downward movement of the anterior tricuspid valve shows that the septal valve of the tricuspid valve moves away from the root of the mitral valve, but the reference structure of the posterior and anterior tricuspid valve is rarely reported. All the three valvular lobes of tricuspid valve are attached to tricuspid annulus, while the tricuspid annulus is a cardiac fibrous scaffold structure composed of dense connective tissue. Ultrasound shows hyperechoic light band, and the coronary sinus is located above the tricuspid annulus [4]. The posterior tricuspid valve is distant from the tricuspid annulus in the two-chamber view of the apical right heart [5]. In this study, in 40 children with posterior tricuspid valve displacement, the downward movement of the tricuspid valve was evaluated by ultrasound in the view of the apical right cardiac chamber and the inflow tract of the right ventricle, with the tricuspid annulus and the inferior edge of the coronary sinus as reference structures. Results were confirmed by operation. It is suggested that the downward displacement of the posterior tricuspid valve can be well evaluated by taking the tricuspid annulus and the inferior edge of the coronary sinus as reference structures in the two- chamber view of the right portion of the apical heart.
Downward movement of the anterior tricuspid valve is rare. When the anterior tricuspid valve moves downward, the anterior tricuspid valve is distant from the tricuspid annulus. Ultrasound shows that the tricuspid annulus has a strong echo band, which can show the downward movement of the anterior tricuspid valve. Of the two children with anterior tricuspid valve displacement in this study, one case showed that the anterior tricuspid valve moved away from the tricuspid annulus in the apical four-chamber and two-chamber views of the right heart. The ultrasonic diagnosis of the downward displacement of the anterior tricuspid valve was consistent with the results of the operation. In the other case, the downward movement of the septal and posterior tricuspid valves was diagnosed by ultrasound, and it was found that in addition to the downward movement of the septal and posterior tricuspid valves, there was also a slight downward movement of the anterior valve, which may have resulted from the large area and three-dimensional structure of the anterior tricuspid valve. Among them, part of the slight downward movement of the structure was not related to the change of hemodynamics. The position of the tricuspid annulus attached to the anterior tricuspid valve is sometimes difficult to display. Ultrasound can be expected to show a strong echo light band between the right atrium and the right ventricle from multiple angles, such as the apical four-chamber section, the right cardiac two-chamber section and the right ventricular inflow tract. Detailed attention is required to observe whether the anterior tricuspid valve is attached to the anterior position of the tricuspid annulus. In this study, the ultrasound of one patient with downward displacement of the anterior tricuspid valve showed that there was a hyperechoic light mass in the anterior tricuspid valve attached to the anterior wall of the right ventricle on the apical four-chamber section, which may have been caused by the myocardial echo contrast of the implantation of the root of the anterior tricuspid valve into the anterior wall of the right ventricle. It is suggested that the implantation a of strong echo light mass at the root of the anterior tricuspid valve into the anterior wall of the right ventricle may have been a sign of the downward movement of the anterior tricuspid valve in the apical four-chamber section.
The area of the anterior tricuspid valve was the largest among the three valves, and it was semicircular, accounting for 2/3 of the function. The hemodynamic changes of the downward movement of the anterior tricuspid valve were significantly greater than those of the other two valves, the right atrium was significantly enlarged, the atrial right ventricular wall had become thinner, and cardiac function was poor. Obvious enlargement of the right atrium must sometimes be distinguished from the right atrial aneurysm when the tricuspid annulus and the anterior tricuspid valve move downward at the same time. When the anterior tricuspid valve moved downward in this study, the position of the tricuspid annulus was normal, and only the anterior tricuspid valve moved downwards. The strong echo light mass at the root of the anterior tricuspid valve was implanted into the anterior wall of the right ventricle, and color Doppler showed that the direction of tricuspid regurgitation shifted to the anterolateral direction. This may also have been a sign of downward movement of the anterior tricuspid valve.
The downward movement of the tricuspid valve is more common with downward movement of the tricuspid septal valve, posterior valve, and the lengthy and increased amplitude of the anterior tricuspid valve [6,7]. It is rare that the position of anterior and posterior tricuspid valve is downward, and the position of septal valve is normal, but no matter which valve moves downward, the position of tricuspid annulus remains unchanged, and the position of tricuspid opening remains far away from tricuspid annulus. In this paper, 42 patients with tricuspid regurgitation were shown by color doppler ultrasonography, which suggested that the downward position of tricuspid regurgitation was an important sign in the diagnosis of tricuspid regurgitation.




No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.