Comparison of Outcome Between Proximal Femoral Plate and Cephalomedullary Nail for Intertrochanteric Femur Fracture Fixation in Dr. Sardjito General Hospital
Introduction
Hip fractures are most common medical problems in many west countries like North America, Europe, and Oceania, with estimated will be increasing every year in the world until reach 6,26 million cases in the year of 2050 [1]. Pertrochanter fractures is a fracture occurring in the region beginning from bacillar neck extracapsular proximally until minor trochanter region before developing to medullary canal. The intertrochanter and peritrochanter are the common terms for pertrochanter fractures [2]. There’re still many controversies regarding the best operative treatment for this kind of fractures especially in osteoporotic and unstable pattern type [3]. These operative treatments including using either intramedullary or extramedullary implant, and many studies already describe and compare the outcome of these several type of fixation [4].
Methods
This is a retrospective study with analytical comparative between two groups of subjects that followed up after more than 6 months postoperative. These groups including the Cephalomedullary group and the Proximal femoral plate group. All the subjects are adult traumatic intertrochanter fracture patients that came to emergency unit in Sardjito general hospital Yogyakarta between January 2013 until December 2017 that underwent fixation surgery using either of both implant with exclusion criteria’s including multiple trauma patients, pathologic fractures due to tumors, bone metabolism problems, history of hip surgery and any previous limitation of range of movement. All datas obtained from patient’s medical records. Functional outcome measured with standardized Harris Hip Score (HHS) questionnaire6, interviewed and examined by author and 2 assistants by telephone conversation and outpatient clinic examination. HHS for all subjects in both groups collected in 1 month period of July 2018. The collected data from medical records, interview, and examination then analyzed statistically using SPSS software.
Results and Discussion
There’re 211 cases of intertrochanter fractures that came to emergency unit Sardjio general hospital between January 2013 until December 2017, with 51 cases that meets inclusion and exclusion criteria’s. Divided two groups with 26 cases of PFNA surgery fixation and 25 cases with PFP surgery fixation. The data then categorized to preoperative data (including demographic data’s), intraoperative data, postoperative data, and follow up data (conducted after more than 6 months post-surgery). The detailed datas shown in below tables. The Table 1 showed a demographic distribution and the preoperative status between two groups. All datas distributed normally measured using Saphiro Wilk test and analyzed using t-test. The results show a non-significant difference between two groups and indicated that all the samples are homogen and comparable. Surgery duration, intraoperative blood loss, and number of patients that need transfusion are better in the PFNA group, but statistically the significant results only occur for blood loss and number of patient transfused variables with p < 0.05 shown in Table 2.
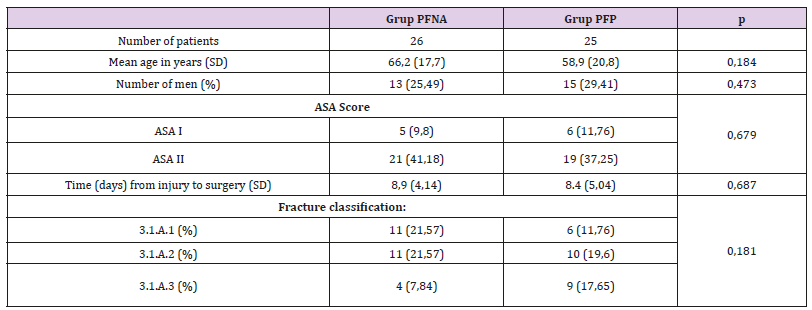 Table 2: Intraoperative Variables Data.
Table 2: Intraoperative Variables Data.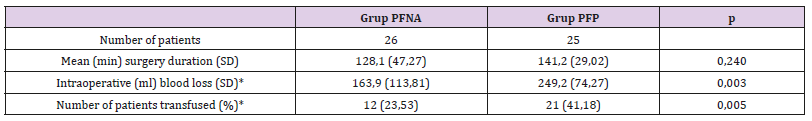 Note: *Significant differences statistically (p < 0,05).
Note: *Significant differences statistically (p < 0,05).It could be because the approach used in PFNA was closed approach while the PFP mostly by open approach. And the ability of the radiographer in operating the fluoroscope machine also contribute to the longer duration of surgery in PFNA group. Many other studies shows the PFNA have shorter duration of surgery compared to extramedullary implant fixation surgery [7]. Table 3 showed the complication rate and length of hospital stay between two groups are similar results. The follow up data obtained after 6 months postoperative at minimum showed that the HHS (describe the functional outcome status) between both groups have similar good results (more than 80) with no significant difference statistically (Table 4). Other study that compare the functional outcome between PFNA and other fixation implant also showed similar results of the HHS score with no significant different statistically [7]. There’s a weak negative correlation between the variable Age with the HHS score with p < 0.05 (Table 5).
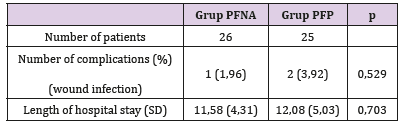 Table 4: Follow up Variables Data.
Table 4: Follow up Variables Data.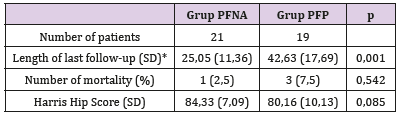 Note: *Significant differences statistically (p < 0,05).
Note: *Significant differences statistically (p < 0,05).Table 5: Perioperatif Variables Data Correlation to HHS (Spearman rho).
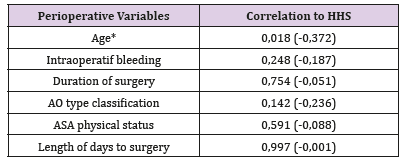 Note: *Significant differences statistically (p < 0,05).
Note: *Significant differences statistically (p < 0,05).Conclusion
Both PFP and PFNA fixation in intertrochanteric femur fracture patients resulting good functional outcome with HHS more than 80 at more than 6 months follow-up, however PFNA had advantages in lower intraoperative blood loss and the number of patients need to be transfused postoperatively. Also, the age of patients at the time of surgery correlate negatively with the HHS postoperative.
More BJSTR Articles : https://biomedres01.blogspot.com



No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.